Audit Report | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
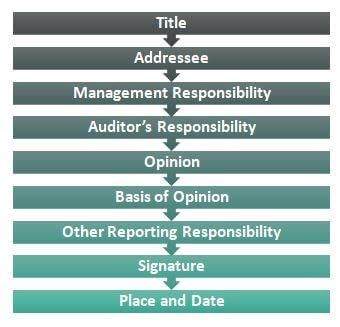
| Audit Report |

|
| Importance of an Audit Repoprt |

|
| Types of Audit Report |

|
| Audit Committees |

|
Audit Report
An audit report is a statement through which an auditor submits his findings and expresses his opinion on the state of affairs of the company’s business. In other words, it is a statement through which an auditor summarizes result of his audit work. In short it is the medium through which an auditor expresses his opinion on the financial statement of a business.
Characterstics of Audit Report
- It is the medium through which an auditor expresses his opinion on the financial statement.
- It is the end product of audit.
- It is based on factual information.
- The audit report may be short or long.
- The audit report may be in the form of letter or statement.
- The audit report is attached to the balance sheet.
Importance of an Audit Repoprt
 It is a statutory requirement in the case of a company audit. It is the end product of audit. It summarizes the result of the audit work done by the audit.
It is a statutory requirement in the case of a company audit. It is the end product of audit. It summarizes the result of the audit work done by the audit.
It is the medium through which an auditor submits his findings and expresses his opinion on the state of affairs
An audit report ensures to the shareholder that the accounts of the company are properly maintained. It is evidence in the court of law
Contents of Audit Report
An audit report has to contain matters as per section 227(3) of the companies act of 1956 the audit report of a company cannot contain the following matters:
- Whether he has obtained all the information and explanation.
- Whether proper books of accounts as required by law have been kept by the company.
- Whether the company’s balance sheet and profit and loss account are in agreement with the books, accounts and returns.
- Whether any other statements have been concluded as required by the central govt.
- Whether in his opinion
a) Balance sheet represents true and fair view of the state of affairs.
b) Profit and loss account represents correct profit or loss for the financial year.
Essentials of an Audit Report
- It must be a statement of facts.
- The report must contain the auditor’s opinion.
- The report should not give vague statement.
- The report should be convincing.
- The report must be coherent.
- It must be simple to understand.
- It must be forceful.
- It should be unbiased.
- The information given in the report should be clear and concise.
- The report must convey to the client the material facts known to the auditor.
- The report must be signed by the auditor.
- The report must be attached to the balance sheet.
Types of Audit Report
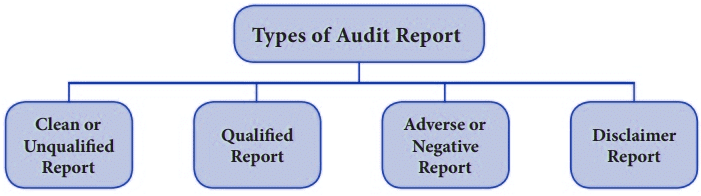
Clean or unqualified report:
When an auditor is satisfied with the affairs of the company and the fairness of the balance sheet and profit and loss account of the concern, he gives in his report the various matters without any reservations, qualifications or modifications. Such a report is called a clean report or unqualified report. A clean report is given by an auditor when he is satisfied as to the truthfulness and fairness of the accounts and the financial statements of the company
Qualified or Adverse Report:
When an auditor finds some irregularities in the books of accounts or in the financial statements, the auditor gives a report mentioning the irregularities. Such a report is called a qualified report. A qualified report is a report in which the auditor inserts any qualifications, modifications or reservations.
A qualified report is given by an auditor under the following circumstances:
- When he is not satisfied with the accounts or financial statements.
- When proper books of accounts as required by law have not been maintained.
- When there is a violation of the companies act
- Where report is a material misstatement in the financial statement.
- Where there is an omission of a material disclosure.
- When the explanations sought by the auditor are not made available to him.
- Where the assets are over or under valued.
- Where secret reserve have been created.
- Where there is insufficient provision for depreciation.
- Where there is inadequate provision for bad and doubtful debts.
Auditing In Electronic Data Processing Environment (EDP)
Computerized information system environment or electronic data processing environment means an environment where computers are extensively used in an enterprise for the processing of significant financial information. In other words, data processing done with the help of electronic computers is popularly known as electronic data processing or computerized information system (CIS) environment.
A report should contain all the information which are required by the interested parties. Hence, some principles are followed while drafting a report. These principles are simply guidelines.
