What are Modals | English Grammar for Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Modals |

|
| List of Modals |

|
| Uses of Modals |

|
| Rules of Modals |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
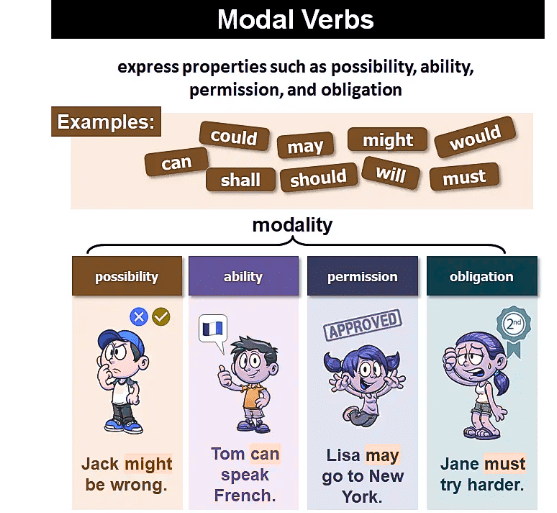
Modals
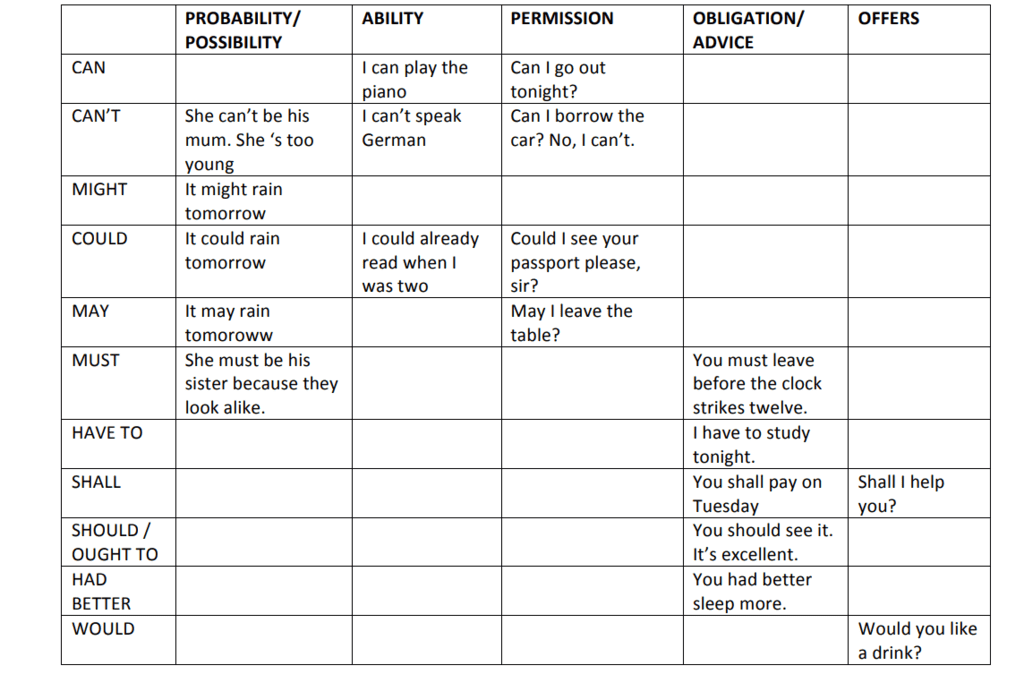
Modals are auxiliary (helping) verbs used with other verbs to express ability, possibility, permission, or obligation.

List of Modals
- Can
- Could
- May
- Might
- Will
- Would
- Shall
- Should
- Ought to
- Must
- Need
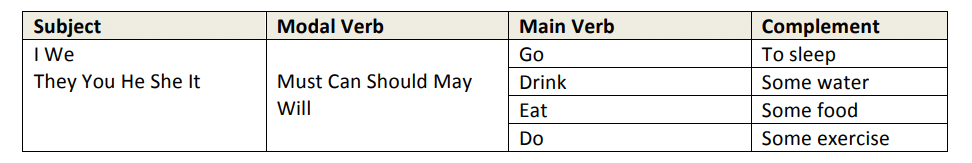
Structure
Uses of Modals
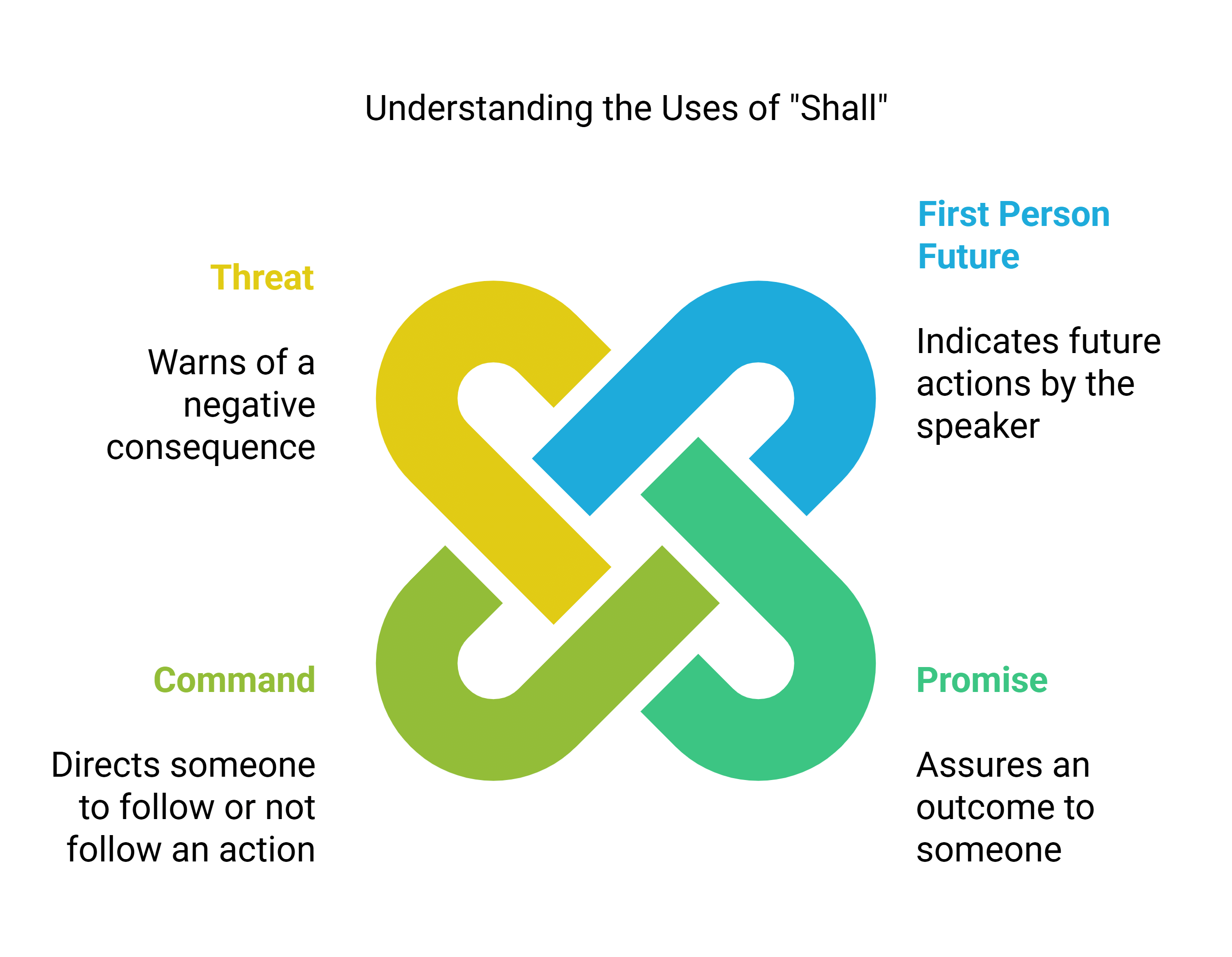
1. Uses of Shall
With the 1st person (I, we) to show future:
- Example: I shall be in my class at this time tomorrow. (Indicates a future action)
- Example: We shall decorate our houses for Deepawali. (Indicates a planned future event)
With the 2nd and 3rd person to show:
- Promise:
- Example: You shall get a prize. (A promise to give a prize)
- Example: We shall get Rs. 500. (A promise to receive money)
- Command:
- Example: You shall not come to my house. (A command not to visit)
