Corporate Tax Planning: Concepts & Significance - UGC NET PDF Download
- Understanding Corporate Tax Planning in India
- Significance of Corporate Taxes
Businesses in India are subject to taxation based on their annual profits, forming a substantial part of the government's income. Adherence to tax regulations is vital for preventing disputes and fostering a conducive business environment. - Importance of Corporate Tax Planning
Implementing a corporate tax planning system is essential to mitigate the impact of taxes on a company's earnings. This system aims to minimize tax liabilities and maximize retained income. - Techniques for Effective Tax Planning
Various strategies and techniques exist within corporate tax planning to help businesses enhance their profitability by optimizing their tax obligations.
- Significance of Corporate Taxes
- UGC NET Commerce Exam Syllabus
- Inclusion of Corporate Tax Planning
The UGC NET Commerce Exam syllabus covers fundamental concepts like corporate tax planning and corporate income tax planning, often presented through case studies and exam questions. - Topics to Expect
Aspirants can anticipate encountering core aspects of corporate tax planning, essential principles, and strategies for corporate income tax planning during the examination.
- Inclusion of Corporate Tax Planning
- Introduction to Corporate Tax Planning
- Defining Corporate Tax Planning
Corporate tax planning involves the strategic management of a company's tax obligations to leverage advantages and minimize drawbacks. - Pros and Cons
Understanding the benefits and potential disadvantages of corporate tax planning is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions regarding their tax strategies.
- Defining Corporate Tax Planning
- Related Topics
- Explore Additional Subjects
Apart from corporate tax planning, topics like the audit of financial statements and audit reports are also integral areas of study for commerce students.
- Explore Additional Subjects
Understanding Corporate Tax in India
Corporate tax is a crucial aspect of financial management that affects both domestic and foreign companies operating in India. It is governed by the Indian Income Tax Act of 1961, mandating that businesses pay taxes on their incomes. Let's delve deeper into this concept:
Domestic Companies and Taxation
- Domestic companies, as defined by the Indian Companies Act, are required to pay taxes on their global income, encompassing earnings from both India and other nations.
- Non-compliance with tax regulations can result in severe penalties, potentially leading to the cessation of business operations.
Foreign Companies and Tax Obligations
- Foreign companies with operations in India are also liable to pay taxes, specifically on the income generated within the country.
- Understanding and adhering to the tax laws of India is crucial for foreign entities to ensure compliance and avoid legal repercussions.
Corporate Tax Planning for Long-Term Benefits
- Corporate tax planning involves strategies aimed at reducing tax liabilities, thereby securing long-term advantages for the company.
- By leveraging legal tax exemptions and optimizing financial structures, businesses can effectively lower their tax burdens.
Significance of Tax Compliance
- Ensuring compliance with tax laws is essential for the sustainability and growth of companies, as non-compliance can lead to significant financial penalties and legal consequences.
Advance payment of tax is an integral aspect of corporate tax management that warrants further exploration for a comprehensive understanding of tax planning strategies.
Corporate Tax Planning: Maximizing Profits through Strategic Tax Management
- Understanding Corporate Tax: Corporate tax mirrors individual income taxes but applies to businesses. By leveraging exemptions and deductions, companies can minimize tax burdens, leading to increased funds for growth and dividends.
- Exploring Corporate Tax Planning: Corporate tax planning revolves around reducing tax liabilities to enhance profitability. Businesses need to engage in ongoing tax planning to optimize their financial outcomes.
- Nature of Corporate Tax Planning:
- The process involves meticulous planning and forecasting. Companies predict their revenues and strategize tax-exempt investments for the fiscal year.
- Corporate tax planning encompasses both short-term and long-term organizational goals.
- Accurate income reporting is crucial for determining tax responsibilities by adhering to relevant tax brackets and regulations.
- Benefits of Corporate Tax Planning: Effective tax planning empowers companies to create financial roadmaps. This enables them to assess their tax obligations and allocate funds judiciously throughout the year.
