Sound Wave | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Speed of Sound |

|
| Characteristics of Sound |

|
| Properties of Sound Wave |

|
| Musical Scale |

|
| Noise Reduction in Recording Media |

|
| Sonar |

|
| Human Ear |

|
Sound is a form of energy that creates the sensation of hearing through vibrations. Sound waves are mechanical longitudinal waves and need a medium to travel through; they cannot move through a vacuum. When a sound wave transitions from one medium to another, its speed and wavelength change, but its frequency stays the same. There are three types of sound waves based on frequency:
- Infrasonic waves: Frequencies between 0 and 20 Hz.
- Audible waves: Frequencies between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz.
- Ultrasonic waves: Frequencies above 20,000 Hz.
Speed of Sound
The speed of sound is different in different media.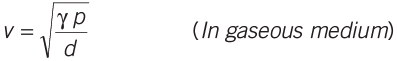 where, p is pressure, d is density, γ is ratio of specific heats.
where, p is pressure, d is density, γ is ratio of specific heats. where, Y = Young’s modulus.
where, Y = Young’s modulus. where, = Bulk modulus.
where, = Bulk modulus.
- Speed of sound ≈ 332 m/s (in air), 1483 m/s (water) and 5130 m/s (in iron). If vs , vl and vg are speed of sound waves in solid, liquid and gases, then vs > vl > vg .
- Sound waves cannot be heard on the surface of the moon and in outer space because there is no air on the moon.
Some important points related with speed of sound waves are
- The speed of sound waves in air increases with increase in temperature.
- The speed of sound increases by 0.61 m/s per °C rise in temperature.
- The dependence of speed of sound wave is given as v ∝ √T ,
where, v = speed of sound, T = temperature. – - The sound waves is faster in humid air and slower in dry air. –
- The speed of sound in air is very slower as compared to the speed of light in air. Therefore, in rainy season, the flashing of lightning is seen first and the sound of thunder is heard a little later.
Characteristics of Sound
Some characteristics of sound are as follows
Intensity
- It is the characteristic of sound by which weak and loud sounds can be identified. The intensity is proportional to the square of the amplitude of vibration of the source. It is also a measure of quality of sound. It is generally represented by I.
- When two sound waves of nearly equal frequency interfere, then intensity of resultant wave increases and decreases with time. This phenomenon is known as beats and beat frequency is equal to difference of frequencies of two waves.
Loudness
It is related with sound level (β) given by β = 10 log10 (I/I0) dB,
where, I is intensity of the source, producing sound waves.
and I0 = reference intensity = 10−12 W / m2
Pitch
It is related with frequency of the source. It distinguishes a shrill note from a grave note.
Properties of Sound Wave
Reflection
- The bouncing back of sound when it strikes a hard surface, is called reflection of sound.
- The laws of reflection of light are also obeyed during reflection of sound.
- The working of megaphone, sound boards and ear trumpet is based on reflection of sound.
- The repetition of sound due to reflection of sound waves, is called an echo.
- The persistence of hearing on human ear is 1/10th of a second.
- The minimum distance from a sound reflecting surface to hear an echo is nearly 17 m.
- Sound proof rooms are made of two layers of walls having vacuum between them.
- Reverberation arises due to multiple reflection of sound.
- While designing an auditorium for speech or musical concerts, one has to take proper care for the absorption and reflection of sound.
- Time taken by reverberant sound to decrease its intensity by a factor of 106 is called reverberation time.
Refraction
- When a sound wave move from one mechanical medium to another mechanical medium, it shows deviation from the original path of the incident wave.
- This phenomenon is called refraction. It is due to difference is speed of sound in media.
Diffraction
- When sound waves originated by a vibrating source, they spread in the medium and if the medium is homogeneous, this leads to bending of sound waves around the edges. Which is known as diffraction.
- The sound waves diffracted broadly and one can easily hears the voice of the another person.
Musical Scale
In theory of music, a musical scale is a set of musical notes by the frequencies of which are in simple ratios to one another. Sa, re, ga, ma, pa, dha, ni is one such scale called the diatonic scale. The frequencies of these notes are: sa (256), re (288), ga (320), ma (341.3), pa (384), dha (426.7) and ni (480). The next note denoted by sa has a frequency 512, twice that of sa. The interval sa-sa is called an octave (8).
Noise Reduction in Recording Media
Five types of noise reduction system exists in recording media as discussed below
- Dolby A noise reduction system, intended for use in professional recording studios. It provided about 10 dB of broadband noise reduction.
- Dolby B was developed to achieve about 9 dB noise reduction primarily for cassettes. It was much simpler than Dolby A and therefore less expensive to implement in consumer products.
- Dolby C provides about 15 dB noise reduction.
- Dolby SR (Spectral Recording) system is much more aggressive noise reduction approach than Dolby A. Dolby SR is much more expensive to implement than Dolby B or C, but it is capable of providing upto 25 dB noise reduction in the high frequency range.
- Dolby S is found on some Hi-Fi and semi-professional recording equipment. It is capable of 10 dB of noise reduction at low frequencies and upto 24 dB of noise reduction at high frequencies.
Sonar
- SONAR stands for Sound Navigation And Ranging. It is used to measure the depth of a sea, to locate the enemy submarines and shipwrecks.
- The transmitter of a sonar produces pulses of ultrasonic sound waves of frequency of about 50000 Hz. The reflected sound waves are received by the receiver.
Human Ear
We are able to hear with the help of an extremely sensitive organ of our body called the ear.
There are three parts of human ear
- The outer ear is called pinna. It collects the sound from the surroundings. The middle ear transmits the amplified pressure variations received from the sound wave to the inner ear.
- In the inner ear, the pressure variations are turned into electrical signals by the cochlea. These electrical signals are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve and the brain interpret them as sound.
|
482 videos|1427 docs|310 tests
|
FAQs on Sound Wave - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What is the speed of sound in air and how does it compare to the speed of light? |  |
| 2. What are the main characteristics of sound waves? |  |
| 3. How do properties of sound waves like frequency and amplitude affect the pitch and volume of a musical scale? |  |
| 4. How does noise reduction in recording media work to improve sound quality? |  |
| 5. How is sonar used to detect objects underwater and what role does the speed of sound play in this technology? |  |




















