Worksheet Solutions: Playing with Constructions | Mathematics (Maths) Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| True/False |

|
| Practical Application Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which tool would you use to draw a perfect circle with a 5 cm radius?
(a) Ruler
(b) Compass
(c) Set square
(d) Protractor
Ans: (b) Compass
Solution: A compass is designed to draw perfect circles by setting the radius.
Q2: What is the measure of each angle in a square?
(a) 45 degrees
(b) 60 degrees
(c) 90 degrees
(d) 120 degrees
Ans: (c) 90 degrees
Solution: Each angle in a square is a right angle, which measures 90 degrees.
Q3: When drawing a rectangle, which of the following is true about its diagonals?
(a) They are always parallel.
(b) They bisect each other at right angles.
(c) They are equal in length.
(d) They form acute angles with each other.
Ans: (c) They are equal in length.
Solution: The diagonals of a rectangle are equal in length.
Q4: To draw a square with a side length of 6 cm using a compass and ruler, what is the first step?
(a) Draw one side of the square.
(b) Draw a diagonal.
(c) Measure a 6 cm length on the compass.
(d) Draw a perpendicular bisector.
Ans: (a) Draw one side of the square.
Solution: Start by drawing one side, then use it as a reference for the other sides.
Q5: If you want to find a point that is equidistant from two given points, which tool would you use?
(a) Ruler
(b) Compass
(c) Protractor
(d) Set square
Ans: (b) Compass
Solution: A compass can be used to find points that are equidistant from two given points by drawing arcs.
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The distance from the center of a circle to any point on the circle is called the _______.
Ans: Radius
Solution: The radius is the distance from the center of a circle to any point on the circumference.
Q2: The tool used to draw perfect circles and arcs is called a _______.
Ans: Compass
Solution: A compass is an instrument used to draw circles and arcs by fixing one point and rotating the other.
Q3: The sum of all angles in a rectangle is _______ degrees.
Ans: 360
Solution: A rectangle has four right angles, and the sum of all angles in any quadrilateral is 360 degrees.
Q4: A square has _______ equal sides and _______ right angles.
Ans: 4, 4
Solution: A square has four sides of equal length and four right angles.
Q5: To draw a perpendicular line through a point on a line segment, you would typically use a _______.
Ans: Set square or a compass
Solution: A set square or a compass is used to draw perpendicular lines from a point on a line segment.
True/False
Q1: All the sides of a rectangle are of equal length.
Ans: False
Solution: In a rectangle, opposite sides are equal in length, but adjacent sides may differ.
Q2: The diagonals of a rectangle are always equal.
Ans: True
Solution: The diagonals of a rectangle are equal in length due to the properties of parallel sides and right angles.
Q3: A rotated square is still a square as long as all sides remain equal and angles remain 90 degrees.
Ans: True
Solution: Rotating a square does not change its properties; it remains a square.
Q4: The point where the two diagonals of a rectangle intersect divides the diagonals into two equal parts.
Ans: True
Solution: The diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other, creating two equal segments.
Q5: A compass can be used to measure the length of a side without a ruler.
Ans: True
Solution: A compass can be used to transfer measurements from one side to another without needing a ruler.
Practical Application Questions
Q1: Draw a square with a side length of 5 cm using a compass and ruler.
Instructions:
- Use a ruler to draw a straight line of 5 cm. Label the endpoints as A and B.
- Place the compass point on A, set it to a 5 cm radius, and draw an arc.
- Without changing the compass width, place the compass point on B and draw another arc that intersects the first arc. Label the intersection as point C.
- Draw lines from A to C and B to C.
- Repeat steps 2-4 to find point D opposite to C, completing the square by connecting A to D and B to D.
Ans:  Solution: By ensuring each side of the square is 5 cm and connecting the lines correctly, the shape formed will be a square.
Solution: By ensuring each side of the square is 5 cm and connecting the lines correctly, the shape formed will be a square.
Q2: Construct a rectangle with sides of 4 cm and 6 cm. Verify if the diagonals are equal.
Instructions:
- Draw a line segment of 6 cm using a ruler. Label it AB.
- At points A and B, use a set square or compass to draw perpendicular lines.
- From point A, measure 4 cm along the perpendicular line and mark it as point D.
- From point B, measure 4 cm along the perpendicular line and mark it as point C.
- Connect points C and D to complete the rectangle ABCD.
- Draw the diagonals AC and BD using a ruler.
Ans: Measure AC and BD; both diagonals should be equal at approximately 7.21 cm.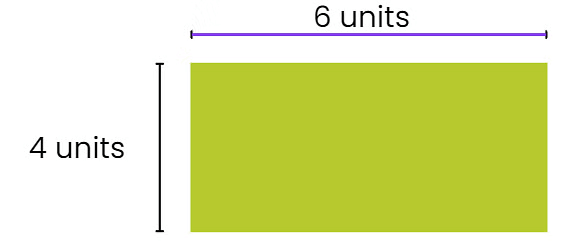
Solution: In a rectangle, the diagonals are always equal. By measuring, students confirm that AC = BD.
Q3: Using a compass, draw a circle with a radius of 3 cm. Then, draw another circle with the same radius but with a different center.
Instructions:
- Set the compass to a radius of 3 cm.
- Place the compass point on a chosen point (O) on the paper and draw the first circle.
- Choose another point (P) at least 6 cm away from O.
- Place the compass point on P and draw the second circle with the same 3 cm radius.
Ans: The student should have two circles with the same radius but different centers.
 Solution: The circles are congruent, as they both have a radius of 3 cm, even though their centers are different.
Solution: The circles are congruent, as they both have a radius of 3 cm, even though their centers are different.
Q4: Draw a rectangle on a dot grid and draw its diagonals. Measure the angles created by the intersection of the diagonals.
Instructions:
- Choose four dots on the grid to form the vertices of a rectangle. Label them A, B, C, and D.
- Connect the dots to form the rectangle ABCD.
- Draw diagonal AC by connecting A to C and diagonal BD by connecting B to D.
- Measure the angles formed at the intersection point (O) of the diagonals.
Ans: The angles formed at the intersection will all be equal at 90 degrees if the rectangle is perfectly aligned with the grid.
Solution: In a rectangle, the diagonals bisect each other, and the angles formed at the intersection are right angles (90 degrees).
Q5: Construct a 4-sided figure where all sides are equal, but it is not a square. What is the shape called?
Instructions:
- Draw a line segment of 5 cm using a ruler. Label it AB.
- Set the compass to 5 cm and draw arcs from points A and B to find points C and D such that AC = BD = 5 cm.
- Adjust the compass to an angle less than 90 degrees to connect points C and D.
- Connect all points (ABCD) to complete the figure.
Ans: The figure formed is a Rhombus.  Solution: A rhombus has all sides of equal length, but unlike a square, its angles are not 90 degrees, giving it a distinctive slanted shape.
Solution: A rhombus has all sides of equal length, but unlike a square, its angles are not 90 degrees, giving it a distinctive slanted shape.
|
92 videos|348 docs|54 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Playing with Constructions - Mathematics (Maths) Class 6
| 1. What are constructions in geometry and why are they important? |  |
| 2. What tools do I need to complete constructions in geometry? |  |
| 3. How can I improve my skills in geometric constructions? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific techniques for constructing angles and triangles? |  |
| 5. How do I check if my geometric construction is correct? |  |





