- Threat:
- Example: You shall be punished for your misconduct. (A threat of punishment)
- Example: You shall be punished for your misconduct. (A threat of punishment)
2. Uses of Should
- Obligation:
Example: We should serve our parents. (It is our duty to serve our parents) - Advice or Recommendation:
Example: You should take milk, not coffee. (A suggestion for better health) - Probability or Expectation:
Example: He was in the final year of MBBS. He should be a doctor now. (An expectation based on his studies)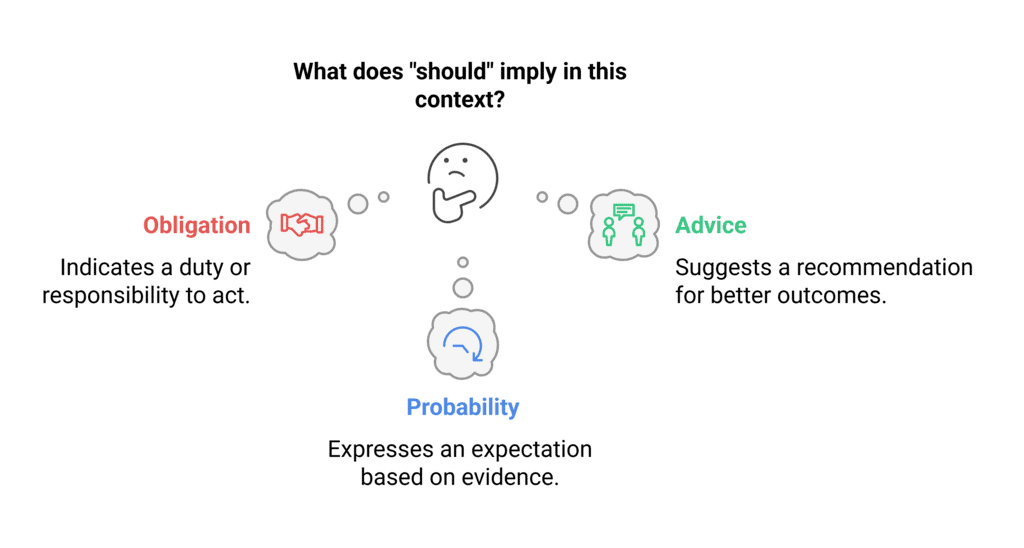
3. Uses of Will
- With the 3rd person to show future:
Example: He will be in his office at this time tomorrow. (A future action for someone else) - With the 1st and 2nd person to show:
Wish:
Example: I will go home now. (Expressing a decision or wish)
Request:
Example: Will you please lend me your scooter? (Polite request for a favor)
Determination:
Example: I will find out the truth. (Determined to achieve something)
Willingness:
Example: I will lend you my pen. (Willing to help)
Threat:
