Plant Tissue | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Anatomy of Plants |

|
| Meristematic Tissues |

|
| Permanent or Mature Tissues |

|
| Wood |

|
Anatomy of Plants
Plant anatomy focuses on the internal structure of plants, particularly their tissues. Tissue refers to a group of cells with a common origin and function.
Meristematic Tissues
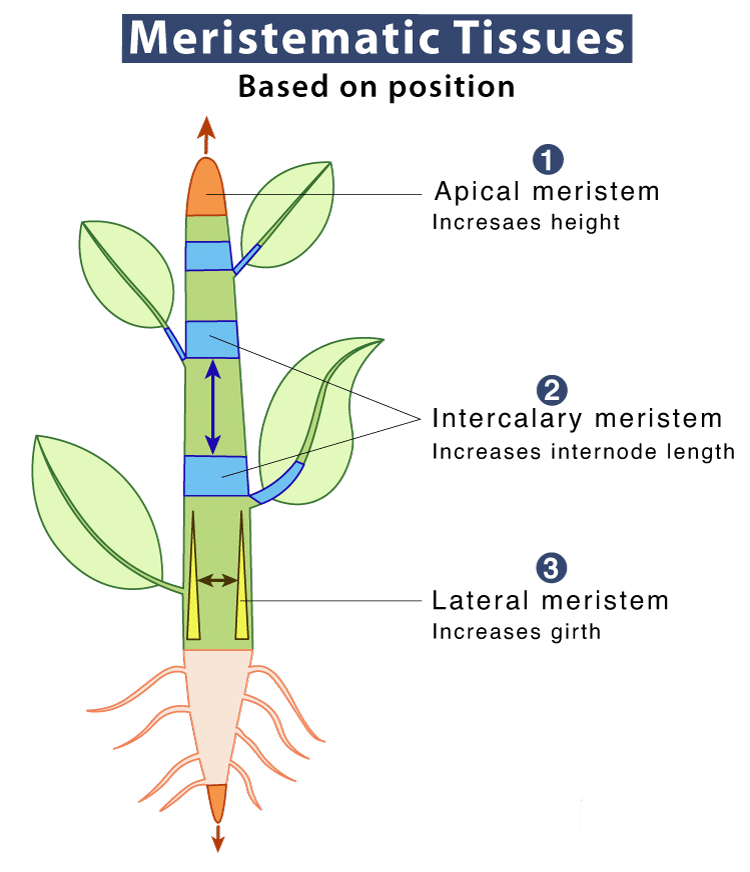
Meristematic tissues or meristems are groups of cells that remain undifferentiated and continue to divide throughout the plant’s life. These cells are typically small, cuboidal, with large nuclei, small vacuoles, and thin walls.
Types of Meristems
- Apical Meristem: Located at the tips of roots and stems.
- Intercalary Meristem: Found between mature tissues.
- Vascular Cambium: Located between xylem and phloem.
- Cork Cambium: Located on the outer side of the stem.
Permanent or Mature Tissues
Permanent Tissues result from the differentiation of meristematic tissues and have specific shapes, sizes, and functions. They are classified into three types:
Simple Permanent Tissue: Composed of similar cell types:- Parenchyma: Thin-walled living cells involved in storage and photosynthesis.
- Collenchyma: Thick-walled cells providing mechanical support.
- Sclerenchyma: Cells with very thick walls offering mechanical support to plant organs.
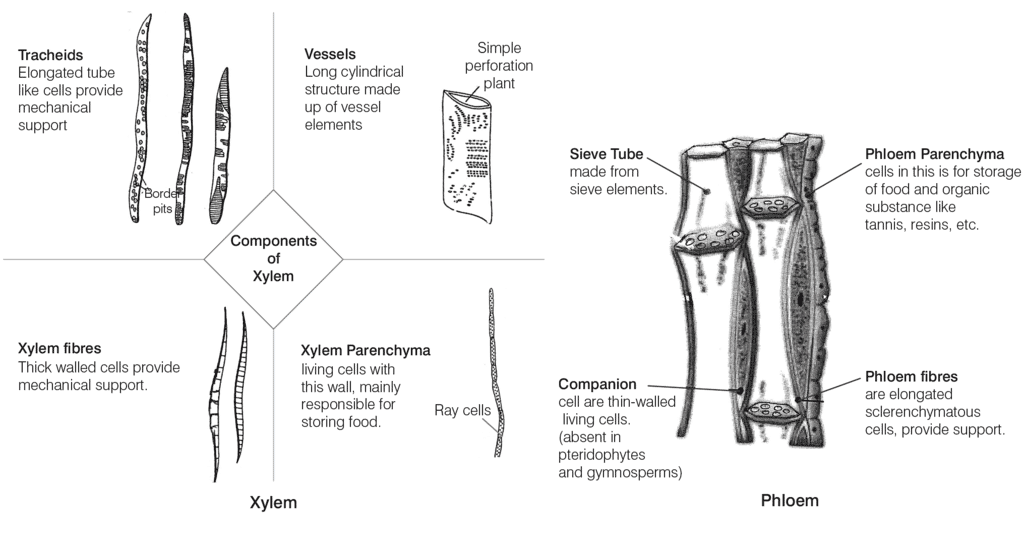
- Xylem: Conducts water.
- Phloem: Transports food and sap.
Special Tissues: Special tissues are also called as secretory tissue. They are involved in secretion of substances. There are two types of special tissue, i.e. glandular and laticiferous (latex secreting tissue).
