Speaker | Constitutional Law - CLAT PG PDF Download
Introduction
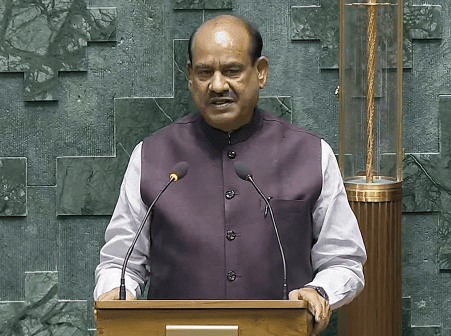
- The Speaker of the House of the People (Lok Sabha) is the presiding officer of the Lok Sabha, the lower house of Parliament in India. Elected by the members of the Lok Sabha during their first meeting after general elections, the Speaker is responsible for ensuring the smooth functioning of the House and is considered the guardian of Indian parliamentary democracy.
- The Speaker holds significant administrative and discretionary powers as outlined in the Constitution of India.
Article 93 - The Speaker and Deputy Speaker of the House of the People
The House of the People (Lok Sabha) is responsible for electing its Speaker and Deputy Speaker from among its members as soon as possible after the formation of the House, and whenever a vacancy arises in either position.
Election of Speaker and Deputy Speaker
- The Speaker and Deputy Speaker of the Lok Sabha are elected by a simple majority of the members present and voting in the House.
- There are no specific qualifications required for becoming the Speaker, other than being a member of the Lok Sabha.
- However, a good understanding of the Constitution, laws, and parliamentary procedures is considered beneficial for the Speaker.
Speaker of the Lok Sabha
- The Speaker of the Lok Sabha is the presiding officer of the House of the People.
- They are responsible for maintaining order and decorum in the House.
- The Speaker has the authority to take disciplinary action against members if necessary.
Deputy Speaker of the Lok Sabha
- The Deputy Speaker assists the Speaker in their duties.
- In the absence of the Speaker, the Deputy Speaker presides over the sessions of the Lok Sabha.
- Like the Speaker, the Deputy Speaker is also elected from among the members of the Lok Sabha.
Article 94 - Vacation and Resignation of Speaker and Deputy Speaker
According to Article 94 of the Indian Constitution, a Speaker or Deputy Speaker of the House of the People must vacate their office under the following circumstances:
- If they cease to be a member of the House of the People.
- If they resign from their position.
- If they are removed from office by a majority resolution of the House.
Role and Responsibilities of the Speaker of Lok Sabha
- Presiding Officer: The Speaker of the Lok Sabha is both a member of the House and its Presiding Officer. They conduct the business of the House and maintain order and discipline.
- Bill Classification: The Speaker decides whether a bill is a money bill or not, which is an important aspect of parliamentary procedure.
- Discipline and Decorum: The Speaker has the authority to punish members for unruly behavior by suspending them. They ensure that the House functions smoothly and maintains decorum.
- Motions and Resolutions: The Speaker permits the moving of various types of motions and resolutions, such as the motion of no confidence, motion of adjournment, motion of censure, and calling attention notice, as per the rules.
- Agenda Setting: The Speaker decides on the agenda for discussion during the meeting, determining the topics to be addressed by the members.
- Joint Sittings: The Speaker presides over joint sittings of Parliament when there is a disagreement between the two Houses on a legislative measure.
- Disqualification Powers: Following the 52nd Constitutional Amendment, the Speaker has the power to disqualify a member of the Lok Sabha on grounds of defection.
- Obituary References: The Speaker makes obituary references in the House, formal references to significant national and international events, and delivers the valedictory address at the end of each Session of the Lok Sabha and when the House's term expires.
- Voting: Although the Speaker is a member of the House, they do not vote except in rare cases of a tie. The Speaker's casting vote has not been used to date.
- Acting Speaker: When the office of the Speaker is vacant due to absence, resignation, or removal, the Deputy Speaker or a member appointed by the President performs the duties of the office.
Article 95 - Power of the Deputy Speaker or Other Person to Perform the Duties of the Office of, or to Act as, Speaker
- Article 95 (1) states that when the office of the Speaker is vacant, the Deputy Speaker will take over the responsibilities of the Speaker. If the Deputy Speaker's position is also vacant, the President can appoint a member from the House of the People to act as Speaker.
- Article 95 (2) indicates that if both the Speaker and Deputy Speaker are absent during a sitting of the House of the People, a member present in the House will be chosen to act as Speaker according to the House's rules. If no such member is available, the House will select someone else to fill the role.