Example: I will surely punish him. (A threat to punish)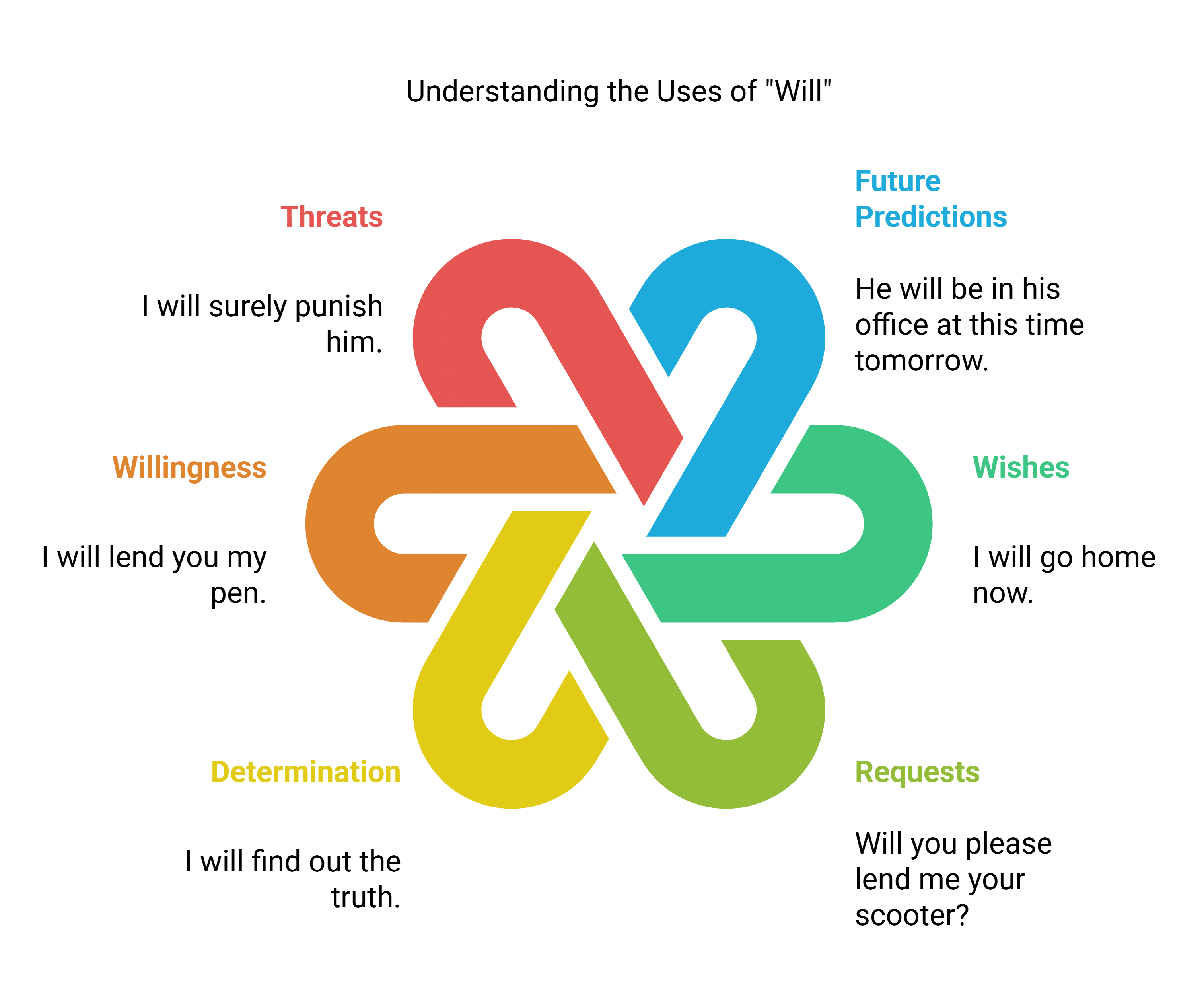
4. Uses of Would
- Polite Request:
Example: Would you lend me your pen? (A polite way of asking for something) - Enquiry about the Wish:
Example: Would you like to have a cup of tea? (Asking about someone's preference) - Wish:
Example: Would that I was the Prime Minister! (A wishful thinking)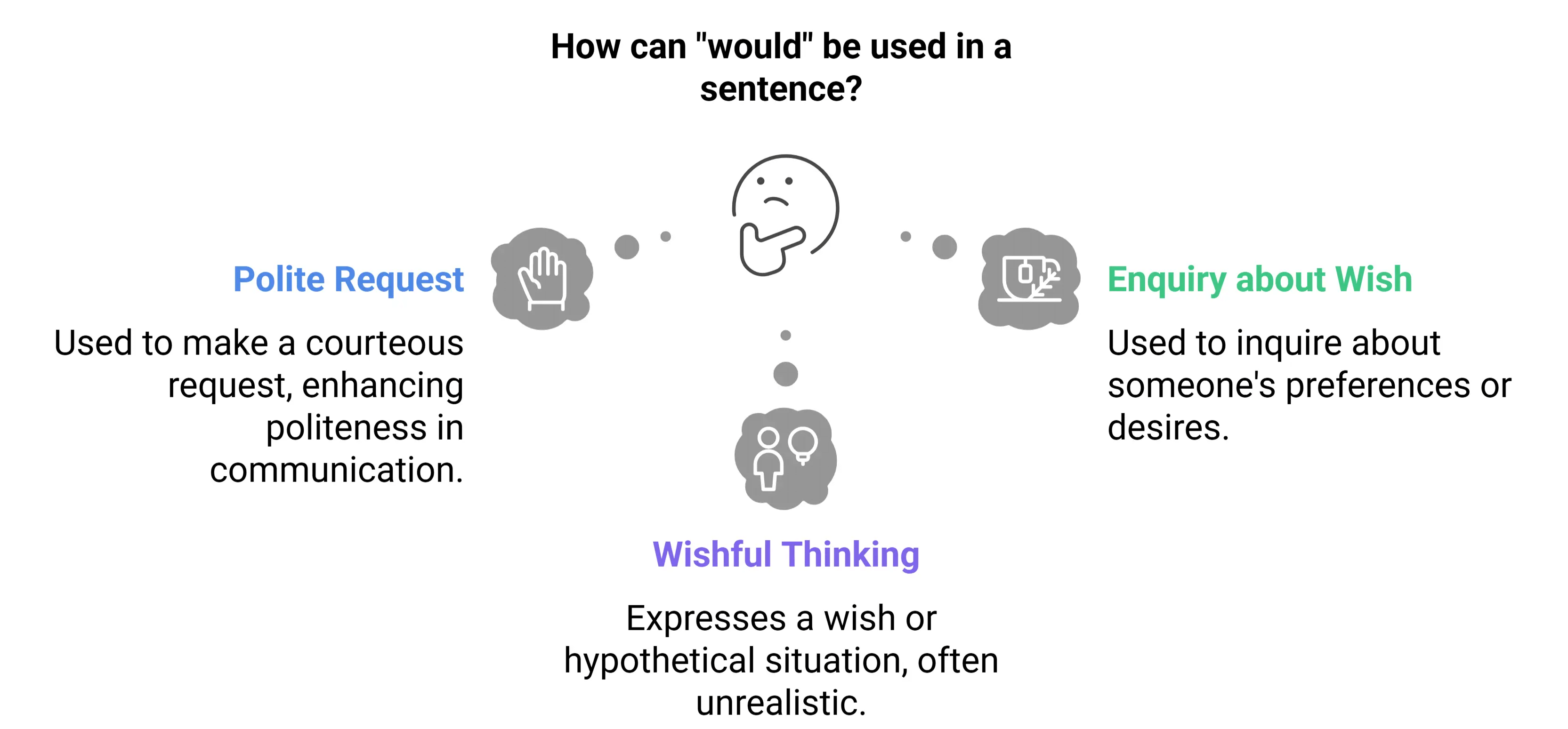
5. Uses of Can
- Ability:
Example: He can teach you how to speak English. (Shows someone's skill) - Possibility:
Example: He can come at any time. (Indicates that coming is possible)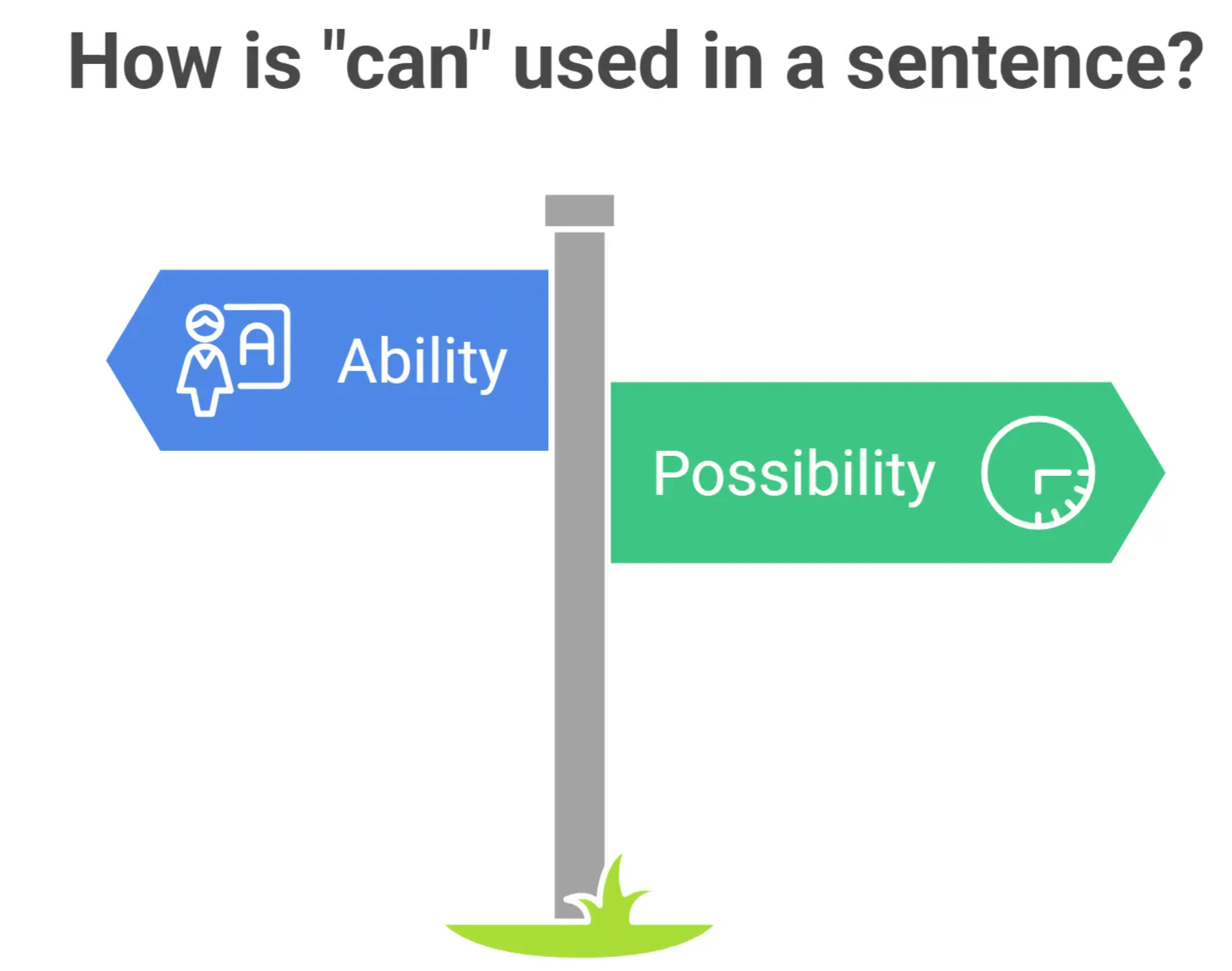
6. Uses of Could
- Past Ability:
Example: He could swim well at the age of ten. (Past ability to swim) - Permission:
Example: Could I see what is in your hands? (Asking for permission) - Polite Request:
Example: Could you pass on the salt, please? (A polite way to ask for something)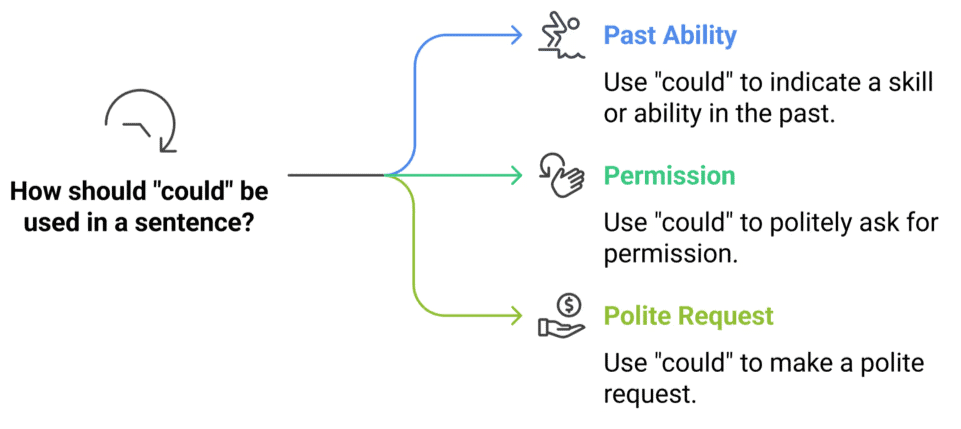
7. Uses of May
- Permission:
Example: May I come in, Sir? (Asking for permission to enter) - Possibility:
Example: It may rain today. (Indicating a possible event) - Purpose:
