Op Amp: Working Principle | Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Calculus Derivative Function as Basis to Compute Capacitor’s Current |

|
| Some Features of Op-Amps |

|
| Comparator |

|
| Square-Wave Converter |

|
| Bargraph Driver |

|
An operational amplifier or op-amp is simply a linear Integrated Circuit (IC) having multiple-terminals. The op-amp can be considered to be a voltage amplifying device that is designed to be used with external feedback components such as resistors and capacitors between its output and input terminals. It is a high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and usually a single-ended output.
Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today as they are used in a vast array of consumer, industrial and scientific devices.
Brief History
- In 1947, the first operational amplifier developed from vaccum tubes by John R. Ragazzini of Columbia University.
- With the development of silicon-based transistor, the concept of ICs became a reality. In the early 1960s, Robert J. Wildar of Fairchild Semiconductor fabricated opamp, the μA702.
- In 1968, the μA741 was released, leading it to wide production.
Modern day op-amps are available in:
- The metal can package (TO) with 8 pins
- The dual-in line package (DIP) with 8/14 pins
- The flat package of flat pack with 10/14 pins
Op-amp Circuit Construction
The inner schematic of a typical operational amplifier looks likes this:

The terminal with a (-) sign is called inverting input terminal and the terminal with (+) sign is called non-inverting input terminal.
The V+ and V− power supply terminals are connected to the positive and negative terminals of a DC voltage source respectively. The common terminal of the V+ and V− is connected to a reference point or ground, else twice the supply voltage may damage the op-amp.
Types of Op-Amps
An op-amp has countless applications and forms the basic building block of linear and non-linear analogue systems. Some of the types of op-amp include:
- A differential amplifier, which is a circuit that amplifies the difference between two signals.
- The instrumentation amplifier, which is usually built from three op-amps and helps amplify the output of a transducer (consisting of measured physical quantities).
- The isolation amplifier, which is like an instrumentation amplifier, but having tolerance to common-mode voltages (that destroy an ordinary op-amp).
- A negative-feedback amplifier, which is usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network.
- Power amplifiers to amplify small signals received from an input source such as microphone or antenna.
Op-Amp Operation
Ideally, an op-amp amplifies only the difference in voltage between the two, also called differential input voltage. The output voltage of the op-amp Vout is given by the equation:
Vout = AOL (V+ – V–)
where AOL is the open-loop gain of the amplifier.
In a linear operational amplifier, the output signal is the amplification factor, known as the amplifier’s gain (A) multiplied by the value of the input signal.
Op-Amp Parameters
|
Some other important electrical parameters to consider are:
- Input offset voltage: It is the voltage that must be applied between the input terminals of an op-amp to nullify the output.
- Input offset current: It is the algebraic difference between the currents into the (-) input and (+) input.
- Input bias current: It is the average of the currents entering into the (-) input and (+) input terminals of an op-amp.
- Input resistance: It is the differential input resistance as seen at either of the input terminals with the other terminal connected to ground.
- Input capacitance: It is the equivalent capacitance that can be measured at either of the input terminal with the other terminal connected to ground.
- Slew rate: It is defined as the maximum rate of change of output voltage caused by a step input voltage. The slew rate improves with higher closed loop gain and DC supply voltage. It is also a function to temperature and generally decreases with an increase in temperature.
Note:- Although an ideal op-amp draws no current from the source and its response is independent of temperature, a real op-amp does not work this way.
An op-amp only responds to the difference between the two voltages irrespective of the individual values at the inputs.
External resistors or capacitors are often connected to the op-amp in many ways to form basic circuits including Inverting, Non-Inverting, Voltage Follower, Summing, Differential, Integrator and Differentiator type amplifiers. An op-amp is easily available in IC packaging, the most common being the μA-741.