Article 96 - The Speaker or Deputy Speaker's Role During Removal Consideration
- Presiding Restrictions: When the House of the People is considering a resolution to remove the Speaker or Deputy Speaker, the respective official (Speaker or Deputy Speaker) cannot preside over the meeting, even if present.
- The rules from Article 95(2) apply, as if the Speaker or Deputy Speaker were absent.
Speaker's Rights During Removal Proceedings
- Participation: The Speaker can participate in discussions and debates while a resolution for their removal is being considered.
- Voting: The Speaker is entitled to vote on the resolution or any other matter during these proceedings, but only in the initial instance, not in case of a tie.
Legislative Assembly
Article 178: The Speaker and Deputy Speaker of the Legislative Assembly
- Election of Speaker and Deputy Speaker: The Legislative Assembly of a State is required to elect a Speaker and a Deputy Speaker from among its members as soon as possible.
- Vacancy: If the position of Speaker or Deputy Speaker becomes vacant, the Assembly must elect another member to fill the role.
- Role of the Speaker: The Speaker presides over the Assembly and remains in office until they cease to be a member. They do not vacate their position when the Assembly is dissolved and continue until a new Speaker is elected.
- Removal of the Speaker: The Speaker can resign or be removed from office if a majority of members pass a resolution.
- Role of the Deputy Speaker: If the Speaker is absent or the position is vacant, the Deputy Speaker performs the duties of the Speaker.
- Constitution of the House: The House cannot be properly constituted without the Speaker or Deputy Speaker presiding over it.
Article 179: Vacation and resignation of, and removal from, the offices of Speaker and Deputy Speaker.
- Office Vacancies: A Speaker or Deputy Speaker must vacate their office if they cease to be a member of the Legislative Assembly.
- Resignation: Either the Speaker or Deputy Speaker can resign by submitting a written notice to the other.
- Removal: They can be removed from office by a majority resolution of the Assembly, with a 14-day notice period required before such a resolution can be moved.
- Speaker's Tenure After Dissolution: When the Assembly is dissolved, the Speaker remains in office until the first meeting of the new Assembly.
Article 180: Power of the Deputy Speaker or other person to perform the duties of the office of, or to act as a Speaker.
- Deputy Speaker's Role: When the office of Speaker is vacant, the Deputy Speaker takes on the Speaker's duties. If the Deputy Speaker's position is also vacant, the Governor appoints a member of the Assembly to fulfill this role.
- Acting Speaker: In the absence of the Speaker during a sitting, the Deputy Speaker or another designated person will act as Speaker.
Article 181: The Speaker or the Deputy Speaker not to preside while a resolution for his removal from office is under consideration.
- Presiding Over Removals: When a resolution to remove the Speaker or Deputy Speaker is being considered, they cannot preside over the meeting, even if present.
- Right to Participate: The Speaker or Deputy Speaker has the right to speak and participate in the Assembly's proceedings during their removal consideration, and they can vote on the resolution, but only in the initial instance, not in case of a tie.
Anti-Defection Laws
The 52nd Amendment Act, enacted in 1985, led to amendments in Articles 101, 102, 190, and 191 of the Constitution. This was done to establish grounds for the vacation of seats and the disqualification of members. Additionally, the Tenth Schedule was inserted into the Constitution.
Background of the Amendment
- The amendment was prompted by concerns over political defections, which were seen as a threat to the foundation of democracy.
- The statement of objects and reasons highlighted the need to combat political defections to protect democratic principles.
Grounds for Disqualification
- According to Rule 2 of the Tenth Schedule, a member of a house belonging to a political party can be disqualified under the following circumstances:
- If the member voluntarily gives up their membership of the political party.
- If the member votes or abstains from voting in a manner contrary to the directions of the political party.
- However, a member will not be disqualified if they obtain prior permission or if the party condones the action within 15 days.
- A disqualification also occurs if an independent candidate joins a political party after the election or if a nominated member joins a political party after six months from the date of their nomination.
Exemptions from Disqualification
- Rules 4 and 5 outline exemptions from disqualification:
- A member of the house shall not be disqualified if their original political party merges with another party, and they become members of the new party or a party formed by the merger.
- They are also exempt if they do not accept the merger and choose to function as a separate group.
- Rule 3 states that there will be no disqualification for members representing a faction of the original party resulting from a split. A split is considered actionable if at least one-third of the members defect.
Loopholes in the Anti-Defection Law
The Anti-Defection Law in India, though intended to maintain political stability, has certain loopholes that can be exploited. Here are some of the key criticisms and issues:
1. Power to the Speaker
- The Speaker of the House or Chairman has significant authority under Rule 6 of the Tenth Schedule to decide on disqualifications due to defection.
