MCQ & Extra Questions: Measurement of Length and Motion | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Extra Questions
Q1: What is the SI unit of length?
The SI unit of length is the metre (m).
Q2: How is the length of a curved line measured?
The length of a curved line can be measured using a flexible measuring tape or by using a thread to trace the curve and then measuring the thread with a scale.
Q3: Why is it important to use standard units of measurement?
Standard units ensure consistent and accurate measurements worldwide, avoiding confusion and enabling reliable comparisons and communication.
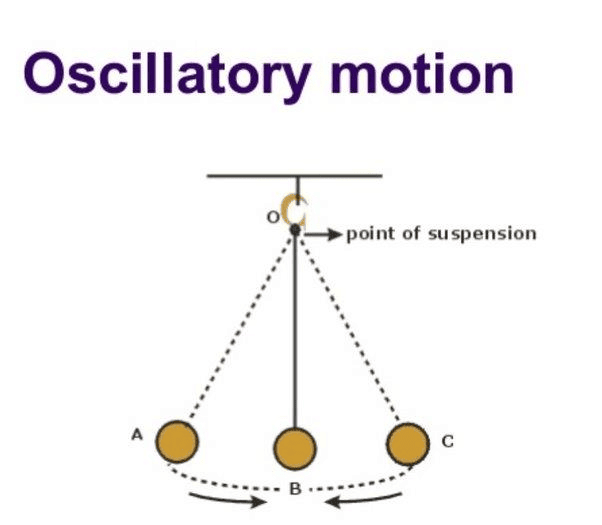
Q4: What type of motion does a pendulum exhibit?
A pendulum exhibits oscillatory motion, moving back and forth around a fixed position.
Q5: How can you measure the thickness of a single page in a book?
To measure the thickness of a single page, you can measure the thickness of a stack of pages, count the number of pages, and then divide the total thickness by the number of pages.
Q6: What is a reference point in the context of motion?
A reference point is a fixed point used to determine the position or movement of an object.
Q8: What is linear motion?
Linear motion is when an object moves in a straight line.
Q9: Why should scales be placed correctly when measuring length?
Scales should be placed correctly in contact with the object along its length to ensure accurate measurements.
Q10: How many millimetres are there in a centimetre?
There are 10 millimetres in a centimetre.
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which of the following is an example of linear motion?
a) The motion of a car moving on a straight road
b) The motion of a swing
c) The motion of a merry-go-round
d) The motion of a pendulum
Ans: a) The motion of a car moving on a straight road
Linear motion occurs when an object moves along a straight path.
Q2: What is the smallest unit of length that can be measured using a typical 15-cm scale?
a) Metre
b) Centimetre
c) Millimetre
d) Inch
Ans: c) Millimetre
A typical 15-cm scale is divided into millimetres, with each millimetre being one-tenth of a centimetre.
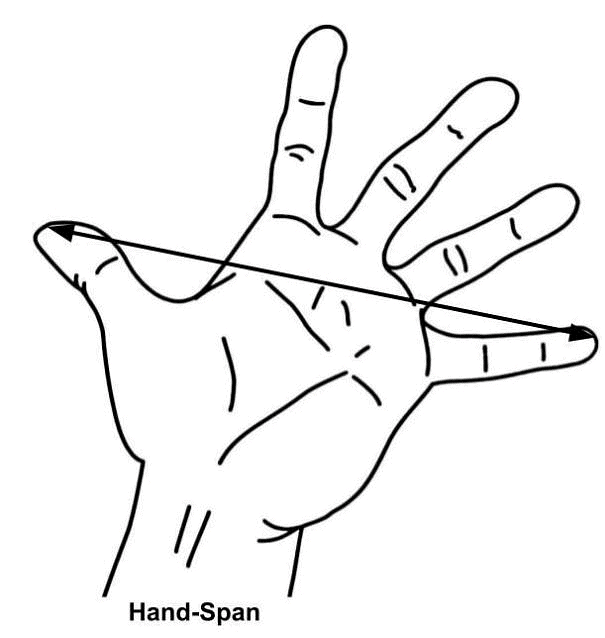
Q3: Which of the following is not a standard unit of measuring length?
a) Kilometre
b) Handspan
c) Centimetre
d) Millimetre
Ans: b) Handspan
Handspan is a non-standard unit of measurement that varies from person to person.
Q4: What type of motion does a child on a swing exhibit?
a) Linear motion
b) Circular motion
c) Oscillatory motion
d) Rotational motion
Ans: c) Oscillatory motion
A child on a swing moves back and forth around a fixed point, which is an example of oscillatory motion.
Q5: How can a broken scale still be used to measure length?
a) By starting from any other full mark
b) By estimating the length
c) It cannot be used
d) By aligning the broken end with the object
Ans: a) By starting from any other full mark
If a scale is broken and the zero mark is missing, you can still measure length by starting from another full mark (e.g., 1 cm, 2 cm). You just need to subtract the starting point from the final measurement to get the accurate length.
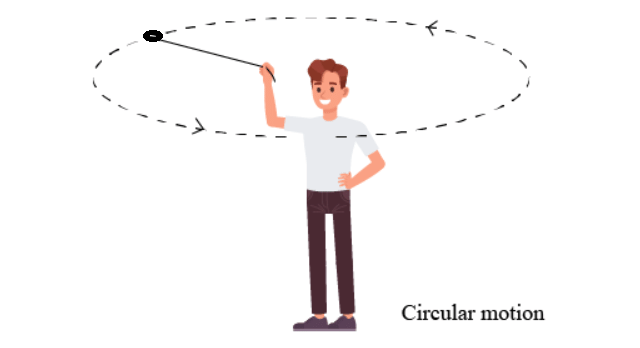
Q6: When an object moves along a circular path, its motion is called:
a) Linear motion
b) Circular motion
c) Oscillatory motion
d) Periodic motion
Ans: b) Circular motion
Circular motion is the movement of an object along a circular path.
Q8: If the distance between your school and home is 1.5 km, how many metres is this?
a) 15 m
b) 150 m
c) 1500 m
d) 15000 m
Ans: c) 1500 m
1 kilometre is equal to 1000 metres, so 1.5 kilometres is 1500 metres.
Q9: Which of the following statements is true about the metre scale?
a) It is only used to measure small objects
b) It can measure lengths up to 1 km
c) It is divided into 100 equal parts called centimetres
d) It is used to measure volume
Ans: c) It is divided into 100 equal parts called centimetres
A metre scale is divided into 100 equal parts, each representing a centimetre.
Q10: Where should your eye be positioned when reading the scale to measure length accurately?
a) Above the middle of the object
b) Directly above the starting point of the object
c) At any angle to the object
d) Above the zero mark of the scale
Ans: d) Above the zero mark of the scale
To avoid parallax error and ensure an accurate reading, your eye should be directly above the point on the scale that aligns with the object's length. This prevents any distortion in the measurement due to viewing the scale from an angle.
|
69 videos|288 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ & Extra Questions: Measurement of Length and Motion - Science for Class 6
| 1. How do you measure length accurately? |  |
| 2. What are the different units used to measure length? |  |
| 3. How can you convert centimeters to meters? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between distance and displacement? |  |
| 5. How can you determine the speed of an object in motion? |  |