The accountant should not feel that he has to conform to a set of rules that places him in a straight jacket. However, there are few guides that he should keep in mind. The rules will not be valid in all cases because of the difference in capabilities of top management to digest information and because of variations in the form in which management wants that information.
Therefore, a report is prepared by considering the following points.
Qualities or Characteristics of Good or Essential report
1. Suitable Title:
A suitable title has to be provided to each report according to the nature of contents. It should also highlight upon its origin and the person for whom it is being prepared.
2. Simple:A report should be readable by an ordinary layman and in known language. Such type of simple style of language is used in the report preparation. As far as possible, scientific or technical language is best left out of reports, unless it becomes unavoidable. In case the reports are of regular nature, it is preferable to get language more or less standardized.
3. Promptness:A report should be prepared and submitted within short span of time or time stipulated by the request letter. Information delayed is information denied. At the same time, accuracy of information should not be given up at the cost of achieving objective of promptness. The following steps may be taken to collect the information as early as possible.
- Accounting records should be kept in such a way that fulfill the requirements of submission of different reports.
- Mechanical devices can be used for record keeping at the maximum to avoid clerical errors and increase productivity.
- Accounting work should be departmentalized in order to prevent bottle necks in reporting.
- In the case of prevailing abnormal or extra-ordinary situation, the employees are asked to report the same immediately.
Sometimes a report is prepared with some comparative information. In this case, a standard information is compared with actual information. If not so, current year information is compared with last year information. In certain cases, the prospective information is prepared well in advance and the actual information is compared. The main objective of comparability is to highlight significant variations.
5. Consistency:A report should be prepared for many years from the same type of information and statistical data. If so, there is a possibility of preparing a report in consistency. It is possible if same accounting principles and concepts are used for collecting, classifying, tabulating and presenting the information. The usage of report is increased through consistency.
6. Precise and Accurate:A report should be precise, accurate and specific. It can be just a bad reporting practice to supply too much information which over whelms the order; as too little which leaves him guessing. If report is quite long or detailed, then a synopsis should be prepared to cover all significant facts and conclusions.
7. Relevant Information:Relevant accurate data is alone included in the report. If not so, it will involve unnecessary expenditure and the reports will be a waste.
8. Presented to Required Person or Group or Department:The reports should be specific and presented only to the person in need. Sometimes, reports are sent to various departments in a routine way, if so, the reports are prepared in such a way that includes common information.
9. Routine Details:Every report should contain the routine details like the period of time of preparing report, the period covered in the report, date of presentation of report, the units of information, the name of the person preparing and presenting it, names of persons to whom it is being submitted. etc.
10. Timeliness:A report should be prepared and presented within the stipulated time. If a report is received late, there is no meaning of preparing such report and no use for management. If the report is presented in time, necessary actions may be taken.
Obviously financial data are more valuable when the events are fresh in the minds of users. The element of time elapsing between the events and the report determines to a large extent, the value of financial reports. Timeliness is generally more important than a high degree of accuracy in the figures.
11. Adaptability:The format and contents of the report should be suitable to the person or group of persons who are going to use the report and the purpose for which it is required. A report can be adoptable if it is prepared and presented according to the needs of the different levels of management (top, middle and lower).
12. Ability to Control:The reports should give full details of variances such favorable and unfavorable. In the case of unfavorable variances, the report should contain a massage about the unfavorable variances which are controllable at that point. If so, corrective controllable actions may be taken by the appropriate level of authority. Moreover, some unfavorable variances which are beyond the control of the executive receiving the report should be mentioned separately or highlighted in the report.
13. Economy or Cost Consciousness:This cost of preparing and presenting the report should also be considered. This cost should also be considered. This cost should not be more than the advantage derived from such reports. The cost of preparing the report should be reasonable so that reporting may be used by all types of concerns.
14. Effective Communications:If the management executives have taken the action on the basis of report and the report influence decisions, there is an effective communication.
In order to be useful to management, accounting information must be communicated to managerial personal. Communication implies that a person receiving the information understands the nature and significance of material contained in the reports he receives when communication is genuinely effective, management’s actions and decisions are likely to be based on the facts which they receive rather than on untested impressions and guesses.
However, there is a reason to believe that accounting reports to management have not always achieved their intended purpose because the reports were not understood, recipients lacked time required to grasp the meaning or contents of reports was not relevant to problems facing the persons who received them.
15. Principle of Exception:The principle of exception should be followed while preparing and presenting the reports. If so, trouble spots and/or illuminating priority areas are calling for management attention and action. In this case, some benefits are derived such as essential matters only included in the report to the user of the report, more concentration is possible and minimum data is included in the report. Even though, this principle has limited use.
