Unit Test (Solutions): The Human Eye and The Colourful World | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each
Q1: Bifocal lenses are used to correct which condition is mentioned below. (1 Mark)
(i) Astigmatism
(ii) Coma
(iii) Myopia
(iv) Presbyopia
Ans: (iv)
Presbyopia is corrected by the use of the bifocal lens. Bifocal lenses have an upper and lower point. The upper point has a concave lens used for distant vision, while the lower point contains a convex lens responsible for near vision.
Q2: Define the term “accommodation of the eye”. (1 Mark)
Ans: The ability of the eye to focus on near and distant objects, by adjusting its focal length, is called the accommodation of the eye.
Q3: Which of the following statements about the iris is true? (1 Mark)
(i) It is responsible for producing tears.
(ii) It controls the amount of light that enters the eye.
(iii) It is the outermost layer of the eye.
(iv) It is responsible for detecting color and fine details.
Ans: ii)
It controls the amount of light that enters the eye.
Q4: Which of the following statements about the blind spot in the eye is true? (1 Mark)
(i) It is located in the center of the retina.
(ii) It is the area where the optic nerve exits the eye.
(iii) It is responsible for detecting color and fine details.
(iv) It controls the amount of light that enters the eye.
Ans: (ii)
The blind spot in the eye is the point where the optic nerve exits the eye and there are no photoreceptor cells (rods or cones) present. This makes it incapable of detecting light, hence no image is formed at this point.
Q5: The clear sky is blue because (1 Mark)
(i) The atmosphere absorbs the blue light.
(ii) There is the absorption of ultraviolet radiation in the atmosphere.
(iii) There is a scattering of violet and blue light more by the atmosphere when compared to the other colours.
(iv) Light of all other colours is scattered more than the violet and blue light by the atmosphere.
Ans: (c)
The short wavelength of blue and violet colours is responsible for their scattering more than the light of other colours by the molecules in the atmosphere.
Q6: State the function of each of the following parts of human eye: (2 Marks)
(i) Cornea
(ii) Pupil
Ans:
(i) Cornea: It is a transparent bulge on the front surface of eyeball which refracls most ol lhe light rays entering the eye.
(ii) Pupil: It controls the amount of light entering into the eye.
Q7: A lens of power -4.5 D is required by a person to correct his vision. State the defect of vision he is suffering from, calculate the focal length and name the corrective lens. (2 Marks)
Ans: The vision defect is myopia or short-sightedness.
Focal length = 1/power = -100/4.5 = -22.2 cm.
The person has to use a concave lens to correct the vision.
Q8: Why is the red light used in the danger signals? (2 Marks)
Ans: The red light is used in the danger signals because it has the maximum value in the entire spectrum. Red light’s penetration power in the air is maximum of all and due to this reason, it can be seen from a further distance. So this colour is used to depict the danger.
Q9:
(a) List two causes of hypermetropia.
(b) Draw ray diagrams showing (i) a hypermetropic eye and (ii) its correction using suitable optical device. (3 Marks)
Ans:
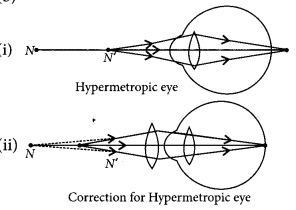
(a) Hypermetropia is caused due to following reasons:
(i) Shortening of the eyeball
(ii) Focal length of crystalline lens is too long.
Q10: A person may suffer from both myopia and hypermetropia defects.
(a) What is this condition called?
(b) When does it happen?
(c) Name the type of lens often required by the persons suffering from this defect. Draw labelled diagram of such lenses.(3 Marks)
Ans:
(a) This condition is called presbyopia.
(b) It happens due to gradual weakening of ciliary muscles and diminishing flexibility of eye lens due to agening.
(c) It can be corrected by using bifocal lenses.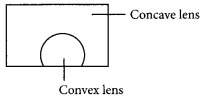
Q11: Explain hypermetropia. What are the causes and how can they be corrected? (3 Marks)
Ans: Hypermetropia is also known as far-sightedness. It is the inability of the eye in viewing nearby objects. The near point of our eye is more than 25 cm and the image is formed behind the retina.
Hypermetropia occurs due to the low converging power of our eye lens. The size of the eyeball is smaller.
It is corrected by use of a convex lens. This convex lens converges and also shifts the image to the retina from beyond.
Q12: A student is unable to see clearly the words written on the black board placed at a distance of approximately 3 m from him. Name the defect of vision the boy is suffering from. State the possible causes of this defect and explain the method of correcting it. (5 Marks)
Ans: Student is suffering from myopia.
The two possible reasons due to which the defect of vision arises are : excessive curvature of the eye lens and elongation of the eye ball.
A student with myopia has the far point nearer than infinity, thus, the image of a distant object is formed in front of the retina.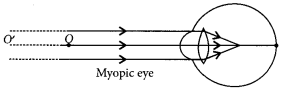
Correction of myopia: This defect can be corrected by using a concave lens of suitable power as it brings the image back on to the retina, thus the defect is corrected.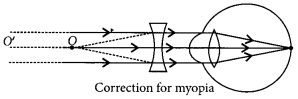
Q 13: What is ‘dispersion of white light’? State its cause. Draw a ray diagram to show the dispersion of white light by a glass prism. (5 Marks)
Ans: Splitting of white light into its seven constituent colours due to refraction is known as dispersion of white light.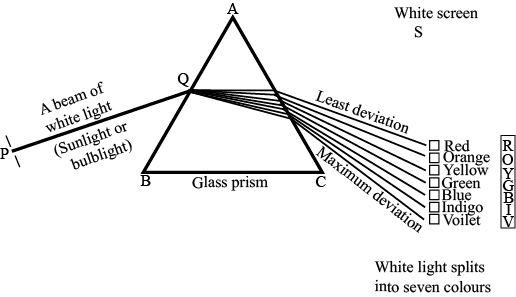
Cause of dispersion: When a beam of white light enters a prism, it gets refracted and splits into seven constituent colours. The splitting of the light ray occurs due to the different bending angle for each colour. Thus, each colour ray when passing through the prism bends at different angles with respect to the incident beam, thus giving rise to a spectrum.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): The Human Eye and The Colourful World - Science Class 10
| 1. How does the human eye work? |  |
| 2. Why do we see different colors? |  |
| 3. How do glasses and contact lenses help in correcting vision problems? |  |
| 4. What are some common eye disorders and how can they be treated? |  |
| 5. How can we protect our eyes from damage due to UV rays? |  |

