Example: Work hard so that you may pass. (Purpose for working hard) - Wishes and Hopes:
Example: May he win a scholarship! (Wishing someone success)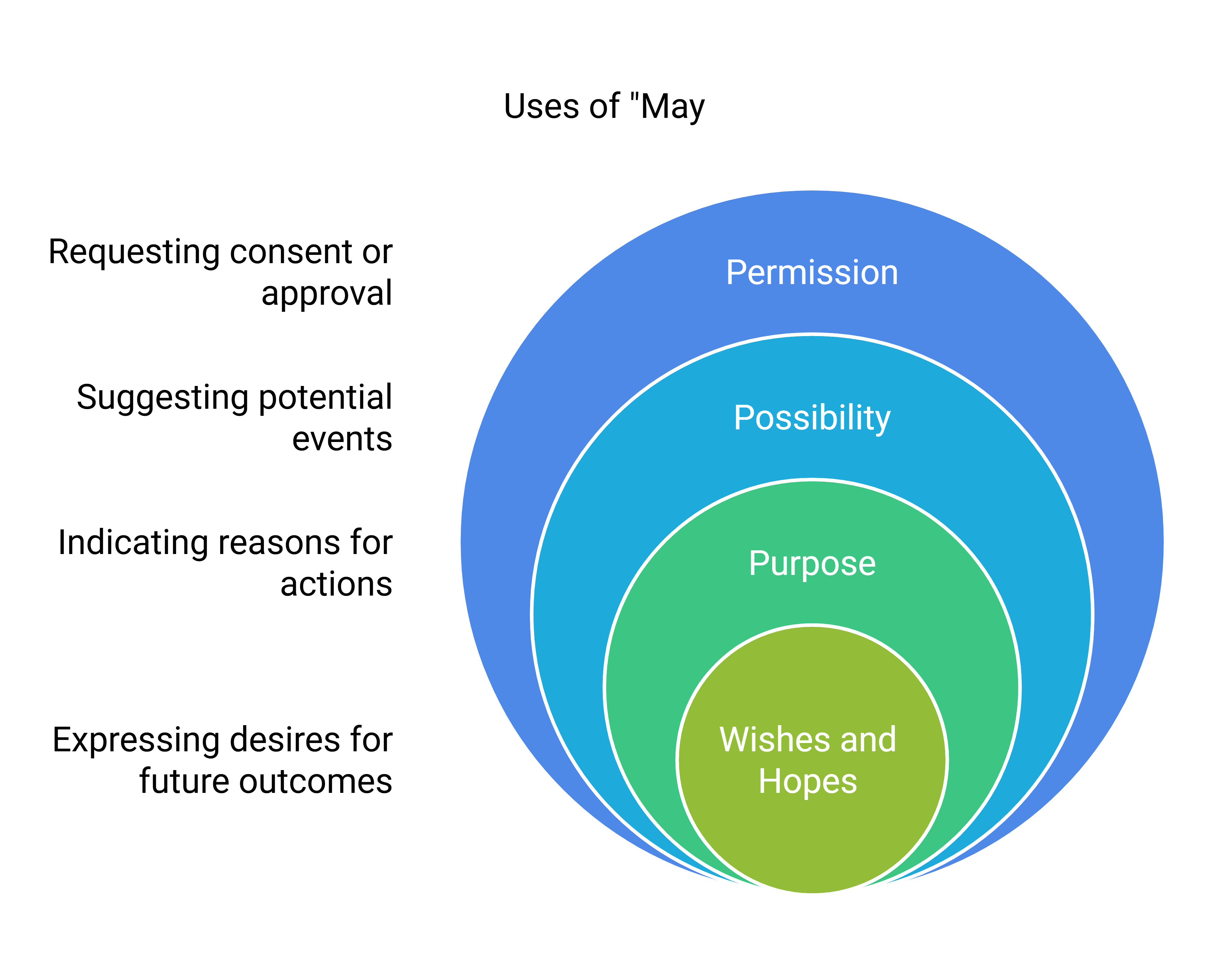
8. Uses of Must
- Obligation:
Example: You must pay your bill by the 7th of this month. (A strong requirement) - Advice or Recommendation:
Example: The patient is serious. You must take him to the hospital. (Strong advice) - Logical Conclusion:
Example: You have worked a lot. You must be tired. (A conclusion based on evidence)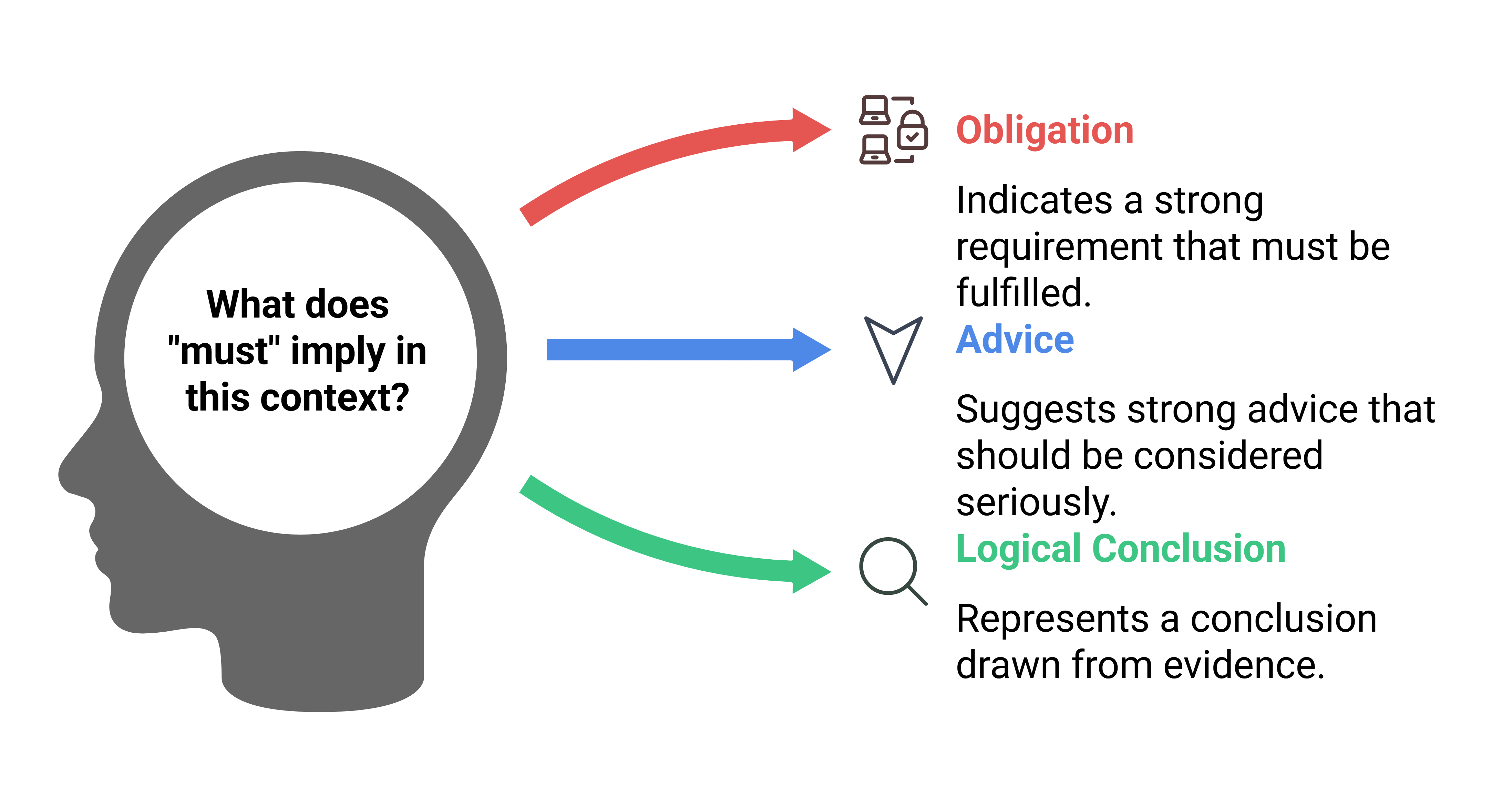
9. Uses of Need
- Obligation or Necessity:
Example: You need not go there now. You are too late. (Indicating no necessity) - Polite Request:
Example: Need I remind you of your promise? (A polite way of asking for a reminder)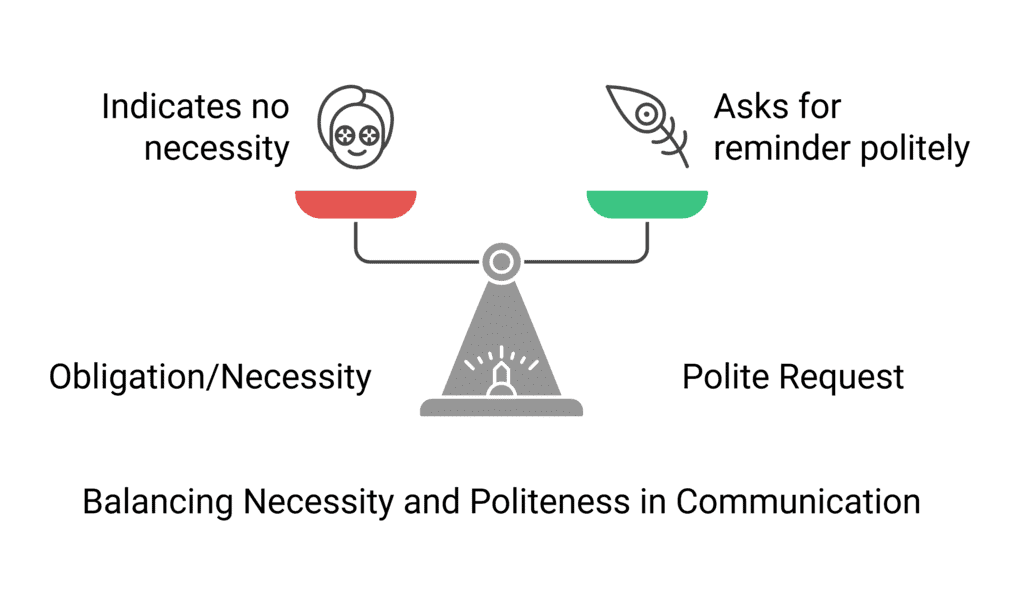
10. Uses of Might
- Possibility:
Example: It might rain, but we can’t be sure. (Indicating a possible event) - Purpose (in the past):
Example: He worked hard so that he might pass. (Purpose for working hard)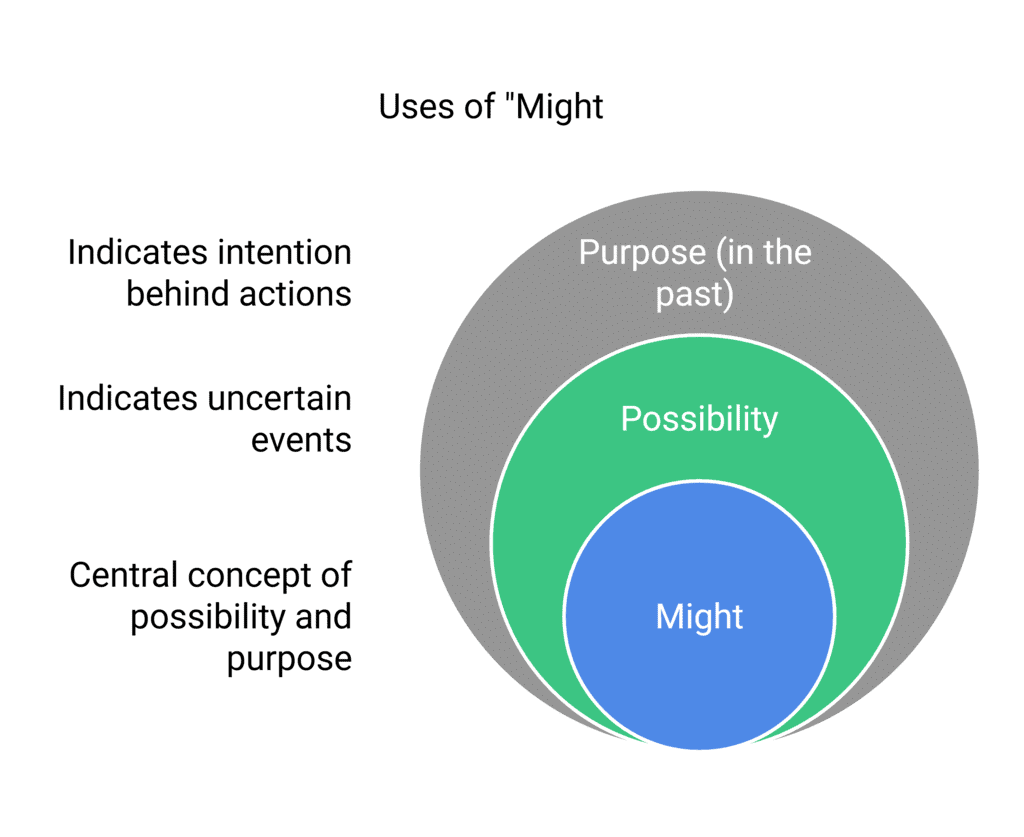
11. Uses of Ought to
- Obligation:
