Metals | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Metals |

|
| Alkali Metals and Their Compounds |

|
| Alkaline Earth Metals and Their Compounds |

|
| Important Metals and Their Uses |

|
Metals

- Metals are generally excellent conductors of heat and electricity, with silver being the best conductor of heat, followed by copper.
- Aluminium is also a good conductor, which is why cooking utensils and water boilers are typically made from copper and aluminium.
- In contrast, mercury has very high resistance to electrical current.
- Metals are generally hard, but sodium and potassium are soft enough to be cut with a knife.
- They are also malleable and ductile, with gold and silver being the most malleable and ductile metals.
- Except for mercury (mp 39°C), caesium (mp 28.4°C), and gallium (mp 29.8°C), which are liquid above 30°C, metals are solids at room temperature.
- Metals are electropositive, losing electrons to form positive ions.
- Most metal oxides are basic, but zinc oxide and aluminium oxide are amphoteric.
Alkali Metals and Their Compounds
- Alkali metals include lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, and caesium.
- They are stored under kerosene or liquid paraffin to protect them from air.
- The solubility in water, base strength, and thermal stability of alkali metal hydroxides increase from lithium hydroxide (LiOH) to caesium hydroxide (CsOH).
- Metallic sodium is produced by the electrolysis of a molten mixture of 40% sodium chloride and 60% calcium chloride in a Down's cell.
- Sodium chloride (NaCl), or common salt, is used in our daily diet and as a preservative for pickles, meat, and fish.
- It is also used in the production of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), chlorine gas (Cl2), and soap.
- In Nelson cells or Castner-Kellner cells, NaCl is the starting material for caustic soda production.
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), or caustic soda, is used in the soap, dye, and artificial silk industries and in refining bauxite.
- Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), or baking soda, is used in effervescent drinks, fruit salts, fire extinguishers, and wool washing.
- Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3·10H2O), or washing soda, is used in glass, soap, and washing powder production and for softening hard water.
- A mixture of sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate is known as fusion mixture.
- Sodium sulphate (Na2SO4·10H2O), or Glauber's salt, is used as a purgative.
- Sodium thiosulphate (Na2S2O3·5H2O), or Hypo, is used in photography as a fixing agent.
- Potassium superoxide (KO2) is used in space capsules, submarines, and breathing masks to produce oxygen and remove carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide.
- Potassium cyanide (KCN) is used in extracting silver and gold and as a germicide in agriculture; it is more poisonous than sodium cyanide.
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH), known as caustic potash, is used in soft soap preparation, and its aqueous solution is called potash lye.
- Potassium carbonate (K2CO3) is known as potash or pearl ash.
- Potassium sulphate (K2SO4) is used as a fertilizer for tobacco and wheat and in manufacturing potash alum and glass.
De-Icing of Roads After Snowfall
De-icing is the process of removing ice from a surface using salts like NaCl (sodium chloride) and sand, which lowers the temperature to −18°C. These salts are corrosive, so a sodium chloride/calcium chloride blend (pre-unix) is used to protect the environment. Nowadays, liquid CaCl2 and MgCl2 are also used for de-icing.
Alkaline Earth Metals and Their Compounds
The alkaline earth metals include beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium. Calcium is the most abundant element in this group within the Earth's crust. Beryllium hydroxide (Be(OH)2) is amphoteric. Magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2), known as milk of magnesia, is used as an antacid.
