SSC CGL Exam > SSC CGL Notes > General Awareness for SSC CGL > Television
Television | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
Introduction
Television is a powerful medium for communication, allowing the transmission and reception of moving images along with sound. Over the years, television technology has evolved significantly, introducing various types and display technologies that cater to different viewing preferences and experiences.
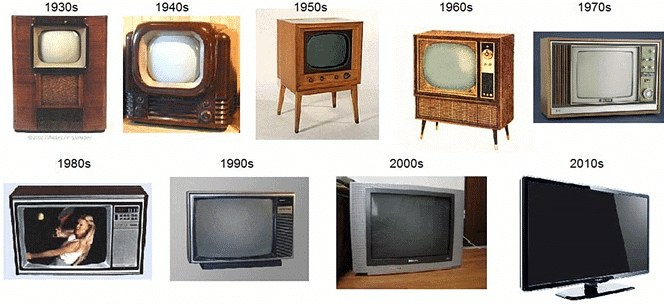
Types of Television
- Digital Television (DTV): DTV transmits both audio and video using digital signals, which are more efficient than the analog signals used by older television systems.
Example: Unlike analog TV, which could suffer from signal degradation, DTV provides clearer picture quality and more channels within the same bandwidth. - High Definition Television (HDTV): HDTV offers a much higher resolution compared to Standard Definition Television (SDTV). It provides a sharper and more detailed picture by using one to two million pixels per frame, which is about five times the resolution of SDTV.
Example: Watching sports or nature documentaries on HDTV gives viewers a more immersive experience due to the enhanced picture quality. - Satellite Television: This type of television is broadcasted via communication satellites and is received by an outdoor antenna, commonly a satellite dish. It is typically paired with a satellite receiver, either as an external set-top box or integrated within the television.
Example: Satellite TV is often used in rural areas where cable TV may not be available, providing access to a wide range of channels. - Internet Television (Online TV): Online TV refers to television services that are streamed over the Internet, often through platforms that use Internet Protocol Television (IPTV).
Example: Popular services like Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video are forms of Internet TV, allowing users to watch content on demand via the internet. - Internet Protocol Television (IPTV): IPTV delivers multimedia services such as television, video, and audio over IP-based networks. These networks are managed to ensure quality of service, security, and reliability.
Example: IPTV services are used by telecom companies to provide TV over broadband connections, often bundled with internet and phone services. - Hybrid IPTV: Hybrid IPTV combines traditional broadcast TV services with video content delivered over managed IP networks or the public Internet, offering a mix of both worlds.
Example: A user can watch live broadcast TV and also stream movies from the internet through the same IPTV service. - Interactive Television: This type of television allows varying degrees of interaction between the viewer and the content. This can range from basic controls like changing channels to more advanced features like interactive games or voting in real-time.
Example: Interactive TV can allow viewers to choose different camera angles during a live sports event or participate in real-time polls during a reality show. - Three-Dimensional (3D) Television: 3D TV creates the illusion of depth by using stereoscopic techniques or other 3D presentation methods, making the content appear more lifelike and immersive.
Example: Watching 3D movies at home, such as "Avatar," can simulate the experience of being in a 3D cinema. - Satellite Media (SM): This technique is primarily used by corporations to broadcast specific messages or information through local television stations, often involving live interactions.
Example: A company may use satellite media to deliver live interviews or announcements across various news channels simultaneously. - Direct-To-Home (DTH) Television: DTH refers to satellite television that is broadcast directly to a consumer's home, offering a broad range of channels and services without the need for a cable provider.
Example: In many countries, DTH services like Dish TV or DirecTV allow users to receive television broadcasts directly via satellite, bypassing traditional cable infrastructure. - Smart TV: A Smart TV integrates internet capabilities, allowing users to access online content, apps, and streaming services directly from the television without needing additional devices.
Example: A Smart TV can stream movies from Netflix, browse the web, and connect to social media platforms directly through its interface.