Advantages of Corporate Tax Planning
Corporate tax planning involves strategies and actions taken by companies to manage their tax liabilities effectively. Here are some key benefits:
Essential Features of Corporate Tax Planning
- Corporate tax planning involves making strategic plans for future earnings and tax savings. It is a forward-looking process that aims to optimize tax obligations.
- By implementing effective tax planning strategies, companies can reduce tax burdens for both individuals and the organization as a whole, leading to increased profitability.
- One important aspect of corporate tax planning is encouraging investments in tax-efficient avenues. This helps in fostering a culture of financial prudence and aligning investments with long-term business objectives.
- Tax planning is a flexible process that can adapt to changes in tax regulations and laws, ensuring that companies remain compliant while maximizing tax benefits.
- It is crucial to emphasize that corporate tax planning is a legal and ethical practice aimed at minimizing tax liabilities within the boundaries of the law.
- Effective corporate tax planning contributes to the realization of short-term financial goals as well as long-term strategic objectives of a company.
Example:
For instance, a multinational corporation may engage in cross-border tax planning to minimize its overall tax burden by taking advantage of tax incentives in different countries while ensuring compliance with international tax laws.
Implications:
Corporate tax planning not only reduces tax liabilities but also enhances financial stability and growth opportunities for businesses, enabling them to allocate resources more efficiently and strategically.
Case Study:
In a recent case study, Company X implemented a comprehensive tax planning strategy that resulted in significant tax savings, allowing the company to reinvest those funds into research and development, ultimately driving innovation and competitiveness in the market.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, corporate tax planning is a vital aspect of financial management for organizations, offering various advantages such as increased profitability, compliance with tax laws, and strategic resource allocation.
Overview of Corporate Tax Planning
Corporate tax planning involves the strategic analysis and management of a company's tax obligations to optimize financial efficiency and compliance. Below are key aspects of corporate tax planning:
Analysis of Company Statements
- Corporate tax planning entails a detailed examination of a company's financial records to understand its tax liabilities and financial standing.
Futuristic Focus
- Tax planning is forward-looking, considering the future financial needs and objectives of the company to make informed decisions.
Income Coverage
- Tax planning encompasses all sources of company income, requiring accurate reporting to ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Alignment with Company Goals
- Effective tax planning is crucial for achieving the company's strategic objectives, involving strategies like diversification and optimizing the company's structure.
Budget Efficiency
- Corporate tax planning plays a vital role in enhancing the company's budget efficiency by managing tax liabilities effectively, which directly impacts financial resources.
Legal Compliance
- Corporate tax planning is bound by the laws and regulations of the country where the company operates, necessitating adherence to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
For further insights, explore basic concepts of Income tax.
Techniques for Corporate Tax Planning
- Expense Management
- The company needs to maintain detailed records of all expenses to ensure no deductions are missed. Proper documentation helps in reducing taxable income.
- Deductions and Exemptions
- Companies should take advantage of all available deductions and exemptions before the end of the financial year to minimize their tax liability.
- Corporation Structure
- Businesses can consider structuring themselves as limited liability companies (LLCs) to benefit from lower tax rates and liability protection.
- International Structure
- Companies with international operations can strategically transfer funds to jurisdictions with lower tax rates to optimize their tax burden. This practice is common among multinational corporations seeking to reduce their overall tax expenses.
One notable aspect to explore further is kaizen costing, a strategy that focuses on continuous improvement and cost reduction within a company.
This revised version provides a detailed and paraphrased explanation of the techniques for corporate tax planning outlined in the original content. It breaks down each point into bullet format, explaining the significance of each technique in managing corporate taxes effectively.Corporate Tax Planning Process
- Setting Goals:
The initial step in corporate tax planning involves setting clear taxation and company objectives for the fiscal year. These goals help in selecting appropriate investment tools that align with the company's financial targets.
Example: A company aims to minimize tax liabilities while maximizing profits, so they set specific goals for reducing taxable income through legal means.
- Information Gathering:
Management must collect comprehensive data regarding the company's finances, including income estimates from various sources and potential tax obligations. This information forms the basis for developing effective tax strategies.