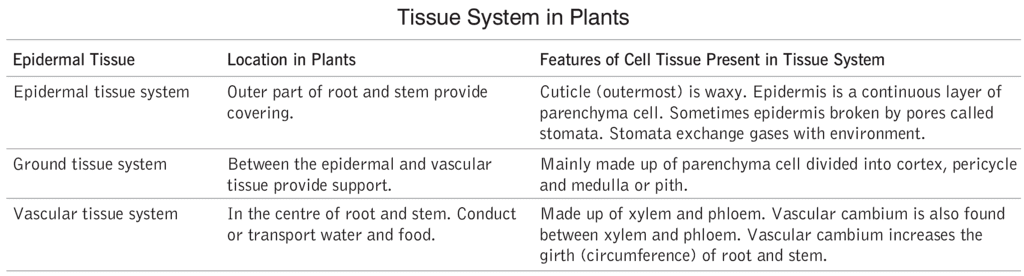
Increase in the diameter of plant is called secondary growth. Due to differential activity of cambium it results to annular rings in general. Thus, we can say secondary growth in a plant results to the formation of wood.
Wood
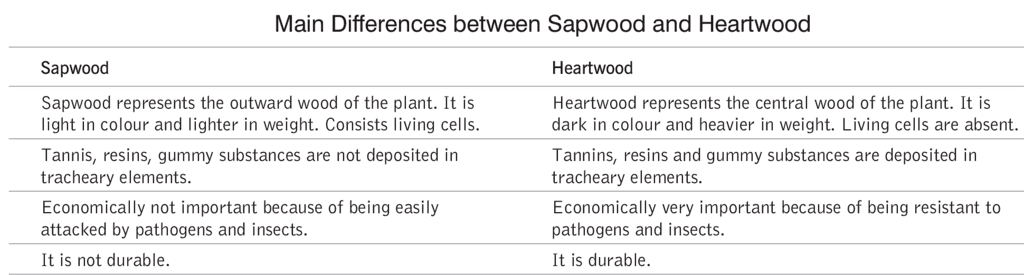
Wood is made up of xylem. The central, dense, and darker area is called heartwood, while the outer, lighter region is known as sapwood.
- Gymnosperm Wood: This type of wood is softer, lacks vessels, and consists mainly of tracheids.
- Angiosperm Wood: This wood is harder due to the presence of numerous fibers.
Growth Rings: The alternating favorable and unfavorable seasons for plant growth lead to variations in the size of xylem cells produced by the cambium throughout the growing season. These variations create rings with visible differences. When there is one growing season per year, these rings are known as annual rings. Counting the rings can determine the age of the tree. The field of study that analyzes growth rings to understand past events and climatic conditions is called dendrochronology.
|
477 videos|1904 docs|395 tests
|
FAQs on Plant Tissue - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What are the two main types of plant tissues? |  |
| 2. What is the function of meristematic tissues in plants? |  |
| 3. What are the characteristics of permanent or mature tissues in plants? |  |
| 4. What is wood and which type of plant tissue does it belong to? |  |
| 5. How do meristematic tissues differ from permanent tissues in terms of cell division? |  |




















