Humanities/Arts Exam > Humanities/Arts Notes > Fine Art for Class 11 > Important Points: Post- Mauryan Trends in Indian Arts and Architecture
Important Points: Post- Mauryan Trends in Indian Arts and Architecture | Fine Art for Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
1. Dynasties and Sects:
- Post-Mauryan rulers: Shungas, Kanvas, Kushanas, Guptas in the north; Satvahanas, Ikshavakus, Abhiras, Vakataks in the south and west.
- Rise of main Brahmanical sects: Vaishnavas and Shaivas.
2. Prominent Sites:
- Sites dating back to the second century BCE: Vidisha, Bharhut (Madhya Pradesh), Bodhgaya (Bihar), Jaggayyapeta (Andhra Pradesh), Mathura (Uttar Pradesh), Khandagiri-Udaigiri (Odisha), Bhaja near Pune, Pavani near Nagpur (Maharashtra).
3. Bharhut Sculptures:
- Tall sculptures like Yaksha and Yakshini.
- Low relief maintaining linearity, narrative relief panels.
- Depiction of Queen Mayadevi's dream and Jataka stories.
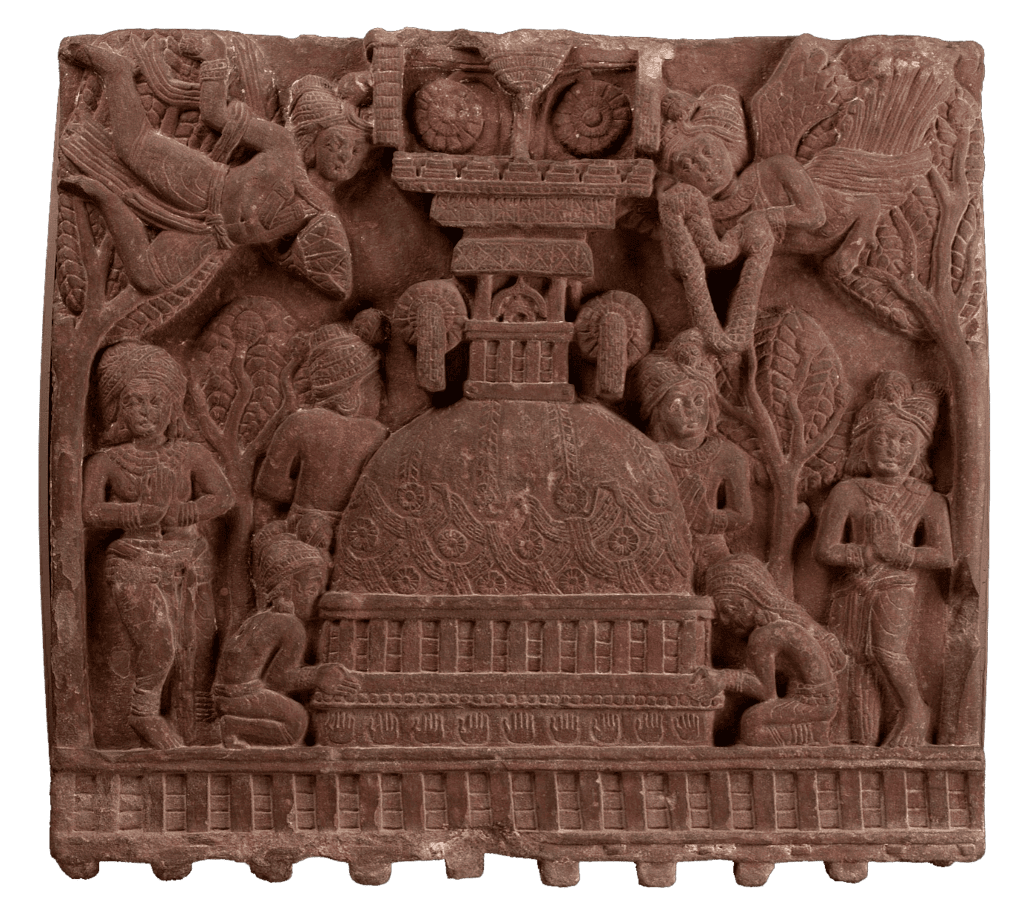
4. Sanchi Sculptures:
- Sculptural development at Sanchi Stupa-1.
- High relief figure compositions, naturalistic postures.
- Elaborated historical narratives.
5. Mathura, Sarnath, and Gandhara Schools:
- Mathura: Human form of Buddha, early Jain Teerthankar images, and Vaishnava and Shaiva images.
- Sarnath: Plain transparent drapery, halo around the head.
- Gandhara: Hellenistic features, Greco-Roman influence.
6. Amaravati Stupa:
- Mahachaitya with narrative sculptures, domical stupa structure.
- Complex sculptural compositions, intense emotions, slender figures.
7. Western India Caves:
- Ajanta: Twenty-nine caves, chaitya-viharas, sculptures, and paintings.
- Ellora: Thirty-four caves, Buddhist, Brahmanical, and Jain caves.
- Karla: Largest rock-cut chaitya hall.
8. Eastern India Caves:
- Guntapalle: Circular chaitya cave with a stupa, vihara caves.
- Udaigiri-Khandagiri: Jain caves with inscriptions of Kharavela Jain kings.
9. Terracotta Figurines:
- Found at many places, showing a parallel tradition with religious lithic sculptures and independent local tradition.
10. Notable Paintings:
- Padmapani Bodhisattva and Vajrapani Bodhisattva in Ajanta Cave No. 1.
- Mara Vijaya sculptural panel in Ajanta Cave No. 26.
The document Important Points: Post- Mauryan Trends in Indian Arts and Architecture | Fine Art for Class 11 - Humanities/Arts is a part of the Humanities/Arts Course Fine Art for Class 11.
All you need of Humanities/Arts at this link: Humanities/Arts
|
10 videos|24 docs|16 tests
|
FAQs on Important Points: Post- Mauryan Trends in Indian Arts and Architecture - Fine Art for Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are some key characteristics of post-Mauryan trends in Indian arts and architecture? |  |
Ans. Post-Mauryan trends in Indian arts and architecture saw the emergence of new styles influenced by interaction with foreign cultures, such as the Greeks and Persians. This period also marked the development of intricate stone carvings, the use of new materials like ivory and stucco, and the construction of elaborate temples and stupas.
| 2. How did the post-Mauryan period influence Indian art and architecture? |  |
Ans. The post-Mauryan period led to a fusion of indigenous styles with foreign influences, resulting in the creation of unique art forms and architectural structures. This period also saw a shift towards more ornate and decorative elements in art and architecture.
| 3. What role did foreign influences play in shaping post-Mauryan Indian arts and architecture? |  |
Ans. Foreign influences, particularly from Greek and Persian cultures, played a significant role in shaping post-Mauryan Indian arts and architecture. These influences led to the incorporation of new techniques, materials, and design elements in Indian art and architecture.
| 4. How did the construction of temples and stupas evolve during the post-Mauryan period? |  |
Ans. During the post-Mauryan period, the construction of temples and stupas became more elaborate and intricate. Temple architecture began to feature intricate carvings and sculptures, while stupas were adorned with decorative elements and elaborate gateways.
| 5. What are some notable examples of post-Mauryan art and architecture in India? |  |
Ans. Some notable examples of post-Mauryan art and architecture in India include the Great Stupa at Sanchi, the Chaitya Hall at Karla Caves, and the temples at Ajanta and Ellora. These structures showcase the unique fusion of indigenous and foreign influences during this period.
Related Searches
















