Basic Amplifiers | Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
An electronic signal contains some information which cannot be utilized if doesn’t have proper strength. The process of increasing the signal strength is called as Amplification. Almost all electronic equipment must include some means for amplifying the signals. We find the use of amplifiers in medical devices, scientific equipment, automation, military tools, communication devices, and even in household equipment.
Amplification in practical applications is done using Multi-stage amplifiers. A number of single-stage amplifiers are cascaded to form a Multi-stage amplifier. Let us see how a single-stage amplifier is built, which is the basic for a Multi-stage amplifier.
Single-stage Transistor Amplifier
When only one transistor with associated circuitry is used for amplifying a weak signal, the circuit is known as single-stage amplifier.
Analyzing the working of a Single-stage amplifier circuit, makes us easy to understand the formation and working of Multi-stage amplifier circuits. A Single stage transistor amplifier has one transistor, bias circuit and other auxiliary components. The following circuit diagram shows how a single stage transistor amplifier looks like.
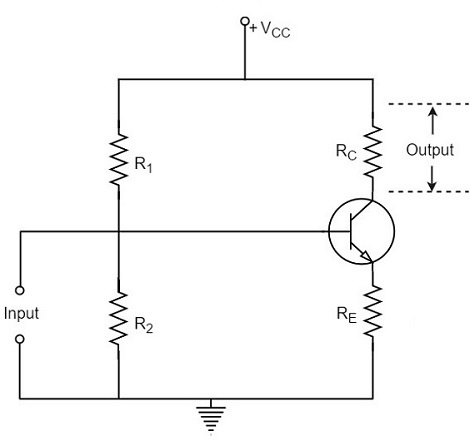
When a weak input signal is given to the base of the transistor as shown in the figure, a small amount of base current flows. Due to the transistor action, a larger current flows in the collector of the transistor. (As the collector current is β times of the base current which means IC = βIB). Now, as the collector current increases, the voltage drop across the resistor RC also increases, which is collected as the output.
Hence a small input at the base gets amplified as the signal of larger magnitude and strength at the collector output. Hence this transistor acts as an amplifier.
Practical Circuit of a Transistor Amplifier
The circuit of a practical transistor amplifier is as shown below, which represents a voltage divider biasing circuit.
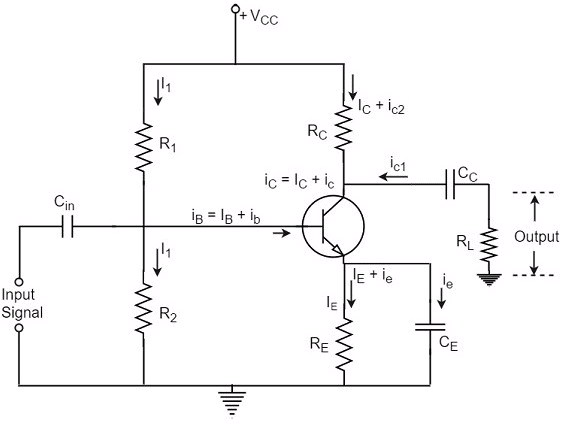
The various prominent circuit elements and their functions are as described below.
Biasing Circuit
The resistors R1, R2 and RE form the biasing and stabilization circuit, which helps in establishing a proper operating point.
Input Capacitor Cin
This capacitor couples the input signal to the base of the transistor. The input capacitor Cin allows AC signal, but isolates the signal source from R2. If this capacitor is not present, the input signal gets directly applied, which changes the bias at R2.
Coupling Capacitor CC
This capacitor is present at the end of one stage and connects it to the other stage. As it couples two stages it is called as coupling capacitor. This capacitor blocks DC of one stage to enter the other but allows AC to pass. Hence it is also called as blocking capacitor.
Due to the presence of coupling capacitor CC, the output across the resistor RL is free from the collector’s DC voltage. If this is not present, the bias conditions of the next stage will be drastically changed due to the shunting effect of RC, as it would come in parallel to R2 of the next stage.
Emitter by-pass capacitor CE
This capacitor is employed in parallel to the emitter resistor RE. The amplified AC signal is by passed through this. If this is not present, that signal will pass through RE which produces a voltage drop across RE that will feedback the input signal reducing the output voltage.
The Load resistor RL
The resistance RL connected at the output is known as Load resistor. When a number of stages are used, then RL represents the input resistance of the next stage.
