Transportation in Human Beings: Circulatory System & The Human Heart - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Human Circulatory System |

|
| Organs of Circulatory System |

|
| Heart |

|
| Blood |

|
The human body is a complex machine, requiring many processes to function efficiently. To keep these crucial processes running without any hitches, vital elements and components need to be delivered to the various parts of the body. This role of transportation is undertaken by the human circulatory system, moving essential nutrients and minerals throughout the body and metabolic waste products away from the body.
Human Circulatory System
The human circulatory system consists of a network of arteries, veins, and capillaries, with the heart pumping blood through it. Its primary role is to provide essential nutrients, minerals, and hormones to various parts of the body.
Alternatively, the circulatory system is also responsible for collecting metabolic waste and toxins from the cells and tissues to be purified or expelled from the body.
Organs of Circulatory System
The human circulatory system comprises 4 main organs that have specific roles and functions.
The vital circulatory system organs include:
- Heart
- Blood (technically, blood is considered a tissue and not an organ)
- Blood Vessels
- Lymph
[Question: 874199]
Heart
Size - 5 × 3.5 inches (almost as big as our fist)
Colour - Pink
Shape - Conical
Weight - 300 gm
Position- The heart is located in the chest, slightly tilted to the left.
Functions- The heart's main function is to pump blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells and removing waste products.
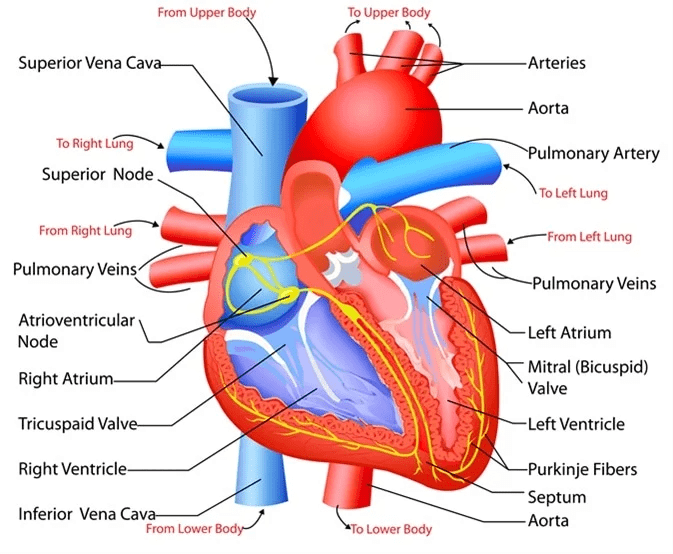 Structure of Human Heart
Structure of Human Heart
- Because both oxygen and carbon dioxide have to be transported by the blood, the heart has different chambers to prevent the oxygen-rich blood from mixing with the blood containing carbon dioxide.
- The human heart is divisible into four chambers. The upper two chambers are auricles (atria) while the lower two chambers are called ventricles.
[Question: 874201]
The Internal Structure of the Heart
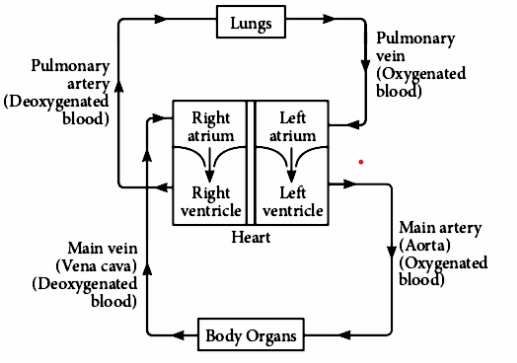
(A) Right Auricle (Atrium)
- The right auricle has the openings of the superior and inferior vena cava.
- Superior vena cava brings deoxygenated blood from the veins of the head, neck and upper limbs to right auricle and inferior vena cava brings deoxygenated blood from rest of the body and lower limbs to right auricle.
- From the right auricle blood passes into the right ventricle through a tricuspid valve, (so-called because it has three cusps, also prevents back flow of blood to right auricle.)
(B) Right Ventricle
- Blood leaves the right ventricle through the pulmonary artery. It is guarded by a semilunar valve.
- This artery enters into the two lungs where they further branch into pulmonary capillaries.
(C) Left Auricle (Atrium)
- This chamber receives oxygenated blood from lungs through pulmonary veins (two from each lung).
- The left auricle empties its blood into the left ventricle through a mitral or bicuspid valve (prevents backflow of blood).
(D) Left Ventricle :
- Blood leaves the left ventricle by the large, main artery of the body called the aorta.
- The opening from the left ventricle into the aorta is guarded by the aortic semilunar valve.
Working of the heart
- The heart of the human works like a pump.
- Pure oxygenated blood enters the left auricle from lungs through pulmonary veins.
- The deoxygenated blood from various parts of the body enters the right auricle through veins .
