Important Formulas: Prime Time | Maths Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
1. Common Multiples: Numbers that are multiples of two or more given numbers.
Example: For numbers 3 and 5, the common multiples are numbers like 15, 30, and 45. These numbers are divisible by both 3 and 5.
2. Factors: A number is a factor of another if it divides the second number without leaving a remainder. For example, 4 is a factor of 12 because 12 ÷ 4 = 3.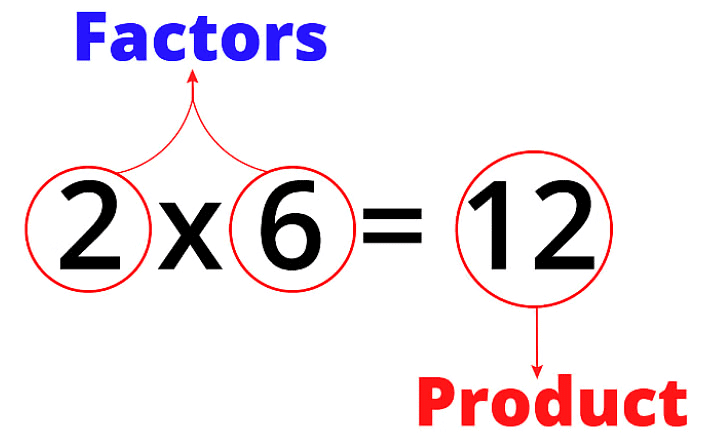
3. Common Factors: A common factor is a number that can evenly divide each of the numbers in a set.
Example: The number 4 is a common factor of 12 and 16 because 12 ÷ 4 = 3 and 16 ÷ 4 = 4.
4. Prime Numbers: A prime number is a number greater than 1 that can only be divided evenly by 1 and itself. For example, 7 is a prime number because the only numbers that divide 7 evenly are 1 and 7.
5. Composite Numbers: A composite number is a number that has more than two factors. This means it can be divided evenly by 1, itself, and at least one other number. For example, 12 is composite because it can be divided by 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. 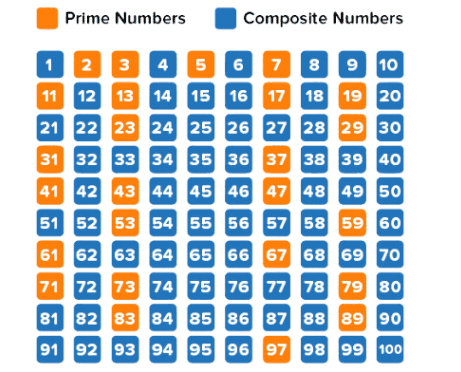
6. Prime Factorisation: Every number greater than 1 can be expressed as a product of prime numbers. For instance, 84 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 7.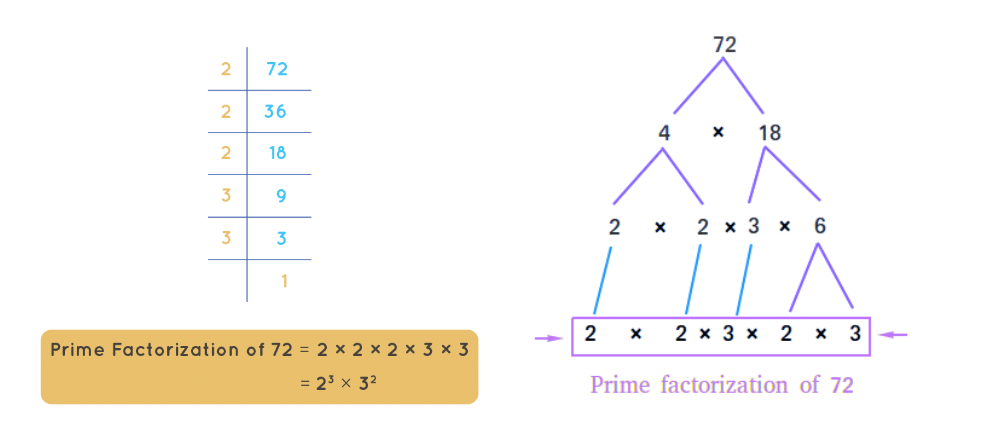
7. Unique Factorisation: There is only one way to factorise a number into primes, though the order of factors can vary.
8. Co-prime Numbers: Two numbers are co-prime if they have no common factors other than 1.
9. Checking Co-primality: To determine if two numbers are co-prime, find their prime factorizations. If there are no common prime factors, they are co-prime.
Example:
- 80 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 5
- 63 = 3 × 3 × 7
10. Factor Inclusion: A number is a factor of another if its prime factorisation is part of the prime factorisation of the other number.
11. Divisibility Tests:
- Divisibility by 10: A number is divisible by 10 if its last digit is 0.
- Divisibility by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if its last digit is 0 or 5.
- Divisibility by 2: A number is divisible by 2 if its last digit is even (0, 2, 4, 6, 8).
- Divisibility by 4: A number is divisible by 4 if the number formed by its last two digits is divisible by 4.
- Divisibility by 8: A number is divisible by 8 if the number formed by its last three digits is divisible by 8.
12. Special Numbers:
- Perfect Square: A number that is the square of an integer (e.g., 9 = 3 × 3).
- Prime Number: A number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself (e.g., 43, 7).
- Perfect Cube: A number that is the cube of an integer (e.g., 27 = 3 × 3 × 3).
|
30 videos|120 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas: Prime Time - Maths Olympiad Class 6
| 1. What is a prime number? |  |
| 2. How can you determine if a number is prime? |  |
| 3. Can 1 be considered a prime number? |  |
| 4. What is the importance of prime numbers in mathematics? |  |
| 5. Are there an infinite number of prime numbers? |  |






