Op-amp Applications
An op-amp has countless applications and forms the basic building block of linear and non-linear analogue systems.
In linear circuits, the output signal varies with the input signal in a linear manner. Some of the linear applications are:
- Adder
- Subtractor
- Voltage to Current Converter (Transconductance Amplifier)
- Current to Voltage Converter (Transresistance Amplifier)
- Instrumentation amplifier
- Power amplifier
Another class of circuits with highly non-linear input to output characteristics are:
- Rectifier
- Peak detector
- Clipper
- Clamper
- Sample and hold circuit
- Log and antilog amplifier
- Multiplier and divider
- Comparator
Thanks to op-amps and associated circuits, they have become an integral part of audio amplifiers, waveform generators, voltage regulators, active filters, 555 timers, A-D and D-A converters.
Long before the advent of digital electronic technology, computers were built to electronically perform calculations by employing voltages and currents to represent numerical quantities. This was especially useful for the simulation of physical processes. A variable voltage, for instance, might represent velocity or force in a physical system. Through the use of resistive voltage dividers and voltage amplifiers, the mathematical operations of division and multiplication could be easily performed on these signals.
Calculus Derivative Function as Basis to Compute Capacitor’s Current
The reactive properties of capacitors and inductors lend themselves well to the simulation of variables related by calculus functions. Remember how the current through a capacitor was a function of the voltage’s rate of change, and how that rate of change was designated in calculus as the derivative? Well, if voltage across a capacitor were made to represent the velocity of an object, the current through the capacitor would represent the force required to accelerate or decelerate that object, the capacitor’s capacitance representing the object’s mass:
 This analog electronic computation of the calculus derivative function is technically known as differentiation, and it is a natural function of a capacitor’s current in relation to the voltage applied across it. Note that this circuit requires no “programming” to perform this relatively advanced mathematical function as a digital computer would.
This analog electronic computation of the calculus derivative function is technically known as differentiation, and it is a natural function of a capacitor’s current in relation to the voltage applied across it. Note that this circuit requires no “programming” to perform this relatively advanced mathematical function as a digital computer would.
Electronic circuits are very easy and inexpensive to create compared to complex physical systems, so this kind of analog electronic simulation was widely used in the research and development of mechanical systems. For realistic simulation, though, amplifier circuits of high accuracy and easy configurability were needed in these early computers.
Advantage of Differential over Single-Ended Amplifier
It was found in the course of analog computer design that differential amplifiers with extremely high voltage gains met these requirements of accuracy and configurability better than single-ended amplifiers with custom-designed gains. Using simple components connected to the inputs and output of the high-gain differential amplifier, virtually any gain and any function could be obtained from the circuit, overall, without adjusting or modifying the internal circuitry of the amplifier itself. These high-gain differential amplifiers came to be known as operational amplifiers, or op-amps, because of their application in analog computers’ mathematical operations.
Some Features of Op-Amps
Modern op-amps, like the popular model 741, are high-performance, inexpensive integrated circuits. Their input impedances are quite high, the inputs drawing currents in the range of half a microamp (maximum) for the 741, and far less for op-amps utilizing field-effect input transistors. Output impedance is typically quite low, about 75 Ω for the model 741, and many models have built-in output short circuit protection, meaning that their outputs can be directly shorted to ground without causing harm to the internal circuitry. With direct coupling between op-amps’ internal transistor stages, they can amplify DC signals just as well as AC (up to certain maximum voltage-rise time limits). It would cost far more in money and time to design a comparable discrete-transistor amplifier circuit to match that kind of performance, unless high power capability was required. For these reasons, op-amps have all but obsoleted discrete-transistor signal amplifiers in many applications.
The following diagram shows the pin connections for single op-amps (741 included) when housed in an 8-pin DIP (Dual Inline Package) integrated circuit:

Some models of op-amp come two to a package, including the popular models TL082 and 1458. These are called “dual” units, and are typically housed in an 8-pin DIP package as well, with the following pin connections:
 Operational amplifiers are also available four to a package, usually in 14-pin DIP arrangements. Unfortunately, pin assignments aren’t as standard for these “quad” op-amps as they are for the “dual” or single units. Consult the manufacturer datasheet(s) for details.
Operational amplifiers are also available four to a package, usually in 14-pin DIP arrangements. Unfortunately, pin assignments aren’t as standard for these “quad” op-amps as they are for the “dual” or single units. Consult the manufacturer datasheet(s) for details.
Practical operational amplifier voltage gains are in the range of 200,000 or more, which makes them almost useless as an analog differential amplifier by themselves. For an op-amp with a voltage gain (AV) of 200,000 and a maximum output voltage swing of +15V/-15V, all it would take is a differential input voltage of 75 µV (microvolts) to drive it to saturation or cutoff! Before we take a look at how external components are used to bring the gain down to a reasonable level, let’s investigate applications for the “bare” op-amp by itself.
Comparator
One application is called the comparator. For all practical purposes, we can say that the output of an op-amp will be saturated fully positive if the (+) input is more positive than the (-) input, and saturated fully negative if the (+) input is less positive than the (-) input. In other words, an op-amp’s extremely high voltage gain makes it useful as a device to compare two voltages and change output voltage states when one input exceeds the other in magnitude.