Example: You ought to attend the class regularly. (A recommendation for regular attendance) - Advice or Recommendation:
Example: He ought to consult a good doctor. (Advice to seek medical consultation)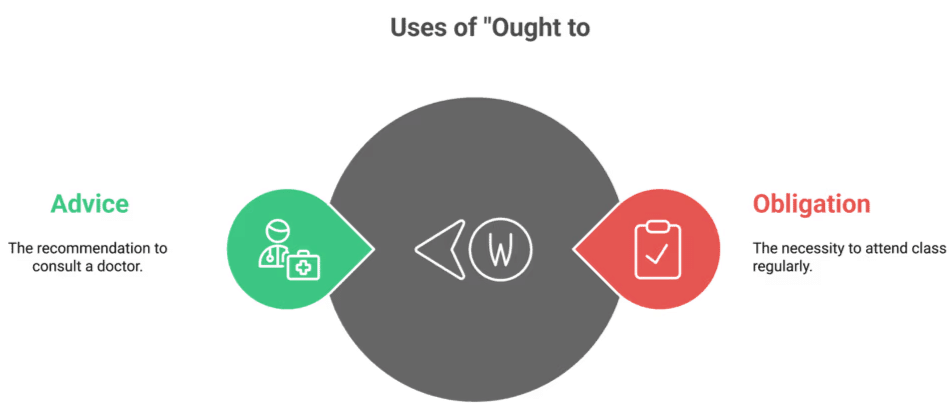
12. Uses of Used to
- Habitual Action in the Past:
Example: I used to fly kites when I was young. (Describing a past habit) - State of Things in the Past:
Example: There used to be a restaurant here ten years ago. (Describing a past state)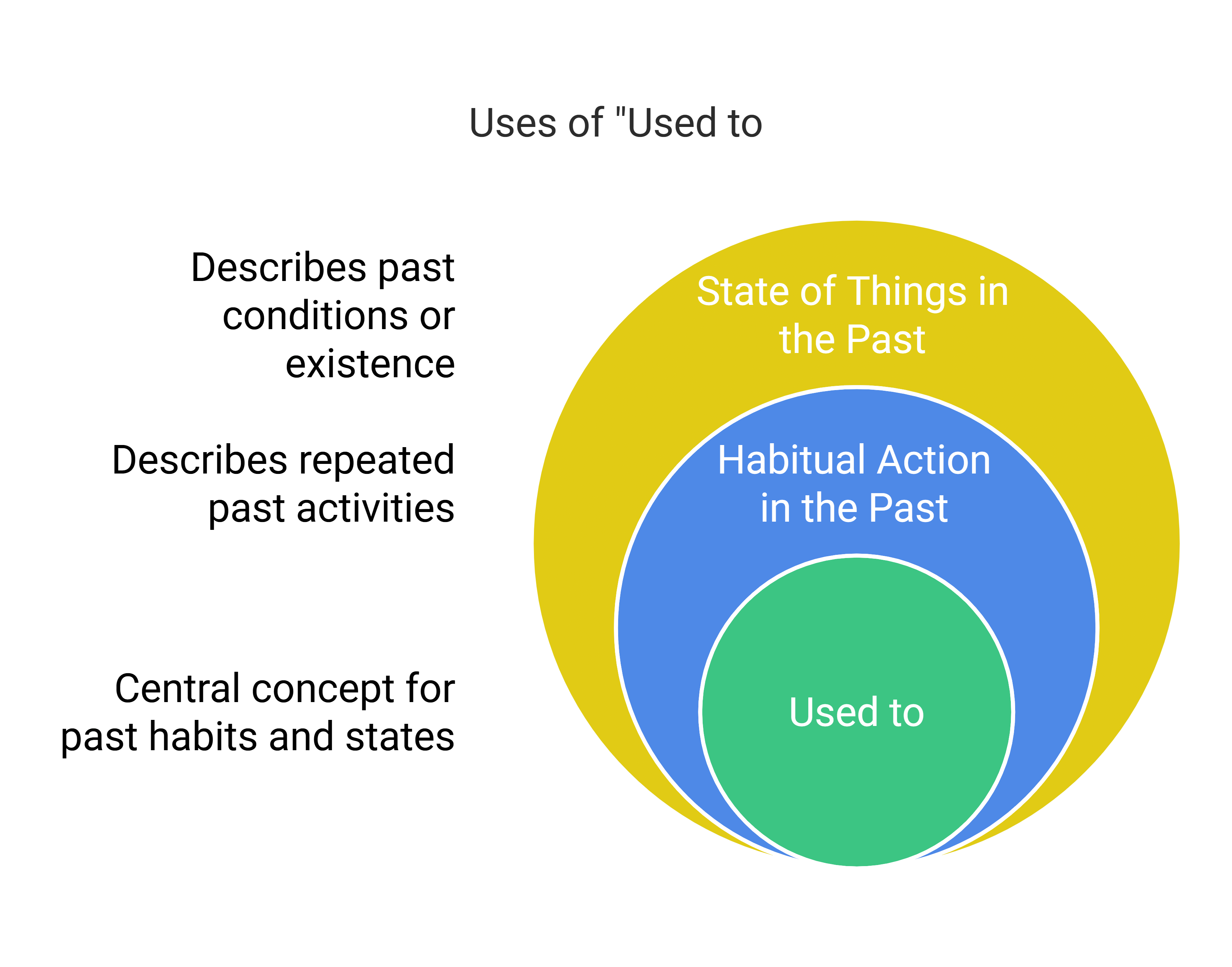
13. Uses of Dare
- Having the Courage:
Example: I do not know how he dares to say all that. (Showing courage or boldness) - Challenge:
Example: I dare you to disobey your parents. (A challenge to act boldly)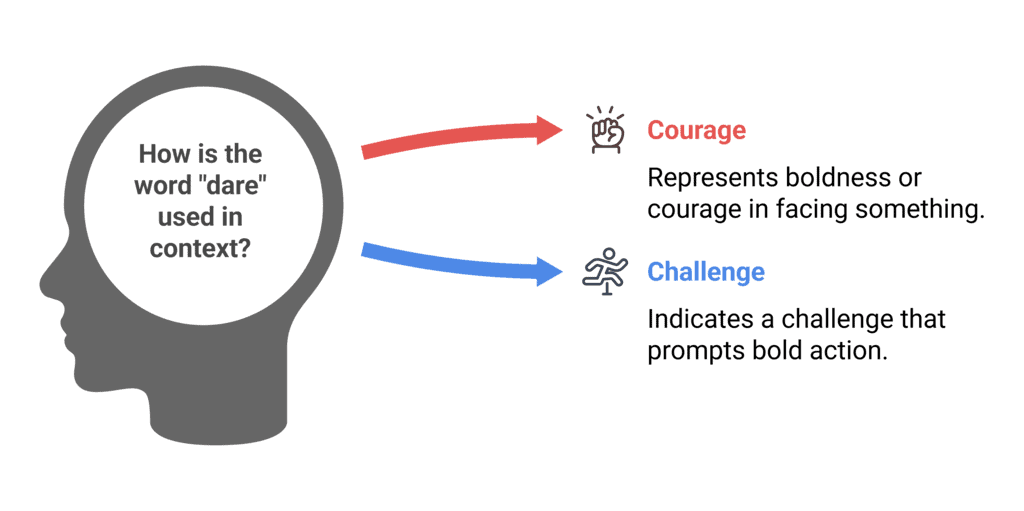
Rules of Modals

No Changes for Third-Person Singular: Modal verbs do not change form for the third-person singular (he, she, it).
Example:- Correct: She can sing.
- Incorrect: She cans sing.
No Need for Additional Auxiliaries: Modal verbs do not require additional auxiliary verbs to form negative or interrogative sentences.