- Calcium oxide (CaO): Also known as quicklime, it is used in the production of glass, calcium chloride, cement, bleaching powder, calcium carbide, slaked lime, and in iron extraction. It also serves as a drying agent for ammonia and alcohol.
- Calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2]: Known as slaked lime, it is used in the manufacturing of caustic soda, sodalime, and for softening hard water.
- Calcium sulphate (CaSO4·2H2O): Known as gypsum, it partially loses its water of crystallization when heated to 120°C to form [CaSO4]2·H2O, which is plaster of Paris. Gypsum is used in the preparation of building plaster, anhydrite CaSO4, and in the production of ammonium sulphate (Sindri fertilizer) and sulphuric acid.
- Plaster of Paris: This white powder hardens when mixed with water and is used for making statues, toys, in medical applications for setting fractured bones, and in dentistry.
- Calcium carbide (CaC2): It is used to prepare acetylene and as a reducing agent in metallurgical processes.
- Barium sulphate (BaSO4): Used as a white pigment either alone or mixed with zinc sulphide (BaSO4 + ZnS) to form lithopone.
Important Metals and Their Uses
 Boron (B)
Boron (B)
Properties: Boron is a metalloid found in nature in compounds like borax (tincal), colemanite, boric acid, and kernite.
Uses:
- Boron and boron carbide rods control nuclear reactions.
- Boron carbide (B4C), also known as Norbia, is one of the hardest artificial substances after diamond.
- Borax (Na2B4O7·10H2O) is used in borax bead tests for qualitative analysis, as an antiseptic, in making optical and borosilicate glass, and in impregnating matchsticks to prevent afterglow.
- Orthoboric acid (H3BO3) is used as an antiseptic and eye wash under the name boric lotion.
Aluminium (Al)
Properties: Aluminium is the third most abundant element in the Earth's crust, extracted from bauxite (Al2O3·2H2O). It is a cheap, lightweight metal.
Uses:
- Making utensils, frames, and bodies of automobiles and aircraft.
- Aluminium powder is used in fireworks, flashlight powder, and thermite welding.
- Aluminium acetate (red liquor) is used as a mordant in dyeing and calico printing.
- Ammonal (a mixture of aluminium powder and ammonium nitrate) is used as an explosive.
- Ruby and sapphire, essentially Al2O3, get their colors from the presence of Cr and Fe/Ti, respectively. Emerald contains Ca/Cr and aluminium silicates (Al2SiO3).
Tin (Sn)
Properties: The main ore of tin is cassiterite (SnO2). Tin has the most natural isotopes.
Uses:
- In cold countries, white tin converts to grey tin (powder), a process known as tin disease or tin plague.
- Tin plating prevents iron rusting.
- Tin amalgam is used in making mirrors.
- Stannic chloride pentahydrate (SnCl4·5H2O), called butter of tin, is used as a mordant in dyeing.
Lead (Pb)
Properties: Lead is mainly found as the sulphide ore galena (PbS).
Uses:
- Making chambers for the chamber process of sulphuric acid (H2SO4), lead pigments, bullets, and lead accumulators.
- Lead blocks protect against harmful emissions from radioactive materials.
- Litharge (PbO) is a buff-colored crystalline lead monoxide, while massicot is a yellow powder. Red lead (Pb3O4) is used for protective paint for iron and in the match industry.
- Lead acetate, known as sugar of lead, is used in medicine for curing skin diseases. Basic lead carbonate is known as white lead.
Titanium (Ti)
Properties: Titanium is a silvery-white metal that is extremely hard, has a high melting and boiling point, and is resistant to corrosion.
Uses:
- As a structural material in jet engines, aircraft frames, turbine engines, and marine equipment.
- Titanium chloride (TiCl4) is used in making screens.
Zirconium (Zr)
Uses: Making the core of nuclear reactors and for pumps, valves, and heat exchangers.
Vanadium (V)
Uses:
- In high-speed tool steels, exhaust valves, and springs.
- Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) is an excellent catalyst for manufacturing sulphuric acid by the contact process.
Chromium (Cr)
Uses:
- An essential component of stainless steel and chrome steel.
- Coating iron articles.
- Potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) is used in qualitative and quantitative estimations, as an oxidizing agent, and in photography for hardening gelatin.
Molybdenum and Tungsten (Mo and W)
Uses:
- Molybdenum promotes iron in the Haber process for ammonia.
- Steel containing Mo or W is extremely hard and used for cutting tools.
- Tungsten filaments are used in electric bulbs, and calcium tungstate is used in X-ray tubes.
Manganese (Mn)
Uses:
- Forming various alloys, such as manganin (Cu + Mn + Ni), used in making resistance coils due to its low resistance coefficient.
- Manganese steel is very hard and used for rock crushers, rails, armor plates, and burglar-proof safes.
- Pure manganese dioxide (MnO2) is used as a depolarizer in dry cells and a decolorizer in glass.
- Useful alloys include ferromanganese (Fe + Mn), manganese bronze (Mn + Cu + Zn), and spiegel (Fe + Mn + C).
- Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) is used as a disinfectant in water.
Iron (Fe)
Properties: Extracted from haematite ore, iron is a reactive metal and does not occur in a free state.
Uses:
- Cast iron, extracted from oxide ore haematite, is the most impure form of iron, containing 2.5–4% carbon.
- Wrought iron or malleable iron is the purest form, containing 0.12–0.5% carbon.
- Iron (II) is present in haemoglobin.
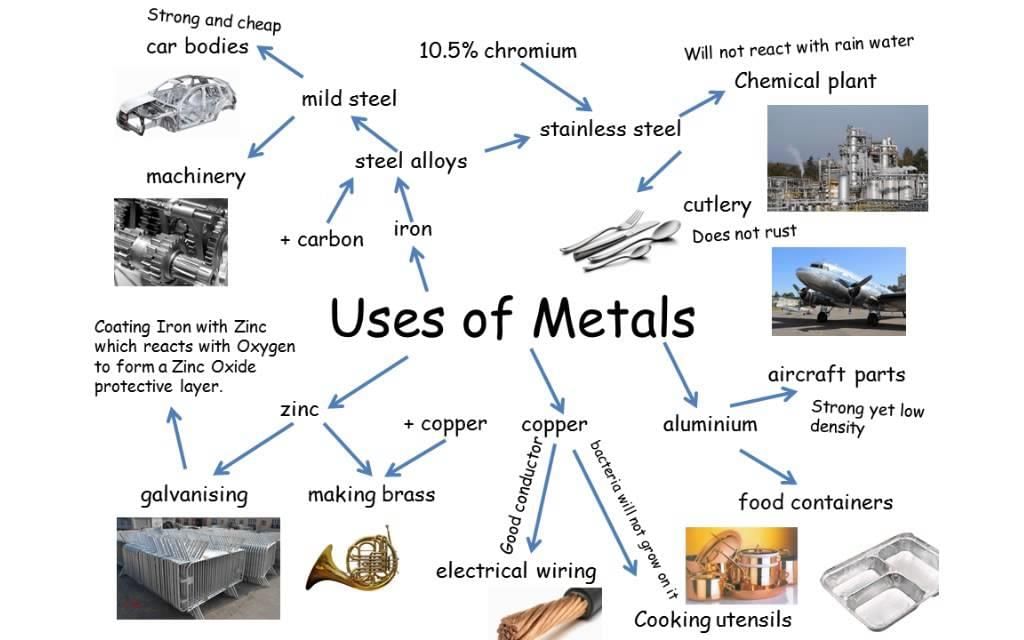
- Mild steel contains 0.25–0.5% carbon, hard steel contains 0.5–1.5% carbon, and soft steel contains up to 0.25% carbon.
- Stainless steel, an alloy of iron, chromium, and nickel, is used for making automobile parts and utensils.
- Ferric chloride (FeCl3) is used as a styptic to stop bleeding from cuts.
- Ferrous sulphate (FeSO4) is used in making blue-black ink.
Nickel and Platinum (Ni and Pt)
Nickel:
- A silvery-white soft metal that adsorbs large amounts of hydrogen.
- Used as an anode in Edison batteries.
Platinum:
- Colloidal platinum is an effective catalyst.
- Platinum black is used as an adsorbent of gases like hydrogen and oxygen.
- Used in jewelry and dentistry.
Copper, Silver, and Gold (Cu, Ag, and Au)
Properties: Known as coinage metals, gold and silver are not affected by air, while copper forms a greenish film upon long exposure.
Uses:
- Making jewelry, coins, and decorative pieces.
- Silver and gold are used in Ayurvedic medicines, with silver also used as amalgam for filling teeth and in silvering mirrors.
- Silver bromide (AgBr) is used in photography.
- Silver nitrate (AgNO3), known as lunar caustic, is used in preparing marking inks and hair dyes.
- Copper sulphate (CuSO4) + lime forms bordeaux mixture, a fungicide.
- Copper sulphate pentahydrate (CuSO4·5H2O) is called blue vitriol or nila thotha, and CuFeS2 is known as fool’s gold.
- Gold purity is expressed in carats, with pure gold being 24 carats. Purple of Cassius is a colloidal solution of gold.
Mercury (Hg)
Properties: Forms alloys with all metals except iron and platinum, so it is transported in iron containers.
Uses:
- Mercuric chloride (HgCl2), also known as corrosive sublimate, is poisonous, with egg white as the best antidote.
- Mercuric sulphide (HgS) is used as a cosmetic in Ayurvedic medicine (Makardhwaja).
Zinc (Zn)
Properties: Impure zinc, known as spelter, is used in galvanization to prevent iron rusting.
Uses:
- Zinc sulphide is used in X-ray screens and, with radium salt traces, in luminous paint for watch dials.
- Zinc oxide, known as philosopher’s wool, is used in cosmetic powders and creams as zinc ointment in medicine.
- Zinc sulphate heptahydrate (ZnSO4·7H2O) is called white vitriol, used as a mordant in dyeing, eye lotion, and for zinc plating.
|
448 videos|1497 docs|288 tests
|
FAQs on Metals - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What are alkali metals and their compounds? |  |
| 2. Can you provide examples of alkaline earth metals and their compounds? |  |
| 3. What are some important metals and their uses? |  |
| 4. How are alkali metals different from alkaline earth metals? |  |
| 5. In what ways are metals important in our daily lives? |  |




