Example: Gathering data on revenue streams, expenses, and potential deductions to accurately assess the company's tax situation.
- Tax Strategies:
After acquiring the necessary information, the company must devise appropriate tax strategies that align with its goals and aim to minimize tax burdens. These strategies should be tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of the organization.
Example: Implementing tax-efficient structures such as tax credits, deductions, or deferrals to optimize the company's tax position.
- Investment:
Based on the chosen tax strategies, the company should proceed to make investments that qualify for tax exemptions or benefits. Keeping detailed records of these investments is crucial for accurate tax planning and compliance.
Example: Investing in tax-exempt municipal bonds or qualified opportunity zone projects to reduce taxable income and gain tax advantages.
- Tax Payments and Returns:
It is imperative for the company to fulfill its tax obligations by paying the required taxes and submitting accurate tax returns that reflect applicable deductions and exemptions. Timely compliance with tax regulations is vital to avoid penalties.
Example: Ensuring timely submission of tax returns with all necessary documentation to claim deductions and credits, thereby optimizing the company's tax position.
Read about E-filing of income tax returns.
This revised content provides a detailed explanation of the corporate tax planning process, breaking down each step with clear descriptions and examples to enhance understanding.Understanding Indian Corporate Tax Rates
When it comes to operating in India, companies must adhere to the regulations and fulfill their tax obligations promptly. Here are the key tax rate guidelines for corporations in India:
Tax Rates for Domestic Companies
Domestic companies in India are those registered under the Companies Act, encompassing both public and private enterprises. Let's delve into the specifics of corporate tax planning for these entities:
Corporate Tax Planning- Domestic businesses are currently subject to a tax rate of 30%.
- If a company's income falls within the range of ₹1 crore to ₹10 crores, a 7% surcharge is applicable. For companies exceeding ₹10 crores in revenue, the surcharge rises to 12%.
- Following the enactment of Section 115BAA in 2019, the effective tax rate for companies reduced to 25.168%. This comprises a base tax rate of 22%, a 10% surcharge, and a 4% Cess, culminating in the effective rate of 25.168%. This tax adjustment proves advantageous for corporations.
It's important to note that these tax rates and provisions significantly impact the financial landscape for businesses in India, influencing their operational and investment decisions.
Example Illustration
Let's consider an Indian domestic company with an annual revenue of ₹15 crores. Given the current tax structure, the company would face a 30% tax rate on its income, along with a 12% surcharge due to revenue exceeding ₹10 crores. This would result in an effective tax rate of 25.168%, aligning with the revised tax framework introduced in 2019.
Understanding and effectively managing corporate taxes in India is crucial for businesses to maintain financial stability and compliance with legal requirements.
Additional Resources
For further insights into corporate financial management, explore topics like Environment Audit to enhance your understanding of regulatory compliance and sustainable business practices.
Understanding Tax Rates for Foreign Companies in India
Foreign companies operating in India are subject to specific tax regulations that influence their corporate tax planning strategies. Let's delve into the key rules governing tax rates for foreign companies:
Corporate Tax Rates
- If a foreign company earns royalties and fees within Indian territory, it is liable to pay a tax rate of 50% on such earnings.
- For other forms of income, the standard tax rate stands at 40%, encompassing various financial balances.
- When the company's income falls within the range of ₹1 Crore to ₹10 Crores, an additional charge of 2% is levied.
- If the company's revenue surpasses ₹10 Crores, an extra charge of 5% applies.
For instance, if a foreign company earns royalties worth ₹2 Crores in India, it would be subject to a 50% tax rate on that specific income.
Additional Charges Imposed
Aside from the core tax rates, companies must also adhere to supplementary charges, including:
- Companies are mandated to pay a health and education cess of 4%, which is applicable across all companies, regardless of their annual incomes.
- Under Section 115 BAA, companies can avoid paying the Minimum Alternate Tax in Section 115JB if they opt for specific benefits.
For instance, if a company's total income amounts to ₹15 Crores, it would be subject to the standard tax rate of 40% along with an additional 5% charge due to its revenue exceeding ₹10 Crores.
