Indian Financial System | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Indian Financial System – An Overview |

|
| Financial Institutions |

|
| Financial Assets |

|
| Financial Services |

|
| Financial Markets |

|
Indian Financial System – An Overview
The Indian Financial System encompasses the services provided by various Financial Institutions, such as banks, insurance companies, and pension funds.
Key features of the Indian Financial System include:
- It is crucial for the country’s economic development, promoting both savings and investment.
- It assists in mobilizing and efficiently allocating savings.
- It fosters the growth of financial institutions and markets.
- It plays a vital role in capital formation.
- It connects investors with savers.
- It is concerned with the provision and management of funds.
The primary objective of a country's financial system is to manage and regulate the production, distribution, exchange, and holding of financial assets or instruments of all types.
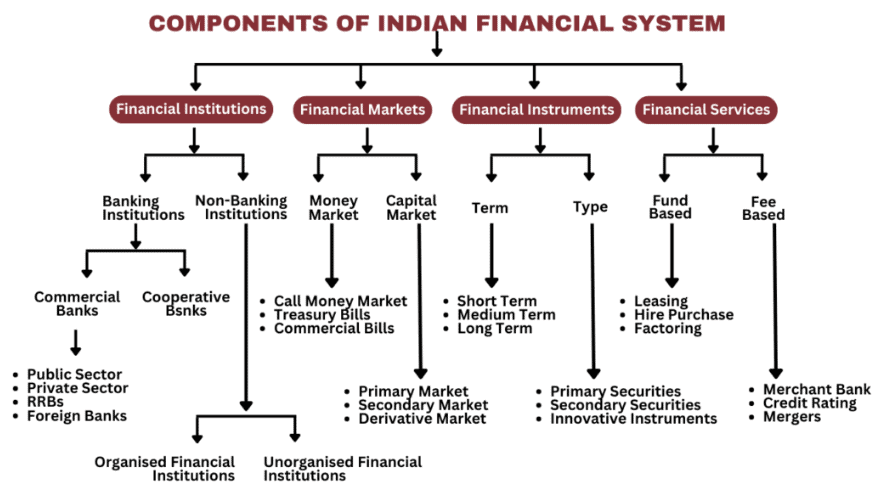
The Indian Financial System comprises four key components: Financial Institutions, Financial Assets, Financial Services, and Financial Markets. Let's explore each of these components in detail.
Financial Institutions
Financial Institutions serve as intermediaries between investors and borrowers, facilitating the mobilization of savings either directly or indirectly through Financial Markets. Their primary functions include converting short-term liabilities into long-term investments, transforming risky investments into risk-free ones, and offering convenience in denomination, such as matching small deposits with large loans or vice versa. Banks are a prime example of Financial Institutions, acting as intermediaries between depositors and borrowers.
Financial Institutions can be categorized into:
- Banking Institutions or Depository Institutions: These include banks and credit unions that collect public deposits and offer loans.
- Non-Banking Institutions or Non-Depository Institutions: These include insurance companies, mutual funds, and brokerage firms, which do not accept deposits but sell financial products.
Additionally, Financial Institutions can be classified into:
- Regulatory Institutions: Organizations like RBI, IRDA, and SEBI that regulate financial markets.
- Intermediates: Commercial banks such as SBI, BOB, and PNB that provide loans and financial assistance.
- Non-Intermediates: Institutions like NABARD and SIDBI that offer financial aid to corporate customers.
Financial Assets
Financial Assets refer to the products traded in Financial Markets, varying based on the needs of credit seekers. Key Financial Assets include:
- Call Money: Loans granted for one day, repayable on the second day, without collateral.
- Notice Money: Loans granted for more than a day but less than 14 days, without collateral.
- Term Money: Deposits with a maturity period beyond 14 days.
- Treasury Bills (T-Bills): Government debt securities with less than a year’s maturity.
- Certificates of Deposit: Electronically generated funds deposited in banks for a specific period.
- Commercial Paper: Unsecured short-term debt instruments issued by corporations.
Financial Services
Financial Services are provided by Asset and Liability Management Companies, helping clients obtain necessary funds and ensuring efficient investment. These services in India include:
- Banking Services: Services provided by banks, such as loans, deposits, debit/credit card issuance, and account management.
- Insurance Services: Activities related to issuing insurance, selling policies, and brokerages.
- Investment Services: Primarily focused on asset management.
- Foreign Exchange Services: Involving currency exchange and foreign exchange transactions.
The core objective of financial services is to assist individuals in selling, borrowing, purchasing securities, enabling payments and settlements, and facilitating lending and investment.
Financial Markets
Financial Markets are platforms where buyers and sellers engage in trading money, bonds, shares, and other assets. These markets are categorized into:
- Capital Market: Focused on long-term investments, dealing with transactions lasting over a year. It includes:
- Corporate Securities Market
- Government Securities Market
- Long-Term Loan Market
- Money Market: A short-term investment market dominated by the government, banks, and large institutions. It is further divided into:
- Organised Money Market
- Unorganised Money Market
- Foreign Exchange Market: A well-developed market dealing with multi-currency requirements and fund transfers based on foreign currency rates.
- Credit Market: A market where short-term and long-term loans are provided to individuals or organizations by various banks and financial institutions.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Indian Financial System - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is the role of financial institutions in the Indian financial system? |  |
| 2. What are the types of financial institutions in India? |  |
| 3. What are money market instruments and how do they function in the Indian financial system? |  |
| 4. How does the government securities market operate in India? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of markets in the Indian financial system? |  |




