Question for TelevisionTry yourself: Which type of television technology provides a much higher resolution compared to Standard Definition Television (SDTV)?View Solution
Various Television Display Technologies
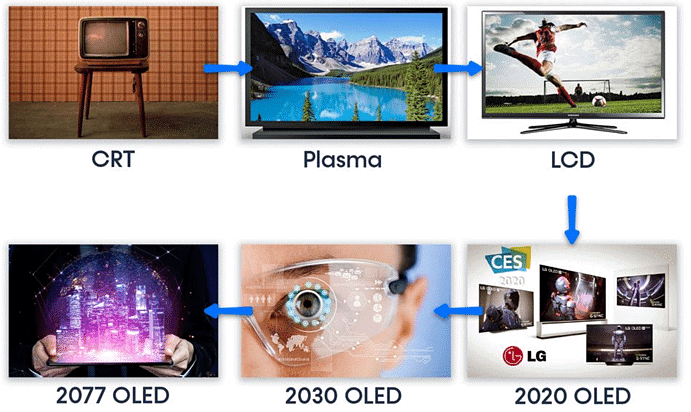
- Plasma Display Panels (PDPs): Plasma displays use small cells containing electrically charged ionized gases to produce images. This technology, first introduced by Fujitsu in 1997, is known for its vibrant colors and deep blacks.
Example: Plasma TVs were popular for home theater systems due to their ability to deliver high contrast ratios and wide viewing angles. - Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs): LCDs use liquid crystals to modulate light and create images on the screen. This technology is widely used in modern flat-screen TVs and is valued for its thin form factor and energy efficiency.
Example: Most of today's affordable flat-panel TVs use LCD technology, offering good picture quality at a reasonable price. - Light-Emitting Diode (LED) Displays: LED displays are a type of LCD that uses LEDs for backlighting, which improves energy efficiency, contrast, and brightness.
Example: LED TVs are a common choice for consumers looking for a television with better picture quality and lower power consumption compared to older LCD models. - Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) Displays: OLEDs are a type of LED where the light-emitting layer is made of organic compounds. This technology allows for even thinner displays, with superior color accuracy and deeper blacks compared to standard LED TVs.
Example: OLED TVs are often considered the best for picture quality, with brands like LG and Sony leading the market. - Closed-Circuit Television (CCTV): CCTV is a video surveillance system that transmits signals to a specific set of monitors, typically used for security purposes.
Example: Businesses and homes use CCTV systems to monitor and record activities for safety and security. - Laser Video Display or Laser TV: Laser TV uses lasers to produce images, replacing traditional lamps with lasers in red, green, and blue colors for a brighter and more vivid picture.
Example: Laser TVs are known for their ability to produce a wider color gamut and are often used in high-end home theater setups. - Ferro Liquid Display/Ferro Electric Liquid Display (FLD): These displays utilize the ferro-electric properties of certain liquids, though they are not technically crystals. These displays are known for their quick response times and durability.
Example: FLDs are used in niche applications where fast display response is critical, such as in some types of military or industrial equipment. - Interferometric Modulator (IMOD) or Mirasol: IMOD technology, used in electronic displays, creates colors through the interference of reflected light. This is an example of Micro-Electromechanical Systems (MEMS)-based technology.
Example: Mirasol displays are energy-efficient and can be used in devices like e-readers and portable gadgets where battery life is crucial. - Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode Display (QD-LED): QD-LED technology uses semiconductor nanocrystals called quantum dots to produce light, offering vibrant colors and high brightness.
Example: QD-LED displays are used in premium TVs, like Samsung’s QLED line, which offer enhanced color accuracy and brightness for a superior viewing experience.
The document Television | General Awareness for SSC CGL is a part of the SSC CGL Course General Awareness for SSC CGL.
All you need of SSC CGL at this link: SSC CGL
|
448 videos|1497 docs|288 tests
|
FAQs on Television - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What are the main types of television? |  |
Ans. The main types of television include LED, OLED, QLED, and Plasma TVs.
| 2. What are the differences between LED, OLED, and QLED TVs? |  |
Ans. LED TVs use backlighting, OLED TVs have pixels that emit their own light, and QLED TVs use Quantum Dot technology to enhance color and brightness.
| 3. How does Plasma TV technology differ from LED and OLED TVs? |  |
Ans. Plasma TVs use charged gas to create images, while LED and OLED TVs use different types of lighting technology.
| 4. What are the advantages of OLED TVs over LED TVs? |  |
Ans. OLED TVs have better contrast ratios, faster response times, and wider viewing angles compared to LED TVs.
| 5. Are Plasma TVs still available in the market? |  |
Ans. Plasma TVs are no longer being manufactured, as they have been largely replaced by LED, OLED, and QLED TVs due to advancements in technology.
Related Searches
