- Critics argue that the Speaker, often a member of the party that nominated them, may lack the legal expertise to make such decisions effectively.
2. Judicial Review
- Rule 7 restricts court jurisdiction, including the Supreme Court and High Courts , from reviewing the Speaker's decisions on disqualifications.
- This limitation has been challenged in court, notably in Kihoto Hollohon v. Zachilhu , where the Supreme Court upheld the law but deemed the restriction on judicial review unconstitutional.
- The Court clarified that the Speaker acts as a tribunal in these cases and that their decisions are subject to judicial review.
- Any law affecting Articles 136 , 226 , and 227 of the Constitution requires ratification by the States under Article 368(2) , which was not met in this case.
- The Supreme Court advised caution in exercising judicial review before the Speaker makes a decision.
3. Lack of Individual Stand for Members
- According to Rule 2 , party members must adhere to party rules and policies, limiting their ability to oppose the party on issues like bad policies or leadership decisions .
- This undermines the principle of representative democracy , where elected officials should act in the best interest of their constituents rather than strictly following party directives.
- The law blurs the line between dissent and defection, leading to disqualification of members who express individual opinions.
- By restricting individual voting rights, the anti-defection law fails to achieve its intended purpose and strengthens party control over members.
4. Ambiguity in 'Voluntarily Giving Up' Membership
- Rule 2(1)(a) of the Tenth Schedule states that a member can be disqualified for voluntarily giving up their party membership, but does not clarify what this means.
- The Supreme Court has interpreted this phrase as having a broad meaning, not limited to formal resignation.
- In cases like Ravi Naik v. Union of India and G. Viswanathan v. Speaker, Tamil Nadu Legislative Assembly , the Court clarified that a member's conduct can indicate voluntary membership withdrawal, even without a formal resignation.
- For instance, a member expelled from a party remains a member for Tenth Schedule purposes until they join another party, at which point they are considered to have voluntarily given up their original party membership.
Rajendra Singh Rana v. Swami Prasad Maurya and Others
- This case broadened the interpretation of "voluntarily giving up membership." It was determined that when an elected party member writes a letter to the Governor requesting the leader of the opposing party to form a government, it constitutes an act of voluntarily relinquishing membership from their party.
Problem with Merger Provision
- Rule 4 of the Tenth Schedule offers some protection against disqualification for members in merger situations. However, there are noticeable gaps in this provision.
- The rule safeguards members of a political party when the original party merges with another, provided that at least two-thirds of the legislature party members agree to the merger.
- The issue lies in the fact that this exception is based on the number of members involved rather than the motives behind the defection.
- Individual members often defect due to attractive offers of office or ministerial positions from the other party. It's plausible that the same motivations could influence the two-thirds majority that agrees to the merger.
- If individual defection is deemed unacceptable, it raises the question of why it would be permissible in the case of mergers simply due to the larger number of participants.
Role of Presiding Officers in Context of Anti-Defection Law
- The 10th Schedule grants presiding officers of legislatures the authority to make decisions regarding cases of defection.
- However, concerns have been raised about the Speaker's impartiality since they rely on the ongoing support of the majority in the House. This can compromise their role as an independent adjudicator.
- There have been instances in the past where Speakers' decisions on disqualifications have been challenged in court due to perceptions of bias.
- Various expert committees, such as the Dinesh Goswami Committee (1998) and the Law Commission (2015), have suggested that defection cases should be resolved by the President or Governor of the respective authorities, based on the advice of the Election Commission .
- This recommendation aligns with the procedure followed for disqualifying legislators on other grounds, like holding an office of profit, as outlined in the Constitution.
- Despite these concerns, the Supreme Court has upheld the presiding officer's authority to make decisions under the Tenth Schedule. The Court argues that Speakers and Chairmen play a crucial role in parliamentary democracy and are responsible for protecting the rights and privileges of the House.
- They are expected to make significant decisions impacting the functioning of parliamentary democracy, and their power to adjudicate under the Tenth Schedule is considered a vital constitutional function.
|
115 docs|26 tests
|
FAQs on Speaker - Constitutional Law - CLAT PG
| 1. What are the main responsibilities of the Speaker and Deputy Speaker of the House of the People? |  |
| 2. What happens if the Speaker or Deputy Speaker resigns or takes vacation? |  |
| 3. Can the Deputy Speaker perform the duties of the Speaker if the latter is unavailable? |  |
| 4. What is the procedure for removing the Speaker or Deputy Speaker from office? |  |
| 5. What are the implications of the Anti-Defection Law on the role of the Speaker? |  |
















