Variance Analysis | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Meaning of Analysis of Variance |

|
| Importance of Variance |

|
| Features of Variance |

|
| Types of Variances |

|
Meaning of Analysis of Variance
- Variance means the deviation of the actual cost or actual sales from the standard cost or profit or sales. Calculation of variances is the main object of standard costing. This calculation shows that whether costs are under controlled or not. A variance may be favourable or adverse.
- The process of computing the amount of variance and isolate the causes of variances between actual and standard. - C.I.M.A. London
- When actual cost is less than standard cost or profit is better than the standard profit, it is known as 'Favourable Variance'. On the other hand, where the actual cost is more than standard cost or profit is better than the standard profit, it is known as 'Unfavourable Variance' or 'Adverse'.
- A mere knowledge of the variances is not sufficient and useful to the management; the causes responsible for these variances should also be brought to the knowledge of the management of the business. The process of finding out the causes of the variances and evaluating their effect is regarded as 'Analysis of Variance'.
- A controllable variance is when a variance is treated as the responsibility of a person with the result that his or her degree of efficiency can be reflected in size. When a variance arises due to some unforeseen factors, it is known as uncontrollable variance. The management should look more carefully at controllable variance, for it is these variances that require examination and possible corrective measures. The uncontrollable variances may be ignored.
Importance of Variance
There is a lot importance of analysis of variance. There are many objects fulfilled with their analysis. Without analysis of variance, there is no use of standard costing. The important points of variances are as under :
- Check and control of wastage is possible.
- It improves the efficiency of the organization by the use of standard costing.
- It exercises control over all cost centers including department, individuals and so on.
- Responsibility of a particular person or department can be fixed.
- In the prediction of production cost, sales and profit, variance analysis is very useful.
- On the basis of variance analysis, delegation of authority could be made effective.
- Variance analysis is easy to introduce, apply and orient result.
- Various operational efficiencies can be measured.
Features of Variance
- In terms of money: For post office, all the variance are calculated and expressed in terms of money. They are always monetary values in as much as the physical variations are the concern of industrial engineers.
- Standard item: The minuend should always be the standard item and the subtrahend the actual figure. The remainder between the minuend and the subtrahend is multiplied by the standard index. In fact, minuend is the figure from which something is subtracted and subtrahend is that something which is subtracted from the minuend. In other words if the performance has, on the whole, been costlier, it is unfavourable variance and when it is cheaper than it was envisaged, it is favourable.
- Budgeted figure : the Minuend: Where the prefix ‘budget’ is used before the variance, the minuend is the budgeted figure based on the normal production. The fixed overhead budget variance is the difference between the budgeted fixed overhead and the actual overhead.
Types of Variances
Initially, standards for all elements of costs should be set and then the actual cost should be compared with the standard costs to obtain the variances. Some deviations are found when actual performances are recorded and compared with the standard set. These deviations are known as variances.
"A variance is the difference between a standard cost and the comparable actual cost incurred during a period" ‐ C.I.M.A. London
Variances are classified on the basis of:
- On the basis of control: On the basis of control, variance may be classified as controllable variance and uncontrollable variance.
- On the basis of profitability: With regard to the profitability or effect, variance may be classified into two:
(i) favourable variance and
(ii) unfavourable variance.
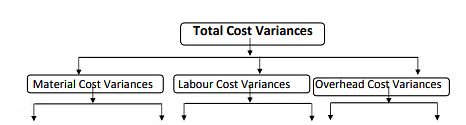
These are also known as credit and debit variance or negative and positive variances. - On the basis of elements of cost: Though different types of variances can be calculated, their use may not be much useful. Variance calculated on the basis of different elements of cost. They are as follows:
Total Cost Variance is a difference between the standard cost value of the output achieved in a period and the total cost incurred.