It is essential for companies, especially foreign entities, to comprehend these tax regulations thoroughly to effectively plan their corporate tax strategies in India.
Corporate Tax Planning: A Comprehensive Overview |
|---|
Introduction to Corporate Tax in IndiaCorporate tax in India is a crucial aspect that companies, both domestic and foreign, need to adhere to. It is essential for understanding the financial obligations that businesses have towards the government. Domestic Companies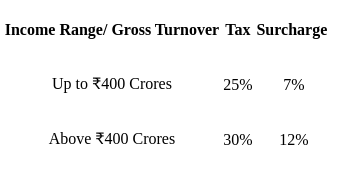 Domestic companies in India are subjected to specific tax regulations based on their operations within the country. Foreign Companies Foreign companies operating in India have their own set of tax obligations and considerations. Objectives of Corporate Tax PlanningCorporate tax planning is essential for businesses to manage their tax liabilities effectively. Let's delve into the key objectives and benefits: 1. Increase SavingsThrough strategic corporate tax planning, companies can reduce their tax burden, leading to increased savings. These savings can be reinvested in the business for growth and development. For instance, a manufacturing company might reinvest tax savings in upgrading machinery. 2. Economic StabilityCorporate taxes contribute significantly to government revenues, supporting economic stability. By planning taxes efficiently, businesses ensure a steady flow of funds to the government, aiding in infrastructure development and overall economic progress. 3. Enhance GrowthEffective tax planning allows companies to allocate more resources towards business growth. For example, a tech startup might use tax savings to hire more skilled employees or expand into new markets, fostering innovation and expansion. 4. Minimization of LitigationBy adhering to legal tax planning strategies, companies can minimize the risk of facing tax-related litigations and fines. This ensures compliance with tax laws and prevents legal complications that could harm the business reputation. |
Corporate Tax Planning and Productive Investments
Corporate Tax Planning
- Companies strategically plan their finances to minimize tax liabilities.
Productive Investments
- Businesses make investments in tax-exempt sectors to reduce tax burdens.
- These investments offer long-term benefits and can be reserved for emergencies or future objectives.
Types of Corporates
Indian taxation laws categorize companies into two main types based on their origin:
- Domestic Companies
- Foreign Companies
Each type of company has distinct corporate tax planning strategies to adhere to specific tax obligations.
Types of Corporate Tax Planning

It is essential to differentiate between these types of companies to effectively manage taxes.
Understanding the variance in tax regulations for domestic and foreign companies is crucial for implementing appropriate tax planning measures.
For instance, domestic companies in India may benefit from tax deductions on investments made in sectors like infrastructure or healthcare, promoting economic growth while reducing tax liabilities.
Types of Tax Planning
Tax planning involves structuring your financial matters to minimize the amount of tax you owe while staying compliant with the law. There are several strategies that individuals and businesses can use to lessen their tax burden effectively. Let's delve into the common types of tax planning:
- Income Splitting: Income splitting is a strategy where income is distributed among family members or legal entities to lower the overall tax burden. For example, a business owner might pay their children a salary for work in the business, effectively shifting income to individuals in lower tax brackets.
- Capital Gains Planning: Capital gains tax applies to the profit made from selling assets like stocks or real estate. Proper planning can involve strategically selling assets to take advantage of lower tax rates or exemptions.
- Retirement Planning: Retirement plans like 401(k)s and IRAs offer tax advantages. By contributing to these accounts, individuals can reduce their taxable income while saving for retirement.
- Charitable Giving: Donations to qualified charities can be tax-deductible. By strategically giving to charitable organizations, individuals and businesses can lower their taxable income.
- Tax Credits: Tax credits directly reduce the amount of tax owed. Utilizing credits for activities like education expenses or renewable energy investments can significantly lower tax liabilities.
- Income Splitting: This strategy involves redistributing income among family members or legal entities to leverage lower tax brackets or exemptions. For instance, a business owner might pay their spouse or children a salary or dividends from the business.
