Worksheet Solutions: Symmetry - 1 | Mathematics (Maths) Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Line of Symmetry |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| True/False |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: How many angles of symmetry does a square have?
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
Ans: (b) 4
Solution: A square has rotational symmetry at angles of 90°, 180°, 270°, and 360°.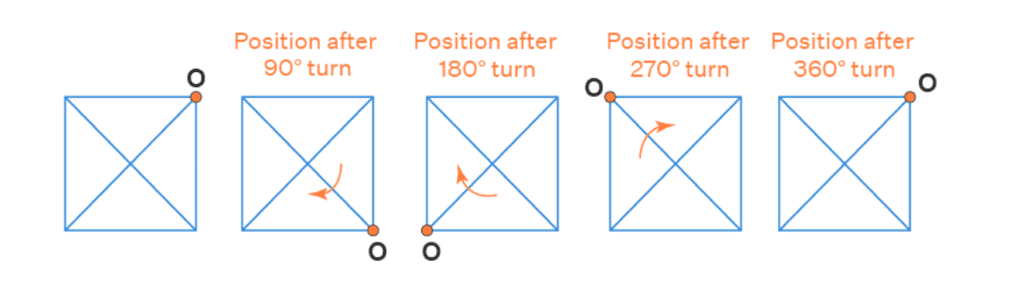
Q2: When a figure is rotated by 180° and it looks exactly the same, the figure has _______ symmetry.
(a) Reflection
(b) Rotational
(c) Translational
(d) No
Ans: (b) Rotational
Solution: A figure with rotational symmetry looks the same after a 180° rotation.
Q3: Which of the following figures has both reflection symmetry and rotational symmetry?
(a) Rhombus
(b) Regular pentagon
(c) Circle
(d) Isosceles triangle
Ans: (c) Circle
Solution: A circle has infinite lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry.
Q4: How many lines of symmetry and angles of symmetry does Ashoka Chakra have?
(a) 12
(b) 24
(c) 48
(d) 10
Ans: (a) 12
Solution: The Ashoka Chakra has 24 spokes spread equally.
24 spokes make 12 pairs. A line through an opposite pair is a line of symmetry.
A line through an opposite pair is a line of symmetry.
Hence, there are 12 lines of symmetry.
Line of Symmetry
Draw Line of Symmetry for the following shapes
(a)
(b)
(c)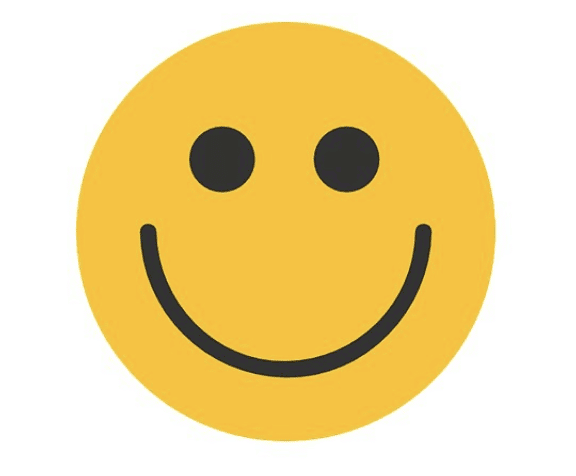
Ans:
(a)
(b)
(c)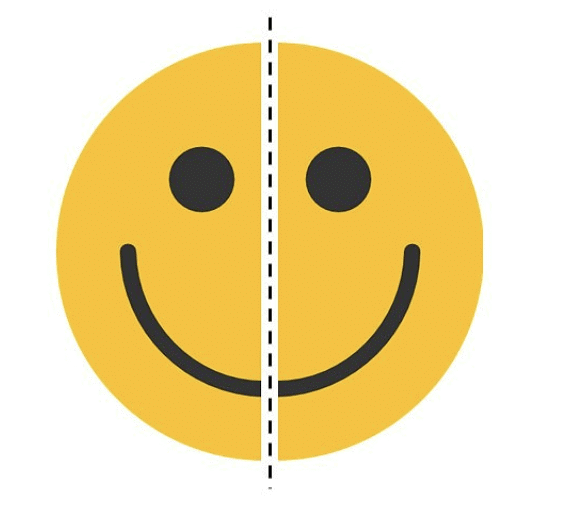
 |
Test: Symmetry - 1
|
Start Test |
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: A line that divides a figure into two identical halves is called a _______ of symmetry.
Ans: Line
Solution: A line of symmetry is a line that divides a figure into two identical parts, where one half is the mirror image of the other.
Q2: The shape of a _______ remains the same when rotated by any angle.
Ans: Circle
Solution: A circle has infinite lines of symmetry and remains unchanged no matter the angle of rotation.
Q3: A square has _______ lines of symmetry.