Various Circuit currents
Let us go through various circuit currents in the complete amplifier circuit. These are already mentioned in the above figure.
Base Current
When no signal is applied in the base circuit, DC base current IB flows due to biasing circuit. When AC signal is applied, AC base current ib also flows. Therefore, with the application of signal, total base current iB is given by
Collector Current
When no signal is applied, a DC collector current IC flows due to biasing circuit. When AC signal is applied, AC collector current ic also flows. Therefore, the total collector current iC is given by
Where
IC=βIB = zero signal collecor current
ic=βib = collecor current due to signal
Emitter Current
When no signal is applied, a DC emitter current IE flows. With the application of signal, total emitter current iE is given by
It should be remembered that
As base current is usually small, it is to be noted that
IE≅IC and ie≅ic
These are the important considerations for the practical circuit of transistor amplifier. Now let us know about the classification of Amplifiers.
An Amplifier circuit is one which strengthens the signal. The amplifier action and the important considerations for the practical circuit of transistor amplifier were also detailed in previous chapters.
Let us now try to understand the classification of amplifiers. Amplifiers are classified according to many considerations.
Based on number of stages
Depending upon the number of stages of Amplification, there are Single-stage amplifiers and Multi-stage amplifiers.
Single-stage Amplifiers − This has only one transistor circuit, which is a singlestage amplification.
Multi-stage Amplifiers − This has multiple transistor circuit, which provides multi-stage amplification.
Based on its output
Depending upon the parameter that is amplified at the output, there are voltage and power amplifiers.
Voltage Amplifiers − The amplifier circuit that increases the voltage level of the input signal, is called as Voltage amplifier.
Power Amplifiers − The amplifier circuit that increases the power level of the input signal, is called as Power amplifier.
Based on the input signals
Depending upon the magnitude of the input signal applied, they can be categorized as Small signal and large signal amplifiers.
Small signal Amplifiers − When the input signal is so weak so as to produce small fluctuations in the collector current compared to its quiescent value, the amplifier is known as Small signal amplifier.
Large signal amplifiers − When the fluctuations in collector current are large i.e. beyond the linear portion of the characteristics, the amplifier is known as large signal amplifier.
Based on the frequency range
Depending upon the frequency range of the signals being used, there are audio and radio amplifiers.
Audio Amplifiers − The amplifier circuit that amplifies the signals that lie in the audio frequency range i.e. from 20Hz to 20 KHz frequency range, is called as audio amplifier.
Power Amplifiers − The amplifier circuit that amplifies the signals that lie in a very high frequency range, is called as Power amplifier.
Based on Biasing Conditions
Depending upon their mode of operation, there are class A, class B and class C amplifiers.
Class A amplifier − The biasing conditions in class A power amplifier are such that the collector current flows for the entire AC signal applied.
Class B amplifier − The biasing conditions in class B power amplifier are such that the collector current flows for half-cycle of input AC signal applied.
Class C amplifier − The biasing conditions in class C power amplifier are such that the collector current flows for less than half cycle of input AC signal applied.
Class AB amplifier − The class AB power amplifier is one which is created by combining both class A and class B in order to have all the advantages of both the classes and to minimize the problems they have.
Based on the Coupling method
Depending upon the method of coupling one stage to the other, there are RC coupled, Transformer coupled and direct coupled amplifier.
RC Coupled amplifier − A Multi-stage amplifier circuit that is coupled to the next stage using resistor and capacitor (RC) combination can be called as a RC coupled amplifier.
Transformer Coupled amplifier − A Multi-stage amplifier circuit that is coupled to the next stage, with the help of a transformer, can be called as a Transformer coupled amplifier.
Direct Coupled amplifier − A Multi-stage amplifier circuit that is coupled to the next stage directly, can be called as a direct coupled amplifier.
Based on the Transistor Configuration
Depending upon the type of transistor configuration, there are CE CB and CC amplifiers.
CE amplifier − The amplifier circuit that is formed using a CE configured transistor combination is called as CE amplifier.
CB amplifier − The amplifier circuit that is formed using a CB configured transistor combination is called as CB amplifier.
CC amplifier − The amplifier circuit that is formed using a CC configured transistor combination is called as CC amplifier.
|
213 videos|208 docs|72 tests
|





