- Tax Credits: Tax credits are deductions directly from your tax liability, not your taxable income. You can benefit from various tax credits like the Child Tax Credit, Education Credits, and Renewable Energy Credits.
- Tax Deductions: These reduce your taxable income, thereby lowering your tax liability. Examples include deductions for mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and business expenses. Maximizing eligible deductions decreases taxable income.
- Tax-Advantaged Accounts: Contributing to accounts like 401(k)s, IRAs, HSAs, and 529 plans can lower taxable income and offer tax benefits. Contributions to these accounts are often tax-deductible or grow tax-free.
- Capital Gains and Losses Management: Timing the sale of investments such as stocks and real estate can affect your capital gains tax. Strategies like tax-loss harvesting can help offset gains with losses.
- Estate Tax Planning: This involves structuring your estate to minimize estate taxes upon your death. Strategies may include setting up trusts, making tax-free annual gifts, and utilizing the applicable exclusion amount.
- Business Tax Planning: Business owners can utilize strategies like selecting the appropriate business structure (e.g., LLC, S-Corporation), depreciating assets, and leveraging available tax deductions.
- International Tax Planning: For individuals and businesses with global interests, strategies like transfer pricing, foreign tax credits, and offshore tax shelters can optimize global tax obligations.
- Tax-Efficient Investing: Opting for tax-efficient investments and holding them long-term can lower capital gains taxes. Index funds and tax-efficient funds can help minimize tax implications.
- State and Local Tax Planning: Tax planning extends beyond federal taxes to minimizing state and local taxes. Strategies may involve moving to a lower-tax area or structuring investments to reduce state tax liability.
- Retirement Tax Planning: Planning for retirement includes strategies like maximizing Social Security benefits, managing RMDs, and planning tax-efficient withdrawals from retirement accounts.
- Real Estate Tax Planning: Real estate investors can utilize strategies such as 1031 exchanges to defer capital gains taxes, optimize deductions, and structure ownership tax-efficiently.
- Tax-Deferred Exchanges: In real estate and certain business transactions, tax-deferred exchanges (e.g., like-kind exchanges) enable deferring capital gains taxes by reinvesting proceeds into similar assets.
- Charitable Giving: Donating to qualified charities can offer tax deductions. Advanced strategies like charitable remainder trusts and donor-advised funds provide additional tax planning opportunities.
- Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) Planning: High-income individuals may need to consider AMT planning to reduce the impact of this parallel tax system.
It's essential to note that tax laws evolve, so consulting a tax professional or financial advisor ensures your tax planning aligns with current codes.
Understanding Double Taxation and its Avoidance Mechanism
Double taxation occurs when a taxpayer is taxed twice on the same income or financial transaction. This can happen when a company's profits are taxed at both the corporate and shareholder levels. To prevent this, various mechanisms are in place to provide relief and avoid double taxation.
Tax Rebates for Companies
Under the Indian Income Tax Act, companies can benefit from tax refunds through various mechanisms:
- Deductions for New Ventures and Exports: Companies can avail deductions for new ventures, operations, and exports under specific circumstances.
- Domestic Dividends: Domestic companies receiving dividends from other domestic companies can deduct this income in specific situations.
- Infrastructure and Electricity Installations: Specific deductions are available for new infrastructure and electricity source installations.
- Venture Capital Funds: Companies involved with venture capital funds can benefit from specific deductions.
- Business Losses: Business losses can be carried forward for a maximum of eight years.
- Interest, Dividends, and Capital Gains: In certain scenarios, these incomes are also deductible for companies.
These rebates enable companies to generate income without facing heavy tax burdens. By engaging in legal corporate tax planning, businesses can effectively reduce their tax liabilities.
Understanding Corporate Tax Planning
- Saving Money in Taxes: Corporate tax planning is a strategic approach that helps businesses reduce the amount of tax they owe to the government. By taking advantage of legal tax-saving opportunities, companies can retain more of their earnings.
- Utilizing Extra Income for Growth: When businesses save money through effective tax planning, they can reinvest these funds into expanding their operations, innovating products or services, and diversifying their business ventures.
