Regulatory Framework of Insurance: IRDA | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is the IRDA? |

|
| Role of IRDA in the Indian Insurance Sector |

|
| How Does IRDA Work? |

|
| Types of Insurance Regulated by IRDA |

|
Introduction
Insurance plays a crucial role in every economy by helping to minimize risks. Individuals can purchase policies to safeguard themselves against financial losses, whether related to their health, property, or other assets. When a financial loss occurs, the insurance company is obligated to compensate the policyholder, provided specific terms and conditions are met. These insurance companies must adhere to government regulations, which are overseen by a regulatory framework established by the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA). All life and general insurance companies in India are required to follow these guidelines, which are designed to protect the interests of policyholders.
What is the IRDA?

- The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA) is the primary body responsible for regulating the insurance sector in India.
- IRDA establishes the necessary rules and guidelines that all insurance companies must follow.
- India’s insurance sector is vast, with many citizens purchasing policies to protect their health, property, and other assets.
- These insurance policies are offered by both government and private companies.
- All companies operate under the regulatory framework established by the IRDA.
- This framework outlines the rules these companies must adhere to and oversees their operations.
- At the helm of the insurance market, the IRDA determines the rates and charges associated with insurance policies.
- Its primary goal is to ensure an efficient insurance system that promotes the overall health of India's insurance market.
- The IRDA places a strong emphasis on protecting the interests of policyholders.
- It ensures that insurance policies are designed with their needs in mind.
- By adhering to the regulatory framework, insurance companies can offer policies that effectively cover uncertain and calculable financial losses.
- This benefits both the companies and the policyholders.
Establishment of the IRDA
- IRDA was established in 2000 to regulate the insurance sector in India.
- It was created following the recommendations of the Malhotra Committee in 1999.
- Functions as the apex regulatory body for insurance in India.
- The IRDA began accepting registration applications for insurance companies in August 2000.
- Allows foreign companies to invest up to 26% in the Indian insurance market.
- Operates under the Insurance Act of 1938 and Section 114A.
- Provides regulations that protect policyholders and govern the registration of insurance businesses.
- Currently, there are 33 general insurance companies and 24 life insurance companies in India.
- All companies operate under the regulatory framework established by the IRDA.
Objectives of the IRDA
- The IRDA's primary objective is to promote and protect the rights and interests of policyholders. The organization also aims to foster the growth of the insurance industry, ensure prompt payment of insurance claims, and prevent fraud within the sector. Additionally, the IRDA works to maintain transparency and order within the insurance market. By regularly updating its regulations, the IRDA contributes to the overall improvement of the economic environment.
Role of IRDA in the Indian Insurance Sector
The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA) plays a critical role in shaping the insurance sector in India. It provides a regulatory framework that ensures the smooth operation of the market and promotes the interests of policyholders. Here’s a look at the role of IRDA:
Protection of Policyholder Interests: IRDA focuses on enhancing the insurance experience for policyholders by implementing straightforward laws that facilitate easy claims.
Industry Growth: The regulatory framework fosters growth by establishing laws that simplify market entry for businesses, leading to better insurance policies and customer protection.
Funding Promotion: IRDA works to increase funding in the insurance market, supporting long-term growth within the industry.
Ensuring Fair Dealings: The IRDA maintains high standards of integrity and fairness in the insurance industry, ensuring that claims are handled equitably.
Grievance Redressal: IRDA has established grievance forums to address complaints, ensuring that clients are treated fairly.
Regulation Enforcement: IRDA takes regulatory action when companies fail to comply with the rules, ensuring better market functioning.
These roles underscore the importance of the IRDA's regulatory framework in guiding businesses and empowering clients to understand and enforce their rights.
How Does IRDA Work?
A strong regulatory framework is essential for the insurance sector, preventing chaos, fraud, and loss of trust, which could destabilize the economy. The IRDA's functioning is crucial for maintaining order in the insurance market. Here’s how it works:
Clarity in Rules: IRDA ensures that its regulations are clear and unambiguous, so businesses fully understand and adhere to them.
Registration Authority: IRDA is responsible for issuing registrations to new insurance companies, ensuring that they comply with the regulatory framework.
Independent Rule-Making: IRDA independently creates regulations focused on protecting policyholders and fostering market growth.
Fair Claim Settlements: IRDA ensures that genuine claims are settled fairly, preventing insurance companies from unjustly denying claims.
Code of Conduct Enforcement: Insurance companies and intermediaries must follow a strict code of conduct enforced by IRDA.
Dispute Resolution: IRDA settles disputes within the industry and regulates insurance rates to prevent excessive premium hikes.
Market Development: IRDA ensures the development of both rural and urban insurance markets by setting specific targets for companies.
IRDA's regulatory framework encompasses everything from basic registration rules to ensuring that insurance is accessible in all regions.
Features of IRDA
The key features of the IRDA's regulatory framework include:
Regulatory Body: IRDA creates and enforces rules that govern the insurance industry.
Policyholder Protection: It safeguards policyholders by preventing fraud and ensuring swift claim settlements.
Legal Basis: The rules are defined under Section 114A of the 1938 Insurance Act, with IRDA responsible for implementing these guidelines.
Registration Authority: IRDA grants registration certificates to insurance companies, ensuring they meet all necessary standards.
Market Oversight: IRDA oversees both individual companies and the overall market to promote sustained development.
Benefits of IRDA
The IRDA's regulatory framework provides several advantages:
Policyholder Priority: Regulations are designed with the policyholders' best interests in mind.
Market Oversight: IRDA ensures that insurance companies adhere to the rules, maintaining a fair and orderly market.
Fraud Prevention: By regulating the industry, IRDA helps prevent fraudulent activities.
Dispute Resolution: IRDA facilitates quick and fair settlements of disputes and insurance claims.
Affordable Policies: IRDA works to prevent excessive increases in insurance rates, making policies more affordable.
Types of Insurance Regulated by IRDA
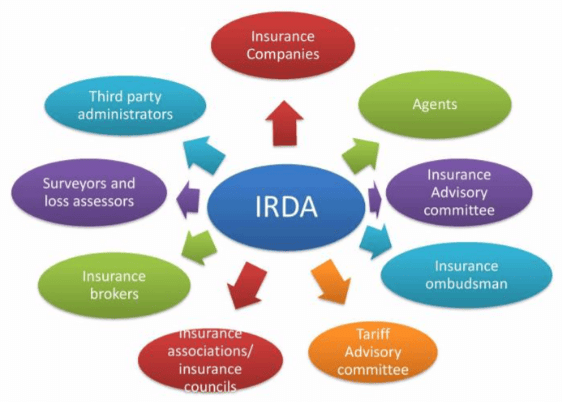
The IRDA regulates two major types of insurance: life insurance and general insurance, each serving to protect policyholders' interests.
Life Insurance: Life insurance provides financial support to a person's family in the event of their death or disability. It’s particularly important for sole earners. Here are the types of life insurance:
Term Plans: Provides coverage for a specific period; the family receives the claim amount if the policyholder passes away during that period.
Endowment Policies: Covers a specific period; the family receives the sum if the policyholder dies within the term, or the policyholder receives the sum if they survive the term.
Unit-linked Insurance Policies: Combines insurance with investment; part of the premium is invested, and the family receives the total amount upon the policyholder's death.
Money-back Policies: Provides periodic payments to the policyholder during the term, with the remaining amount paid at maturity. The family receives the full sum if the policyholder dies.
Retirement Policies: Offers a fixed pension after retirement, with the family receiving the full claim if the policyholder dies.
General Insurance: This category includes non-life policies that cover risks related to health, property, travel, and more. Here are the types of general insurance:
Health Insurance: Covers medical expenses, including testing, hospitalization, and other bills.
Motor Insurance: Covers vehicles, allowing policyholders to claim damages and repair costs for cars or bikes.
Property Insurance: Protects homes or other properties against damages from theft, fire, or other losses.
Travel Insurance: Covers expenses incurred during travel, such as medical bills, baggage loss, and flight delays.
Gadget Insurance: Provides coverage for expensive gadgets like phones or laptops, covering damages or repair costs.
Conclusion
The regulatory framework of insurance, guided by the IRDA, is essential for maintaining the stability and integrity of the insurance sector. Without these regulations, the system could collapse, leading to widespread fraud and loss of public trust, which would negatively impact the economy. Continuous rule-making by the government and IRDA is necessary to ensure the sector operates efficiently and effectively.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Regulatory Framework of Insurance: IRDA - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is the role of IRDA in the Indian Insurance Sector? |  |
| 2. How does IRDA work? |  |
| 3. What types of insurance are regulated by IRDA? |  |
| 4. What is the regulatory framework of insurance in India under IRDA? |  |
| 5. How does IRDA impact the insurance market in India? |  |




