Example:- Negative: You cannot swim. (Not: You do not can swim.)
- Interrogative: Can you swim? (Not: Do you can swim?)
No Infinitives or -ing Forms: Modal verbs do not have infinitive forms (to + verb) or -ing forms.
Example:- Incorrect: She wants to can swim. (Should be: She wants to swim.)
- Incorrect: He is can swimming. (Should be: He is swimming.)
Followed by Infinitive without “to”: Modal verbs are followed by the base form of the verb without “to.”
Example:- Correct: She must go now.
- Incorrect: She must to go now.
Past Forms with “Have” + Past Participle: To express past modal meanings, use the modal verb + “have” + past participle of the main verb.
Example:- She could have gone. (Indicating a past possibility)
- He should have called. (Indicating a past obligation)
Expressing Multiple Meanings: Modal verbs can express more than one meaning depending on the context.
Example:- “Can” can indicate ability (She can swim) or possibility (It can rain today).
Single and Double Concept Modals:
- Single Concept Modal:These modals have one meaning.
- Example: “Must” for obligation (You must study).
- Double Concept Modal:These modals can have two meanings.
- Example: “Could” can indicate past ability (He could swim when he was young) or polite requests (Could you help me?).
- Single Concept Modal:These modals have one meaning.
These rules help ensure the correct and effective use of modal verbs in various contexts.
Solved Examples
Fill in the Blanks with Modals
Q1: I wish that you __________ pass in the first division.
(A) might
(B) may
(C) must
(D) none
Ans: (B) may
"May" is used here to express a wish or hope for someone's success.
Q2: __________ I win the lottery!
(A) May
(B) Should
(C) Must
(D) None
Ans: (A) May
"May" expresses a strong wish or hope for something to happen.
Q3: You __________ work hard if you want to get good marks.
(A) needn’t
(B) daren’t
(C) ought to
(D) none
Ans: (C) ought to
"Ought to" indicates a recommendation or advice to work hard for good marks.
Q4: One __________ respect the old people.
(A) should
(B) mustn’t
(C) shall
(D) none of these
Ans: (A) should
"Should" expresses an obligation or moral duty to respect older people.
Q5: I __________ visit Delhi. But I am not much sure.
(A) must
(B) might
(C) should
(D) none of these
Ans: (B) might
"Might" indicates a possibility or uncertainty about visiting Delhi.
Q6: You __________ take my bicycle if you need.
(A) will
(B) would
(C) can
(D) none of these
Ans: (C) can
"Can" indicates permission or ability to use the bicycle.
Q7: The sage wished that I __________ live long.
(A) may
(B) might
(C) should
(D) none of these
Ans: (B) might
"Might" is used to express a wish for a long life.
Fill in the Blanks with Given Modals
Must, mustn’t, can, can’t
Ans: mustn’t
"Mustn’t" indicates prohibition or something that is not allowed.
(b) __________ you tell me what this is? I don’t know how to read Malayalam.
Ans: Can
"Can" is used to make a polite request for information.
(c) There is a test tomorrow. You __________ miss school.
Ans: mustn’t
"Mustn’t" indicates prohibition; you are not allowed to miss school.
(d) This car __________ be expensive. It is five years old.
Ans: can’t
"Can’t" indicates that something is unlikely or impossible given the information.
|
49 videos|349 docs|46 tests
|