16. Frequency of Reports:The frequency of reports should be decided, well in advance according to the nature of information and its purpose. It means that the reports should be sent regularly when they are demanded or required. Therefore, some reports may be sent daily, some weekly, some once in ten days, some fortnightly, some monthly and so on.
17. Media of Presentation:A report may be prepared for presenting the same in several medias. Therefore, a report may be in written form or oral form or graphic form. An ideal report is presented in the form which carries successful blending of different media.
18. Attractiveness:The style of presenting the report should attract the attention of the user of the report. In meeting this broad requirement for attractiveness in reporting, the accountant assumes the role of an artist. His task is to print a picture that will appeal to the eyes. His report should serve as panorama which is attractive in an artistic sense and therefore one that will be regarded and studied by the potential viewer.
19. Co-ordination of Data:All type of information are collected from various departments including accounting data while preparing the report. In this case, there is a need of coordination of data. It means that data used by different departments should not be unrelated, otherwise a lot of misunderstandings and confusions may arise which would defeat the very purpose of reporting.
20. Up to Date:A report should contain only latest information. Even though, excessive information cannot be included in the report. It means that report should be kept up to date which are necessitated by the changing conditions.
21. Number of Reports:There is no ideal number of reports to be used in an organization. At the same time, a report should be an additional one and should not give birth to be a duplication. Therefore, reports should be prepared and used only for selective areas. The number of reports should be kept as minimum as possible.
22. Good Form and Content:The following points are to be considered while drafting a report.
- A report is prepared in well classified paragraph with suitable heading and sub-heading if possible.
- The title of the report explains the purpose for which the report is prepared and the period covered by the report. For example: Report of the Performance of Sales Representatives of January 2011.
- The title also enables to point out the persons who need the report.
- If statistical figures are to be given only significant figures given in the body of the report and other detailed figures should be given in appendix.
- The reports should contain facts and not opinions. The opinions are given if necessary.
- The report must contain the date of its preparation and date of submission.
- Sometimes a report is prepared on the basis of request made by the management. If so, the report should bear the reference numberof such request or letter.
- A report is prepared to satisfy only one purpose. Separate reports be prepared for different subjects.
- The contents of the report should be in a logical sequence.
Uses or Benefit of Computerized Audit
- Speed : the work of recording of transactions , preparation of books , accounts can be done with greater speed.
- Greater accuracy: the chances of arithmetical errors and human errors are reduced to minimum.
- Greater economy: under the mechanized accounting system, work can be done with minimum staff, with minimum cost.
- Better records: records prepared by machines are neat and clean. It is more legible, systematic and uniform.
- Greater information: various types of information and statistical data regarding the operation of the business can be easily collected.
- Interim accounts: interim accounts can be prepared without delay. This will help the management to declare interim dividend.
- Analysis of data: once the basic information is feed into the computers, it can be sorted in many different ways to provide analysis of statement .
- Avoid overtime: the work of accounts are done quickly , the accounts can be prepared without any loss of time.
- Reduction in audit fee: the work load of audit works is reduced by the computers. Hence the computerized audit reduces audit cost.
- Computerized audit reduces the monotony of audit work:
- Computersised audit enhances the reliability of audit
- Computersied audit ensures flexibility in the audit programme.
- Computersied audit is helpful for the smooth functioning of auditing.
Problems or Disadvantages
- It is not suitable for small business forms.
- Difficulties to detect the errors and frauds.
- Absence of supporting vouchers.
- Storage problem
- Computer frauds and computer virus.
- Easy to make alterations
- It creates unemployment.
- Absence of input documents.
- Lack of visible output
- Coding problem.
Audit Approaches in an EDP Environment
There are three approaches to auditing in an EDP environment . They are
1) Auditing around the computer
2) Auditing with the computer
3) Auditing through the computer
Auditing Around the Computer
Auditing around the computer is an audit approach under which an auditor carries out the audit in the same way as in a traditional or Manual system except that, instead of examining hand written books, he examines computer printouts.
Auditing with computers: - under this approach, the auditor does the audit work with the help of computers that is general software. Under this approach, audit work is carried on in an traditional manner, but the computer software is used for certain operations.
Auditing through the computer
Auditing through the computer means making use of computer in auditing. Under this approach the auditor evaluates the internal control relating to EDP and on the basis of evaluation , he determines the nature , timing , and extent of his sustentative procedures.
Internal Control under an EDP Environment
For the control of various problems connected with the installation and operation of computers in accounting and auditing, there should exist an adequate and satisfactory internal control system in the undertaking . The internal control system should be reliable , effective, and should provide timely , authorized and required data from the system.