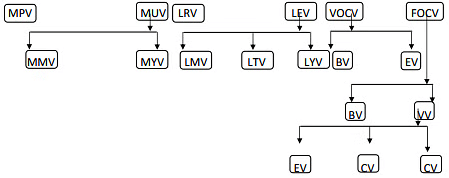
Material Variances (MV)
These variances include Material Cost Variances, Material Price Variances, Material Usage Variances, Material Mix Variances and Material Yield Variances.
- Material Cost Variances (MCV): It is the difference between the standard cost of material specified for the output achieved and the actual cost of direct materials used.
MCV = (Std. Quantity x Std. Price) ‐ (Actual Quantity x Actual Price)
(SQ x SP) ‐ (AQ x AP) - Material Price Variances (MPV): It is that portion of the material cost variance which is due to the difference between the standard price specified and the actual price paid.
MPV = Actual Quantity (Std. Price ‐ Actual Price)
AQ (SP x AP)
Where, Price = Rate - Material Usage Variances (MUV): Material usage variance is a part of Direct Material Cost Variance. MUV is determined by difference found between the standard quantity and the use of actual quantity. Later, the difference found is multiplied by the standard price.
MUV = Standard Price (Std. Quantity ‐ Actual Quantity)
SP (SQ ‐ AQ) - Material Mix Variances (MMV): It is that portion of direct material usage variance which is the difference between the actual quantities of elements used in a mixture at a standard price and the total quantity of elements used at the weighted average price per unit of element as shown by the standard cost sheet.
MMV = Standard Price (Std. Mix ‐ Actual Mix)
SP (SM ‐ AM) Note: When the actual weight of quantity and the standard weight of quantity differ from each other, this formula is used to find new quantity.
Note: When the actual weight of quantity and the standard weight of quantity differ from each other, this formula is used to find new quantity. - Material Yield Variances (MYV): This is "that portion of the direct materials usage variances which is due to the difference between standard yield specified and the actual yield obtained.
MYV = Standard Yield Price (Std. Yield ‐ Actual Yield)
SYP (SY ‐ AY) Note: When the actual weight of quantity and the standard weight of quantity differ from each other, this formula is used to find new quantity.
Note: When the actual weight of quantity and the standard weight of quantity differ from each other, this formula is used to find new quantity.
Labour Variances (LV)
Labour variances occur because of the difference in actual rates and standard rates of labour and the variation in actual time taken by labours and the standard time allotted to them for doing a job. These variances include Labour Cost Variances, Labour Rate Variances, Labour Time or Efficiency Variances, Labour Idle Time Variances, Labour Mix Variances.
- Labour Cost Variances (LCV): This is the difference between the standard direct labour cost and the actual direct labour cost incurred for the production achieved.
LCV = (Std. Time x Std. Rate) ‐ (Actual Time x Actual Rate)
(ST X SR) ‐ (AT x AR) - Labour Rate Variances (LRV): This is that portion of the labour cost variance which is due to the difference between the standard rate specified and the actual rate paid.
LRV = Actual Time (Std. Rate ‐ Actual Rate)
AT (SR ‐ AR)
Note: Actual Time = Actual Hours, Std. Rate = Std. Wage Rate - Labour Time (Efficiency) Variances: (LTV/LEV): It is defined as the difference between the standard hours (Time) for the actual production achieved and the hours actually worked, valued at the standard labour rate.
LTV = Standard Rate (Std. Time ‐ Actual Time)
SR (ST ‐ AT) - Idle Time Variance (ITV): ITV comes up because of idle time of workers on account of abnormal causes. The wages paid for the time during which the workers remained idle due to causes like strikes, breakdown on plant, etc. are treated as idle time variances.
ITV = Idle Time x Standard Rate
IT x SR - Labour Mix Variance / Gang Composition Variance (LMV): It occurs only when more than one grade of workers is employed and the composition of actual grade of workers differs from those specified.
Std. Time x (Revised Std. Time ‐ Actual Time)
ST x (RST ‐ AT)
Overhead Variances (OV)
Overhead is the aggregate of indirect materials, indirect labour and indirect expenses. Analysis of overhead variances is different from that of direct material and direct labour variances by two reasons.
