Electronics | SSC CGL 4 Months Preparation PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Electronics |

|
| Semiconductor Devices |

|
| Transistors |

|
| Digital Circuit |

|
| Universe |

|
| Solar System |

|
| Planets |

|
| Structure of the Earth |

|
| Black Hole |

|
| Galaxy |

|
| Constellation |

|
Electronics
The study of electronics involves understanding semiconductors, which are typically insulators at room temperature but exhibit conductive properties when heated. To enhance their conductivity, impurities are introduced into these materials. Semiconductors can be categorized as extrinsic when doped with impurities, which then transform them into intrinsic semiconductors. Intrinsic semiconductors are classified into two types:
- p-Type: In this type, holes are the majority charge carriers, while electrons are the minority charge carriers.
- n-Type: Here, electrons serve as the majority charge carriers, and holes are the minority charge carriers.
Semiconductor Devices
p-n Junction Diode
A p-n junction diode is created by bringing a p-type semiconductor and an n-type semiconductor into close contact, forming a p-n junction. The device that incorporates this junction is referred to as a p-n junction diode.
Types of Diodes
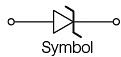
- LED (Light Emitting Diode): Typically made from materials like GaAsP or GaP, LEDs are used as indicator lights in electronic devices.
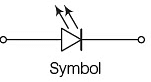
- Zener Diode: Known for its ability to withstand damage, a Zener diode operates in reverse current mode and is primarily used as a voltage regulator.
- Photo Diode: When light hits a photo diode, it generates a photo current that flows through an external load if connected.
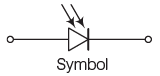
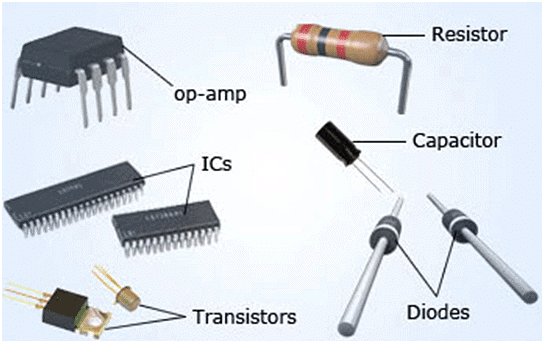
Transistors
It is a combination in which p-n Junctions are joined in series. These are of two types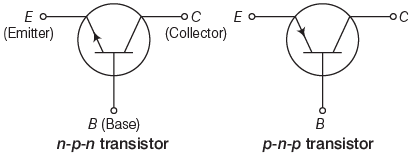
- The combination of transistors forms an IC (integrated circuit) and it is a multifunctional device.
- The combination of IC’s are called microprocessor, which are now a days used in electronic devices.
Digital Circuit
It is a electronic circuit that responds to discrete value of input voltage and produces discrete output voltage level. Usually two levels are used in it
- 0 (OFF)
- 1 (ON)
The digital circuit constitutes gate basically of three types
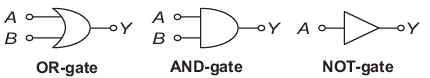
Universe
The universe is commonly defined as the totality of existence including the planets, stars galaxies and all matter and energy.
Solar System
- The sun and all the objects moving around it taken together, is called solar system.
- The sun is a star of mass 2 × 1030 kg and radius 1.4 × 106 km.
- The source of the sun’s energy is the process of nuclear fusion taking place in it.
- The atmosphere It is the inner part of the sun which appears as a bright disc. It is a denser mixture of gases and vapours. Its thickness is about 500 km and its temperature is about 6000 KM.
- The chromosphere It is the outer part of the sun, just above the atmosphere. It is a rarer mixture of gases and vapours.
Planets
The heavenly bodies which revolve around the sun in a fixed orbit, are called planets.
There are eight planets in solar system
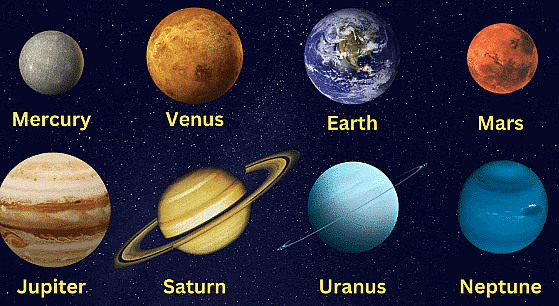
- Pluto, once considered the ninth planet, is now classified as a dwarf planet.
- The four planets closest to the Sun—Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars—are known as terrestrial planets, characterized by their solid surfaces of rocks and soil.
- The four outer planets—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune—are referred to as jovian planets, and they do not have solid surfaces.
- Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun, while Venus is the closest planet to Earth and is also the hottest planet in our solar system.
- Mars is known as the Red Planet.
- Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system, and Saturn is the second largest.
Asteroids and Meteoroids
- Small, rocky, and irregularly shaped objects that orbit the Sun are known as asteroids or minor planets.
- There is an asteroid belt located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
- Ceres is the largest of these asteroids.
- Some asteroids can have their own moons.
- Small fragments of rock traveling through space are referred to as meteoroids. These can come from asteroids, comets, the Moon, Mars, and other sources.
- When a meteoroid enters Earth’s atmosphere, it heats up due to friction and emits light as it vaporizes, creating a streak of light known as a meteor or shooting star.
- If a meteoroid survives its atmospheric entry and lands on Earth, it is called a meteorite.
Structure of the Earth
The Earth's inner structure consists of three distinct layers:- Crust: This is the outermost and thinnest layer, about 10 km thick beneath the oceans and up to 45 km thick under the continents.
- Mantle: Positioned below the crust, the mantle extends to a depth of roughly 3000 km, with temperatures around 1000°C.
- Core: The innermost layer of the Earth, primarily composed of iron. The outer core is molten and has a temperature of about 4000°C, while the inner core remains solid due to extremely high pressure.
Black Hole
 It is a region in space in which the gravitational force is so great that no object can escape from it.
It is a region in space in which the gravitational force is so great that no object can escape from it.
Galaxy

- A galaxy is a massive collection of stars and other celestial objects held together by gravity.
- The universe contains more than 100 billion galaxies.
- Our galaxy is known as the Milky Way.
- The Milky Way contains over 250 billion stars.
Constellation

- A nebula is a cloud of gas and dust particles that collects in space.
- Stars are formed within a nebula. Gravitational forces cause the particles to move toward the center, where their kinetic energy is converted into heat, raising the temperature of the central region.
- As the central region continues to contract and heat up, it eventually reaches a temperature of about 10 million Kelvin, triggering nuclear fusion and resulting in the birth of a star.
- A constellation is a pattern of stars that is recognizable in the night sky.
- Examples of constellations include Ursa Major (the Great Bear), Leo (the Lion), Pisces (the Fish), Taurus (the Bull), Hercules (the Hero), and Orion (the Hunter).
- Ursa Major is known for its seven brightest stars, which form the shape of a great bear.
|
876 videos|2003 docs|751 tests
|
FAQs on Electronics - SSC CGL 4 Months Preparation
| 1. What is the role of transistors in digital circuits? |  |
| 2. How do semiconductor devices work in electronics? |  |
| 3. Can you explain the structure of a black hole in the universe? |  |
| 4. How are planets formed in the solar system? |  |
| 5. What is the Milky Way galaxy and where does Earth fit into it? |  |




















