Textbook Solutions: Agricultural Patterns in India | Footprints Class 7: Book Solutions, Notes & Worksheets PDF Download
I. Tick (√) the correct option.
1.
Ans: (c)
2.
Ans: (b)
3.
Ans: (a)
4.
Ans: (b)
5.
Ans: (a)
II. Fill in the blanks.
1.
Ans: rabi
2.
Ans: cereals
3.
Ans: commercial
4.
Ans: Bagasse
5.
Ans: high-yielding varieties
III. Match the columns.
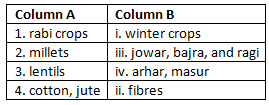
IV. State whether the following statements are true or false. Rewrite the corrected statements in your notebook.
1.
Ans: False
Corrected Statement: Rice grown in the rabi season accounts for roughly 30 per cent of total rice production and is planted from November to January and is harvested in late April.
2.
Ans: True
3.
Ans: True
4.
Ans: True
5.
Ans: False
Corrected Statement: The Nilgiri Hills produce some of India's best coffee.
V. There are two statements given as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read both the statements and choose the correct option.
1.
Ans: (a)
2.
Ans: (a)
 |
Download the notes
Textbook Solutions: Agricultural Patterns in India
|
Download as PDF |
VI. Answer the following questions in brief.
1.
Ans: Rice and maize.
2.
Ans: The major rice-producing regions in India include West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, and Odisha.
3.
Ans: Sugar cane and cotton.
4.
Ans: Sugar cane requires 70 cm to 120 cm of rainfall and temperatures between 20°C and 27°C. It thrives in deep, clayey loam, black cotton, or red and lateritic soils, often with irrigation.
5.
Ans: Tea requires temperatures between 25°C and 30°C and rainfall ranging from 100 cm to 250 cm.
VII. Answer the following questions in detail.
1.
Ans: Wheat requires lower temperatures ranging from 13°C to 25°C and moderate rainfall of 20 cm to 50 cm, while rice requires higher temperatures between 15°C and 30°C and much more rainfall, around 50 cm or more. Additionally, wheat is typically grown in loamy soils, while rice thrives in clayey, alluvial soils with adequate water supply for paddy fields.
2.
Ans:
- Coffee: Coffee grows best in temperatures between 14°C and 28°C, with rainfall between 40 cm and 50 cm, and requires well-drained, rich loamy soils. It is primarily cultivated in the southern plateau region of India.
- Jute: Jute requires temperatures around 24°C, rainfall of over 150 cm, and well-drained alluvial or loamy soils. It is mainly grown in West Bengal, Assam, Bihar, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh.
3.
Ans: Intensive farming is characterized by high-yield production from small farms through the intensive use of labor, fertilizers, high-yielding seeds, irrigation, and small farm machinery. It is commonly practiced in densely populated areas with fertile land, where farmers grow multiple crops annually, and significant capital investment is required for machinery and inputs.
4.
Ans: Dairy farming in India involves the commercial raising of animals, primarily for milk and milk products. It gained significant momentum with the White Revolution and Operation Flood, leading to modernized dairy production and processing. India is now the largest milk producer globally, with cooperatives like Amul and Mother Dairy playing a crucial role. Dairy farming is practiced near large cities to meet the demand for milk, which is processed into various products like butter, cream, and cheese.
5.
Ans: Major challenges facing Indian agriculture include fragmented land holdings, limited access to modern technology, inadequate irrigation, climate change, and fluctuating market prices. To address these challenges, the Government of India has implemented various reforms, including land consolidation, providing soft loans and credit facilities, improving storage and marketing infrastructure, promoting the Green Revolution, and launching the Digital Agricultural Mission to enhance productivity through modern technology. The government also supports agricultural universities and institutes to educate farmers and improve agricultural practices.
|
32 videos|186 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Textbook Solutions: Agricultural Patterns in India - Footprints Class 7: Book Solutions, Notes & Worksheets
| 1. What are the main agricultural patterns observed in India? |  |
| 2. How does subsistence farming differ from commercial farming in India? |  |
| 3. What are the characteristics of plantation agriculture in India? |  |
| 4. How does mixed farming contribute to agricultural sustainability in India? |  |
| 5. What are the factors influencing the choice of agricultural patterns in different regions of India? |  |