- It is difficult to establish Standard overhead rate for fixed overhead because changes in the volume of output will affect the standard overhead rate even if there is no change in the amount of fixed overhead cost.
- For computing overhead variances, there are quite a few terminological options and methods.
The overhead variances include fixed overhead variances and variable overhead variances. Moreover, further analysis of overhead variances is also possible according as the available source information. It is significant to know at the beginning that the overhead variance is not anything but under or over‐ absorption of the overhead.
(a) Variable Overhead Cost Variance (VCOV): VCOV is the difference between the standard variable overhead cost for production and the actual variable cost incurred during the period.
VCOV = (Std. hours for actual Output x Std. variable overhead rate) ‐ Actual overhead cost
Absorbed V. O. ‐ Actual V. O.
(1) Variable Overhead Expenditure Variance (VOEV): VOEV is known as spending variance or 'Budget Variance'. This variance arises due to the difference between standard variable overhead allowed and actual variable overhead incurred.
VCOV = (Std. Variable Overhead Rate x Actual Hours) ‐ Actual overhead cost
Standard V. O. ‐ Actual V. O.
(2) Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance (VOEV): VOEV can occur due to the difference between standard hours allowed for actual output and actual hours
VOEV = (Std. Variable for actual output ‐ Actual hours) x Std. Variable overhead rate
Absorbed V. O. ‐ Standard V. O
Check = V. O. Expenditure Variance + V. O. Efficiency Variance
(b) Fixed Overhead Cost Variances (FOCV): FOCV is the difference between standard fixed overhead cost for actual output and actual fixed overhead.
FOCV = (Std. hours for actual output x Std. F. O. Rate) ‐ Actual F. O.
(Absorbed Overhead ‐ Actual Overhead)
(1) Fixed Overhead Expenditure Variances (FOEV): This is known as spending variance or Budget Variance. It arises due to the difference between budgeted fixed overhead and actual fixed overhead.
FOEV = Budgeted Fixed Overhead ‐ Actual Fixed Overhead
(2) Fixed Overhead Volume Variances (FOVV): It is known as that portion of overhead variance which arises due to the difference between standard cost of overhead absorbed by actual production and the standard allowance for that output.
FOVV = (Std. Time for Actual Output ‐ Budgeted Time) x Std. Rate
Absorbed Overhead ‐ Budgeted Overhead
(i) Efficiency Variances (EV): It classifies that portion of volume variance which reflects the increased or reduced output arising from efficiency above or below the standard which is expected.
EV = (Std. Time for Actual Output ‐ Actual Time) x Std. Rate
Absorbed Fixed Overhead ‐ Standard Fixed Overhead
(ii) Capacity Variances (CV): It classifies that portion of the volume variance which is caused by functioning at higher or lower capacity usage than the standard. It is affected by the factors like strikes, power failure, over demand etc.
CV = (Actual Time Worked ‐ Budgeted Time) x Std. Rate Std.
Fixed Overhead ‐ Budgeted Overhead
Note: Actual Time = Actual Hours
(iii) Calendar Variances (CV): It classifies that portion of the volume variance which is caused by the difference between the number of working days in the budget period and the number of actual working days in the period to which the budget is applied.
This variance arises only in exceptional circumstances because normal holidays are taken into account while laying down the standard.
CV = Actual No. of Working Days ‐ Std. No. of Working Days) x Std. Rate per Day
(Revised Budgeted Time ‐ Budgeted Time) x Std. Rate per Time
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Variance Analysis - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is the importance of Variance Analysis of Variance? |  |
| 2. What are the key features of Variance Analysis of Variance? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of Variances in Variance Analysis of Variance? |  |
| 4. How can Variance Analysis of Variance be used in UGC NET exams? |  |
| 5. How does Variance Analysis of Variance help in decision-making processes? |  |