Ans: 4
Solution: A square can be divided into two identical halves along four lines: two diagonals, one vertical, and one horizontal.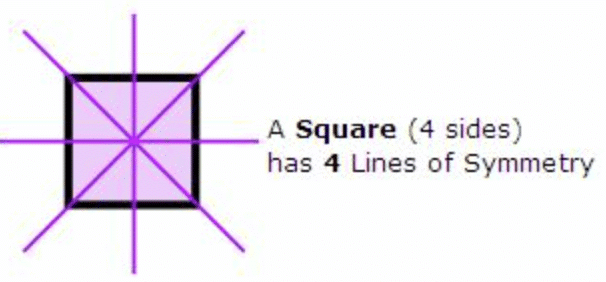 Q4: A figure with no line of symmetry is called _______.
Q4: A figure with no line of symmetry is called _______.
Ans: Asymmetrical
Solution: An asymmetrical figure cannot be divided into two identical halves.
Q5: The _______ is the point around which a figure is rotated in rotational symmetry.
Ans: Centre of rotation
Solution: The center of rotation is the fixed point around which a figure rotates to show symmetry.
True/False
Q1: Every shape with a line of symmetry must also have rotational symmetry.
Ans: False
Solution: Some shapes may have a line of symmetry but lack rotational symmetry, and vice versa.
Q2: A rectangle has two lines of symmetry.
Ans: True
Solution: A rectangle has two lines of symmetry: one vertical and one horizontal.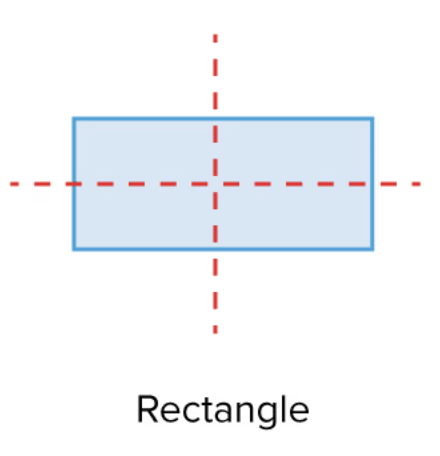
Q3: The number of angles of symmetry in a hexagon is four.
Ans: False
Solution: A regular hexagon has six angles of symmetry, corresponding to rotations of 60°, 120°, 180°, 240°, 300°, and 360°.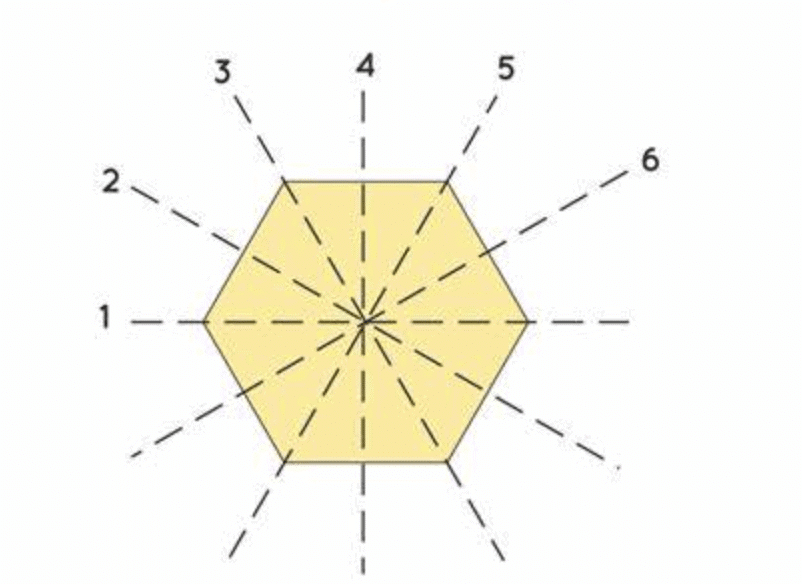
Q4: A circle has an infinite number of lines of symmetry.
Ans: True
Solution: Any circle's diameter can be a line of symmetry, so there are infinite such lines.
Q5: The smallest angle of symmetry in the Ashoka chakra is 30°.
Ans: True
Solution: There are 12 lines of symmetry in Ashoka chakra. Therefore, Smallest angle of symmetry = 360° ÷ 12 = 30°.
|
92 videos|353 docs|54 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Symmetry - 1 - Mathematics (Maths) Class 6
| 1. What is a line of symmetry? |  |
| 2. How can I find the line of symmetry in a shape? |  |
| 3. Are all shapes symmetrical? |  |
| 4. Can a line of symmetry be vertical, horizontal, or diagonal? |  |
| 5. How do you determine the number of lines of symmetry in a shape? |  |




















