SSC CGL Exam > SSC CGL Notes > General Awareness for SSC CGL > Work, Energy and Power
Work, Energy and Power | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Work |

|
| Energy |

|
| Power |

|
| Collision |

|
| Moment of Inertia |

|
Work
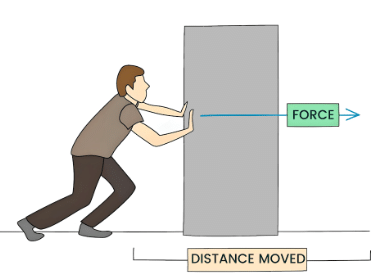
- Work done by a constant force (F) is the dot product of the force applied on a body and the displacement (s) of the body:
- W = F·s = Fs cos θ, where θ is the angle between F and s.
- Work is a scalar quantity. Its SI unit is the joule, and the CGS unit is the erg. 1 joule = 107 ergs.
- The work done by a force is positive if the angle between F and s is acute and negative if the angle θ is obtuse.
The work done by a force is zero when:
- The body is not displaced (s = 0).
- The body is displaced perpendicular to the direction of the force (θ = 90∘).
Work Done by a Variable Force
The work done by a force is equal to the area under the force-displacement graph and is given by W = ∫ F⋅d s.
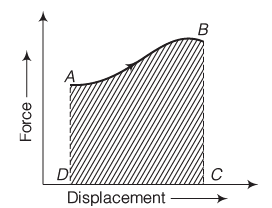
- For example, the work done by a force is represented by the area ABCDA in a graph.
- If a ball is thrown upward, the work done against gravity is W = mgh, where m is the mass of the body, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height through which the ball is raised.
- The centripetal force acts perpendicular to the direction of motion; thus, the work done by or against centripetal force in circular motion is zero.
- If a porter carries a load on his head and moves on a horizontal platform, the work done by the force of gravity is zero since the displacement is perpendicular to the direction of the gravitational force.
Energy
- Energy is the capacity of a body to do work. It is a scalar quantity, and its SI unit is the joule.
- Energy can be transformed into work and vice versa using mechanical devices.
There are two types of mechanical energy:
Kinetic Energy:
- The energy a body possesses by virtue of its motion.
- Kinetic energy of the body of mass m moving with velocity v is given by
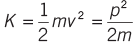 where, p = mv = momentum of the body.
where, p = mv = momentum of the body.
Potential Energy:
The energy a body possesses due to its position or configuration.
- Gravitational potential energy: U = mgh, where m is the mass of the body, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height through which the body is lifted.
Different Forms of Energy:
- Solar Energy: Emitted by the sun and used in solar cookers, solar water heaters, solar cells, etc.
- Fossil Energy: Non-renewable energy from the anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms, including coal, petroleum, and natural gas.
- Hydroelectric Energy: Generated by using the gravitational force of falling or flowing water. In some countries, more than 23% of water is used to produce hydroelectric power.
- Nuclear Energy: Released when a U235 nucleus breaks into lighter nuclei upon being bombarded by slow-moving neutrons. Sources include nuclear reactors and nuclear bombs.
Einstein’s Mass-Energy Relation
- According to Einstein, mass can be transformed into energy and vice versa.
- When a mass Δm disappears, the produced energy E is given by E = Δmc2, where c is the speed of light in a vacuum.
Conservative and Non-conservative Forces
- Conservative Forces: These are non-dissipative forces, such as gravitational and electrostatic forces. For conservative forces, the work done during a round trip is always zero.
- Non-conservative Forces: These are dissipative forces, such as frictional and viscous forces.
Law of Conservation of Energy
- Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transformed from one form to another.
- For conservative forces, the total mechanical energy initially is equal to the total mechanical energy finally.
Question for Work, Energy and PowerTry yourself: Which type of energy is possessed by a body due to its motion?View Solution
Power
- Power is the rate at which a body does work.
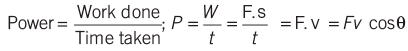
where, θ is the angle between F and v. - It is a scalar quantity and its SI unit is joule second − 1 or watt.
- Other units include kilowatts and horsepower: 1 kilowatt = 1000 W and 1 HP = 746 W
Collision
- A collision is an interaction between two or more particles over a very short time, during which they exert relatively strong forces on each other.
- Physical contact is not necessary for a collision to occur.
- Elastic Collision: Both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. All forces involved are conservative.
- Inelastic Collision: Only momentum is conserved; kinetic energy is not conserved.
- Perfectly Inelastic Collision: The colliding bodies stick together and move with a common velocity. The kinetic energy lost during the collision is not recovered.
Centre of Mass
- The centre of mass of a physical system is a point that characterizes the motion of the system as a whole. When the system moves under an external force, this point moves as if all the mass were concentrated at it.
- For a uniform rod and a solid spherical body, the centre of mass is at the geometrical centre.
Moment of Inertia
- The moment of inertia of a body about an axis of rotation is the sum of the products of the masses of its particles and the squares of their respective distances from the axis of rotation.
Definitions Related to Moment of Inertia
- Radius of Gyration: The distance from the axis of rotation at which the total mass of the body can be considered to be concentrated, such that its moment of inertia remains the same.
I = Mk2 - Theorem of Parallel Axes: The moment of inertia about any parallel axis is the sum of the moment of inertia about the centre of mass and the product of the mass and the square of the distance between the two axes.
- Theorem of Perpendicular Axes: For a laminar body, the moment of inertia about a perpendicular axis is the sum of the moments of inertia about two mutually perpendicular axes in the plane of the body.
The document Work, Energy and Power | General Awareness for SSC CGL is a part of the SSC CGL Course General Awareness for SSC CGL.
All you need of SSC CGL at this link: SSC CGL
|
448 videos|1497 docs|288 tests
|
FAQs on Work, Energy and Power - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. How does work relate to energy? |  |
Ans. Work is the transfer of energy from one object to another by applying a force over a distance. In simple terms, work is done when energy is transferred.
| 2. What is the relationship between power and energy? |  |
Ans. Power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred. It is the amount of work done per unit of time. Therefore, power and energy are related as power determines how quickly energy is transferred.
| 3. How does collision affect energy transfer? |  |
Ans. In a collision, energy can be transferred between objects in the form of kinetic energy. The total amount of energy before and after the collision remains the same, but the distribution of energy among the objects may change.
| 4. What is moment of inertia and how is it related to energy? |  |
Ans. Moment of inertia is a measure of an object's resistance to changes in its rotation. It is related to energy in rotational motion as it affects how the rotational kinetic energy of an object is distributed.
| 5. How can work, energy, and power be applied in real-life situations? |  |
Ans. Work, energy, and power concepts are used in various real-life applications such as calculating the energy consumption of appliances, designing efficient machinery, and understanding the performance of vehicles.
Related Searches















