Exchange Rate Risk & Hedging Techniques | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Exchange Rate Risk? |

|
| How Exchange Rate Risk Functions |

|
| What is Hedging? What are Hedging Strategies? |

|
| Common Hedging Strategies |

|
| Benefits of Hedging |

|
What is Exchange Rate Risk?

Exchange rate risk, also known as foreign exchange (forex) risk, is the potential for financial losses due to fluctuations in currency exchange rates. This risk is inherent in any foreign investment but can be managed through various hedging strategies. To fully eliminate exchange rate risk, an investor would need to avoid international investments altogether. However, effective hedging methods can significantly reduce this risk.
Exchange rate risk arises when the value of an investor's local currency changes relative to the currency of their foreign investments. This risk can be mitigated through tools like currency forwards, futures, and options, or by investing in hedged exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
How Exchange Rate Risk Functions
For U.S. investors, hedging becomes crucial when the U.S. dollar is strong, as this strength can diminish returns from overseas assets. Conversely, for foreign investors, a depreciating local currency can enhance returns on U.S. investments. In such scenarios, it may be advantageous to avoid hedging when the exchange rate movements benefit the investor.
A general rule is to hedge exchange rate risk when the local currency is strengthening against the foreign investment currency, and to forgo hedging when the local currency is weakening.
Ways to Mitigate Exchange Rate Risk:
Invest in Hedged Assets: One straightforward approach is to invest in hedged ETFs, which protect against currency fluctuations. Many ETFs offer both hedged and unhedged versions, tracking various benchmarks or indexes. Although hedged ETFs typically have a slightly higher expense ratio due to the cost of hedging, they provide an efficient way to manage currency risk compared to individual hedging efforts. For instance, the iShares MSCI EAFE ETF (EFA) has an expense ratio of 0.32%, while its hedged counterpart, the iShares Currency Hedged MSCI EAFE ETF (HEFA), has an expense ratio of 0.70%.
Direct Hedging Methods: Investors holding foreign-currency assets may not have automatic currency risk protection. To manage this risk directly, several instruments can be used:
- Currency Forwards: These contracts allow investors to lock in exchange rates for future transactions. They can be customized for specific amounts and maturities but are not always accessible to individual investors. A money market hedge can be an alternative.
- Currency Futures: Traded on exchanges with low upfront margins, these futures contracts offer a way to hedge currency risk but are standardized and have fixed expiration dates.
- Currency ETFs: These ETFs represent specific currencies and can be useful for small-scale hedging. They offer margin eligibility and can be traded long or short, making them suitable for individual investors.
- Currency Options: These options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific currency at a predetermined price before the expiration date. They are available in various denominations, catering well to individual investors.
While it is impossible to completely avoid exchange rate risk in foreign investments, effective use of hedging strategies can substantially mitigate it. Investing in hedged ETFs is a practical solution, but for those holding foreign-currency assets, exploring direct hedging options like forwards, futures, ETFs, or options is advisable.
What is Hedging? What are Hedging Strategies?
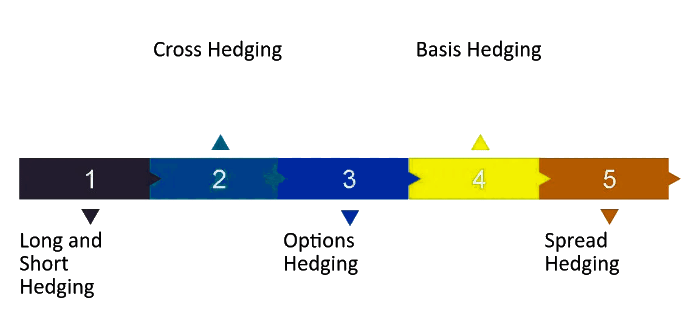
Hedging is a strategy used by investors to protect themselves from potential losses due to market fluctuations. It functions like insurance, helping investors reduce their risk, though it cannot eliminate negative events entirely. This approach is not only applied in everyday scenarios such as car or life insurance but is also commonly used by institutional investors to manage and minimize exposure to various risks.
In financial markets, hedging is used in several areas, including:
- Commodities
- Securities
- Currencies
- Interest rates
- Weather conditions
Hedging can also help investors profit from trading different assets, including commodities, currencies, and securities.
There are three main types of hedging contracts:
- Forward Contracts: These are non-standardized agreements between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date. They can be used for commodities, currencies, and other assets.
- Futures Contracts: These are standardized agreements to buy or sell an asset at a set price on a future date. Unlike forward contracts, futures are traded on exchanges and are standardized.
- Money Market Instruments: These involve short-term borrowing and lending of funds with maturities of one year or less. They cover various financial activities related to currencies and interest rates.
Common Hedging Strategies
- Asset Allocation: This involves diversifying an investment portfolio to include a mix of riskier assets and those that provide stable returns, helping to balance overall risk.
- Portfolio Structuring: Investors may structure their portfolios by combining investments in debt (for stability) with derivatives (for risk protection).
- Hedging with Options: This strategy uses call and put options to directly safeguard an investment portfolio.
Benefits of Hedging
- Limits Losses: Helps to reduce potential losses by providing a safety net against market downturns.
- Protects Profits: Assists in preserving gains made in the market.
- Increases Market Liquidity: Encourages trading across various markets, enhancing liquidity.
- Flexible Pricing: Requires minimal margin outlay and offers a flexible price mechanism.
- Scalable: Enables effective trading and risk management, making it a valuable tool for investors and traders facing market uncertainty.
|
237 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Exchange Rate Risk & Hedging Techniques - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is Exchange Rate Risk? |  |
| 2. How does Exchange Rate Risk function? |  |
| 3. What is Hedging? What are Hedging Strategies? |  |
| 4. What are some common Hedging Strategies? |  |
| 5. What are the benefits of Hedging Exchange Rate Risk? |  |















