Renewal or Replacement of Asset | UGC NET Commerce Preparation Course PDF Download
Importance of Asset Availability in Business
Availability of assets is crucial for the smooth functioning of any business. Assets enable companies to engage in economic activities, generate revenue, and build capital. For instance, a company's land and machinery are vital for its operations and production. Without assets, a company would be unable to offer products or services to customers. Even service-oriented companies require assets such as offices and equipment to operate effectively. This underscores the significance of processes like repair, replacement, renewal, or renovation within a company.
Repairs and Renewals

Repairs and renewals are essential parts of maintaining assets over their lifespan. When assets are used regularly, they can suffer damage, leading to the need for repairs or even replacement. These maintenance activities incur costs for the company, which can be classified as either revenue or capital expenses. The distinction between these types of costs affects budgeting and taxation decisions for the company. Repairing, replacing, renewing, or renovating assets is crucial to prevent disruptions and enhance the company's production efficiency.
What are Repairs?
Repairs involve fixing damages to restore an asset to a functional state. This maintenance can apply to various types of assets, such as land, buildings, or machinery.
- Asset repairs are integral to ongoing production processes, addressing the wear and tear that assets undergo with regular use.
- Repairs become necessary when an asset is unable to fulfill its intended function. For instance, if a machine malfunctions, it can lead to production delays or missed deadlines.
- Timely repairs are vital to maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty. Failure to address asset issues promptly can result in loss of goodwill and clientele to competitors.
Example
Repairing, replacing, renewing, or renovating assets is crucial for businesses. Let's delve into an example to grasp the concept better:
Repair, Replace, Renewal, or Renovation
- A manufacturing company operates a warehouse pivotal for storing and dispatching goods to stores, crucial for revenue generation.
- Recently, a storm damaged the warehouse roof, causing leaks that could harm stored goods. The company must invest in repairing the roof, constituting a repair expense for the asset.
- Repair costs are classified as revenue expenses and can aid in tax deductions. Contrarily, if the company opted to renovate the undamaged roof with a false ceiling solely for aesthetic purposes, it would be deemed a capital expense.
Maintaining assets is critical for business operations. Below are the potential consequences if a company neglects to invest in asset repairs:
- Production may halt if equipment breaks down, resulting in lost orders and sales.
- Product quality can suffer, as malfunctioning machinery may disrupt standardization.
- Products may get damaged due to deterioration of showrooms or warehouses, compromising their quality.
- Failure to repair, replace, or renew assets can lead to employee dissatisfaction due to unfavorable working conditions.
- Neglecting timely repairs may cause permanent damage to assets, leading to higher costs for replacements.
What are Renewals?
Renewal of an asset involves refurbishing or replacing it with the aim of enhancing or restoring its productivity levels. This process can apply to various assets such as machinery or land.
- Asset renewal through repair, replacement, or renovation aims to bring a product back to similar productivity levels.
- It may involve completely replacing an asset. For instance, swapping an old machine with a new one that serves similar functions.
- Renewals are necessary when an asset is damaged, and the company seeks to modernize. The extent of damage must surpass regular maintenance requirements.
- Many assets either cease functioning or become less efficient as they near the end of their useful life. In such cases, a company can choose to refurbish the asset or purchase a new one. Both actions are considered capital expenditures and do not contribute to reducing taxable income.
Example
Repairs, replacements, renewals, or renovations can be better understood through examples. Here’s an illustration of asset renewal:
Imagine a company decides to expand its showroom to accommodate higher production needs. As the company introduces new products or seeks to boost its current inventory, expanding the storage area becomes essential. The company purchases a neighboring plot, demolishes the separating wall, and begins construction to enlarge the space. This expansion of the warehouse is considered a renewal or refurbishment, which qualifies as a capital expense.
On the other hand, if the company needs to fix the damaged flooring in the existing warehouse, that would be categorized as a repair expense.
Effects of not renewing assets
Repair, replacement, renewal, or renovation are vital when a company aims to upgrade its facilities. Below are the consequences of not renewing assets:
- The production capacity of a company can decrease when machinery reaches the end of its life, potentially leading to missed orders.
- Quality may decline as machines near the end of their life, impacting standardization.
- Failure to invest in asset renewals can result in missed opportunities, potentially necessitating increased production to fulfill larger orders.
- Renewals facilitate the modernization of the production process; without them, a company may stagnate in outdated practices.
- Relying solely on traditional processes can hinder the introduction of new technologies into production.
Impact on Taxes and Budgets
The decision to repair, replace, renew, or renovate also has implications for taxes and budgets. Planning for these expenses is crucial for cost-saving measures and enables accurate cost reporting by management. It can also help in taking advantage of tax deductions related to repair expenses.
 |
Download the notes
Renewal or Replacement of Asset
|
Download as PDF |
Planning Point of Renewal or Replacement of Assets
The distinction between repair, replacement, renewal, and renovation is crucial for financial planning. Proper categorization of these expenses is necessary for tax benefits and long-term budgeting.
To fulfill its tax requirements, the company needs to categorize repairs and renewals made throughout the financial year.
- Repair expenses are considered revenue expenses, deducted from profits to lower taxable income and liability.
- Replacement or renewal costs are categorized as capital expenses, impacting the taxable profits of the company.
It is vital for companies to classify repair and renewal costs during their financial year to meet tax obligations effectively.
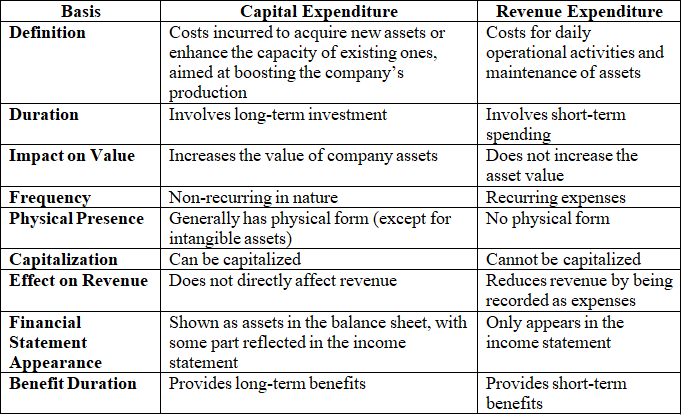
Differences in Revenue and Capital Expenses
To comprehend the disparities between revenue and capital expenses, consider the following table:
Conclusion
In conclusion, deciding whether to repair, replace, renew, or renovate an asset or property is a complex process requiring thoughtful evaluation of multiple factors. Each option presents its own benefits and challenges, and the best choice depends on the particular situation, financial limitations, and future objectives. Repairing is often ideal for fixing minor issues and ensuring continued use, while replacement becomes necessary for assets that are no longer viable. Renewal focuses on updating and extending the asset's life, and renovation offers opportunities for both aesthetic upgrades and functional enhancements.
|
235 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Renewal or Replacement of Asset - UGC NET Commerce Preparation Course
| 1. What is the significance of asset availability in a business? |  |
| 2. How do repairs differ from renewals in asset management? |  |
| 3. What factors should be considered when planning for the renewal or replacement of assets? |  |
| 4. What are the main differences between revenue and capital expenses in the context of asset renewal or replacement? |  |
| 5. How can businesses determine whether to renew or replace an asset? |  |

