- Long-Term Investment Benefits: Corporate tax planning enables companies to allocate resources towards long-term investments that can provide sustainable benefits over time. These investments can also serve as a financial cushion during emergencies.
- Contributing Legal Tax Revenue: By engaging in proper tax planning, businesses ensure they contribute their fair share of taxes to the government. This not only supports public services but also fosters economic growth and stability.
- Avoiding Disputes and Ensuring Compliance: Through corporate tax planning, companies can proactively adhere to tax laws and regulations, minimizing the risk of disputes with tax authorities. By following legal measures to reduce taxes, businesses can maintain financial integrity.
- Facilitating Financial Estimations: Effective tax planning allows companies to forecast and plan their earnings for the year accurately. This aids in financial preparation, budgeting, and making informed business decisions based on reliable financial estimations.
Limitations of Corporate Tax Planning
The limitations of corporate tax planning that business owners need to consider are as follows:
Corporate Tax Planning Limitations:- Corporate tax planning can lead to the tying up of company funds. Businesses are required to invest in tax-exempt sources to minimize taxes.
- There is a risk that businesses might resort to tax evasion by exploiting exemption laws.
- Investments that are tax-exempt often yield lower interest rates.
Examples to understand these limitations:
- Tying up of Company Funds: When a company invests in tax-exempt avenues to reduce taxes, it might restrict the availability of funds for other essential business operations or expansions.
- Tax Evasion: Some businesses, in an attempt to take advantage of tax exemptions, might engage in illegal practices to evade taxes, which can lead to severe legal consequences.
- Low Interest Rates: Investments that offer tax exemptions often come with lower interest rates, affecting the overall profitability and returns for the business.
Corporate Tax Planning
- Businesses must be cautious when engaging in tax planning to ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
- It is essential for companies to seek professional advice to navigate the complexities of tax planning effectively.
Importance of International Business:
Understanding the scope and importance of international business is crucial for companies looking to expand their operations globally. It opens up opportunities for growth, diversification, and access to new markets.
Corporate Tax Planning Overview
- Definition and Importance of Corporate Tax Planning: Corporate tax planning is a crucial process that companies undertake to optimize their tax liabilities within the legal framework. It involves strategic decisions to minimize the tax burden while ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Advantages of Corporate Tax Planning:
- Enhanced Profitability: By effectively managing tax obligations, companies can increase their bottom line, leading to higher profits available for reinvestment or distribution.
- Risk Mitigation: Proper tax planning helps in reducing the risk of penalties or audits by ensuring compliance with tax laws and regulations.
- Resource Allocation: Companies can allocate resources more efficiently when they have a clear understanding of their tax liabilities and plan accordingly.
- Competitive Edge: Strategic tax planning can provide a competitive advantage by lowering costs and improving overall financial performance.
- Disadvantages of Corporate Tax Planning:
- Complexity: Tax laws can be intricate, and navigating through them for planning purposes may require specialized knowledge and expertise.
- Legal Risks: Aggressive tax planning strategies may sometimes push the boundaries of legality, potentially exposing companies to legal risks and reputational damage.
- Costs: Engaging in sophisticated tax planning may incur additional costs in terms of professional fees, software, or other resources.
- Importance of Timely Planning: Corporate tax planning should be a proactive process that starts at the beginning of the fiscal year to ensure that the company can benefit from tax-saving opportunities throughout the year.
- Relevance for UGC NET Exam: Understanding strategic corporate tax planning concepts is essential for exams like UGC NET, where topics such as tax planning, double taxation, and financial analysis are covered.
- Key Topics Related to UGC NET:
- Tax Planning
- Double Taxation and its Avoidance Mechanism
- E-Filing of Income Tax Return
- Cash Flow Analysis
- Advance Payment of Tax
- Cost Audit Recent Trends
- Meaning and Scope of Business Economics
- Make or Buy Decisions Study Notes
- Techniques of Corporate Tax Planning
- Retirement in India


