The various internal controls required to be enforced under an EDP environment may be broadly classified into two categories.
They are,
- General EDP controls
- EDP application controls.
General EDP Controls.
The purpose of general EDP control is to establish a frame work of overall control over EDP activities. Some of the important general EDP controls are,
- Division of responsibility or duties.
- Control over development and maintenance of software
- Control over operators.
- Control over data access and program access.
- Control over editing of data.
- Storage control.
- Hardware control.
EDP Application Control
For the smooth working of EDP system, besides the general EDP controls, there should certain special EDP application controls. The important EDP application controls are
- Control over input
- Control over processing
- Output control
Computer Assisted Auditing Techniques. (CAAT)
Techniques which used computer itself for audit purposes are called computer assisted techniques. The important CAAT are
- Test data
- Integrated test facility
- Controlled processing
- Computer audit program
Recent trend in auditing or current issues:
There are several current issues in auditing. Some of the important current issues or recent trends in auditing are:
- Audit committees
- Social audit
- Inflation audit
- Human resource accounting and auditing
- Energy audit
- Reporting on financial sickness
- Financial forecast and their audit.
Audit Committees
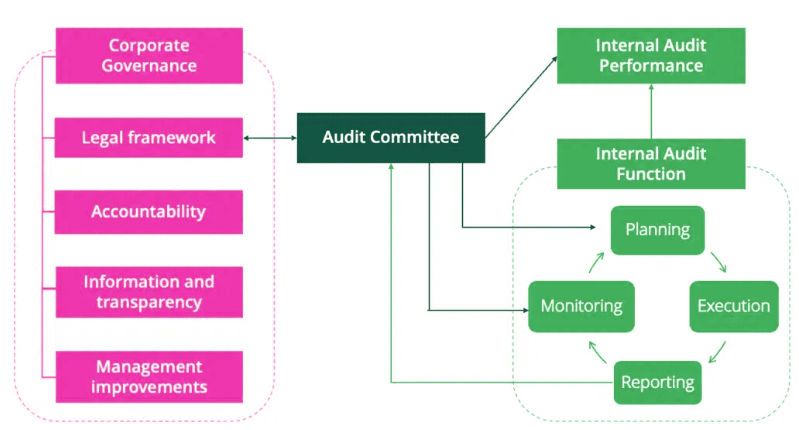
An audit Committee is a subcommittee of the board of Directors formed for the purpose of reviewing the annual financial statements before their submission to the Board of Directors, assisting the Board of Directors in discharging their function efficiently and for acting as a liaison between the board of directors and the external auditor.
The setting up of audit Committee has been supported by Stock Exchange, Corporate law authorities, Professional accounting bodies.
The Composition of audit Committee depends mainly up on the nature and the size of the business. An audit committee, generally, consists three to five members.
Functions of Audit Committee are: -
- To consider questions of appointment, resignation, dismissal, remuneration of the auditor.
- To discuss the nature and scope of duties of external auditor.
- To review the half yearly and annual financial statements.
- To discuss the issues and problems arising from the audits.
- To assist the Board of Directors in the fulfillment of their duties and responsibilities.
- To evaluate the efficiency of the working of the Board of Directors
Social Audit: - Social audit is a systematic study and evaluation of a business enterprise’s social performance as distinguished from its economic performance. Social audit is intended to evaluate the social performance or social contribution of a business organization
Reporting on Financial Sickness: - The Sick Industrial Companies are those company which satisfies following conditions:
- It is an Industrial company.
- It has been registered for a period of not less than five years.
- Its accumulated losses at the end of the financial year equal or exceeds its net worth.
An auditor is required to assess the financial health of an enterprise, identify initial financial sickness and reporting on the same.
Financial forecasts and their Audit : - A forecast is a statement of events likely to occur. A financial forecast is a forecast of the financial position of an enterprise in the future. Now a day, certified accountants are required to report on their client’s profit forecast and financial forecast.
Inflation audit: - The accounting which records the effect of changing price is known as inflation accounting. The auditor is required to consider the price level changes recorded in the books of account.
Human resource accounting and auditing: - It is the accounting and recording of human beings in the organization like other assets. The auditor will be called up on to evaluate the human resource investment.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Audit Report - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is the importance of an Audit Report? |  |
| 2. What are the types of Audit Reports? |  |
| 3. What is the role of Audit Committees in the Audit Report process? |  |
| 4. Why is the Audit Report important for UGC NET exam preparation? |  |
| 5. How can one effectively analyze an Audit Report for UGC NET preparation? |  |