In the above circuit, we have an op-amp connected as a comparator, comparing the input voltage with a reference voltage set by the potentiometer (R1). If Vin drops below the voltage set by R1, the op-amp’s output will saturate to +V, thereby lighting up the LED. Otherwise, if Vin is above the reference voltage, the LED will remain off. If Vin is a voltage signal produced by a measuring instrument, this comparator circuit could function as a “low” alarm, with the trip-point set by R1. Instead of an LED, the op-amp output could drive a relay, a transistor, an SCR, or any other device capable of switching power to a load such as a solenoid valve, to take action in the event of a low alarm.
Square-Wave Converter
Another application for the comparator circuit shown is a square-wave converter. Suppose that the input voltage applied to the inverting (-) input was an AC sine wave rather than a stable DC voltage. In that case, the output voltage would transition between opposing states of saturation whenever the input voltage was equal to the reference voltage produced by the potentiometer. The result would be a square wave:
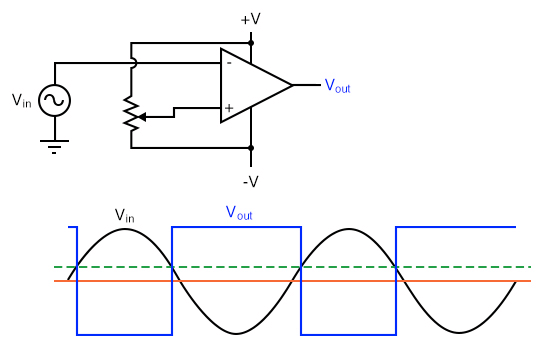 Adjustments to the potentiometer setting would change the reference voltage applied to the noninverting (+) input, which would change the points at which the sine wave would cross, changing the on/off times, or duty cycle of the square wave:
Adjustments to the potentiometer setting would change the reference voltage applied to the noninverting (+) input, which would change the points at which the sine wave would cross, changing the on/off times, or duty cycle of the square wave:
 It should be evident that the AC input voltage would not have to be a sine wave in particular for this circuit to perform the same function. The input voltage could be a triangle wave, sawtooth wave, or any other sort of wave that ramped smoothly from positive to negative to positive again. This sort of comparator circuit is very useful for creating square waves of varying duty cycle. This technique is sometimes referred to as pulse-width modulation, or PWM (varying, or modulating a waveform according to a controlling signal, in this case the signal produced by the potentiometer).
It should be evident that the AC input voltage would not have to be a sine wave in particular for this circuit to perform the same function. The input voltage could be a triangle wave, sawtooth wave, or any other sort of wave that ramped smoothly from positive to negative to positive again. This sort of comparator circuit is very useful for creating square waves of varying duty cycle. This technique is sometimes referred to as pulse-width modulation, or PWM (varying, or modulating a waveform according to a controlling signal, in this case the signal produced by the potentiometer).
Bargraph Driver
Another comparator application is that of the bargraph driver. If we had several op-amps connected as comparators, each with its own reference voltage connected to the inverting input, but each one monitoring the same voltage signal on their noninverting inputs, we could build a bar graph-style meter such as what is commonly seen on the face of stereo tuners and graphic equalizers. As the signal voltage (representing radio signal strength or audio sound level) increased, each comparator would “turn on” in sequence and send power to its respective LED. With each comparator switching “on” at a different level of audio sound, the number of LEDs illuminated would indicate how strong the signal was.
 In the circuit shown above, LED1 would be the first to light up as the input voltage increased in a positive direction. As the input voltage continued to increase, the other LEDs would illuminate in succession, until all were lit.
In the circuit shown above, LED1 would be the first to light up as the input voltage increased in a positive direction. As the input voltage continued to increase, the other LEDs would illuminate in succession, until all were lit.
This very same technology is used in some analog-to-digital signal converters, namely the flash converter, to translate an analog signal quantity into a series of on/off voltages representing a digital number.
|
137 videos|143 docs|71 tests
|
FAQs on Op Amp: Working Principle - Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What is the working principle of an Op-Amp? |  |
| 2. How can calculus derivative functions be used to compute a capacitor's current? |  |
| 3. What are some features of Op-Amps? |  |
| 4. What is the function of a square-wave converter in electronics? |  |
| 5. What is the role of a comparator in electronic circuits? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|

