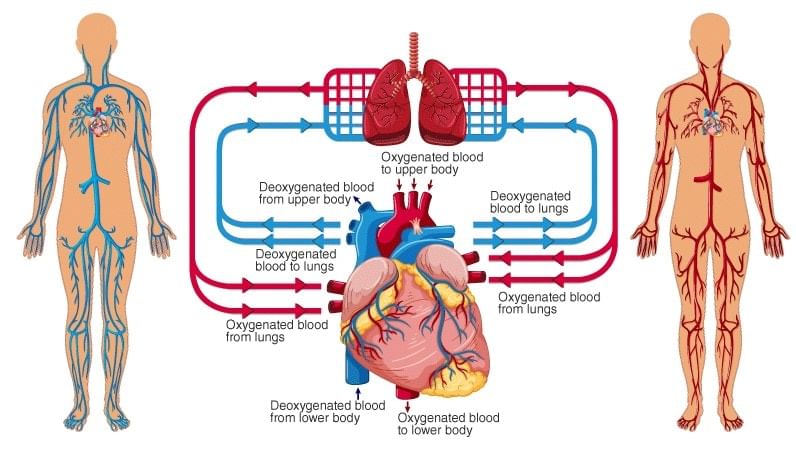
- The two auricles contract simultaneously so the oxygenated blood from the left auricle to the left ventricle and deoxygenated blood from the right auricle is pumped into the right ventricle.
- Now both the ventricles contract simultaneously so the pressure is created on the blood and the valves between auricle and ventricle close and the blood do not go back into the auricle.
- Due to this pressure, the aorta valve opens and the blood comes into the aorta, from here, blood is sent to different parts of the body with the help of various arteries.
- By the contraction of the right ventricle, blood reaches the lungs through pulmonary arteries where it gets reoxygenated.
[Question: 874203]
Heartbeat
- Rhythmic contraction and expansion of the heart is called heartbeat. Contraction and expansion occur separately in the atria and ventricles.
- Heartbeat in humans is 72 times in one minute.
- Each heartbeat has two components, systole, and diastole. Systole represents contraction while diastole represents expansion or distension of heart chambers.
Blood
Blood is an important fluid conducting fluid , which transports the materials to different body parts. In other words, the fluid that circulates in the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins of a vertebrate animal carrying nourishment and oxygen to and bringing away waste products from all parts of the body.
Composition of Blood
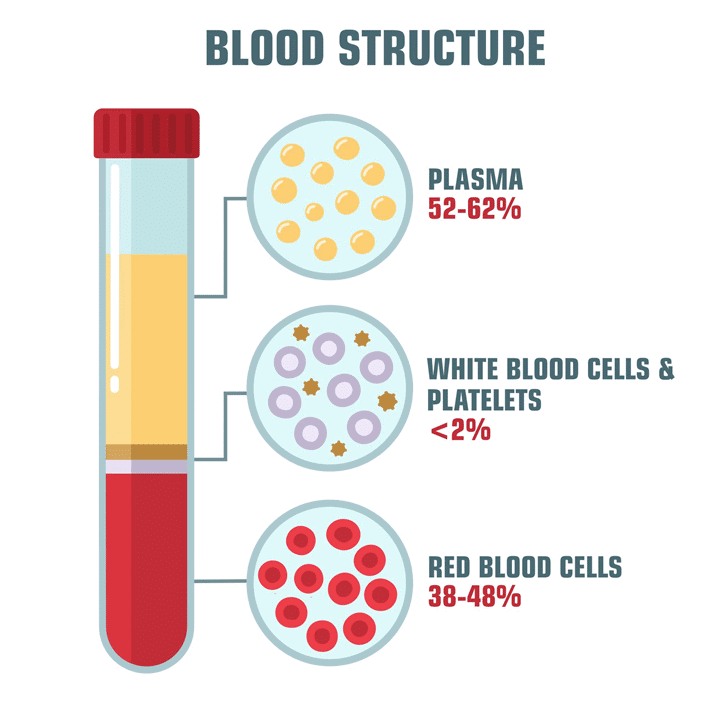 Liquid part - Blood plasma
Liquid part - Blood plasma
Solid part - Blood cells (corpuscles) - (RBC's, WBC's and Platelets)
Blood Corpuscles
- They form 45% part of blood.
- Red Blood Cells (RBC)
- White Blood Cells (WBC)
- Platelets
Plasma
- It composes 55% of blood.
- The plasma has 90-92% water and the remaining 8% -10% are other materials.
- The plasma is a faint yellow viscous fluid.
- Plasma contains some soluble proteins (serum albumin, serum globulins, prothrombin, and fibrinogen), inorganic salts, food materials, waste products, dissolved gases, anticoagulants, and antibodies.
Functions of Blood Plasma
- Transportation of nutrients, respiratory gases, excretion of wastes and hormones of endocrine glands.
- Prothrombin and fibrinogen plasma proteins help in blood clotting at injuries.
- Globulins of blood plasma act as antibodies and provide immunity (disease resistance) to the body.
- Plasma also helps in the transportation of minerals like iron, copper etc.
[Question: 874205]
Functions of Blood
- Transportation of oxygen from lungs to tissues.
- Transportation of carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs.
- Transportation of excretory material from the tissues to the kidneys: Some of the chemical activities in the body form nitrogenous end products, like urea, that are poisonous. These substances diffuse into the capillaries and are carried by plasma. When they eventually reach the kidneys, a large proportion of them is removed and excreted.
- Transportation of digested food from the small intestine to the tissue.
- Distribution of hormones and enzymes.
- Formation of clots to prevent blood loss.
- Distribution of heat and temperature control: Muscular and chemical activities release heat. The heat so produced is distributed locally all around the body by the blood and in this way, an even temperature is maintained in all body regions.
- Prevention of infection and wound healing: WBCs in the blood help in wound healing. Bacteria are destroyed by the WBCs before they can enter the general circulation. Also, the WBCs provide a defence to the body against disease germs and foreign substances.
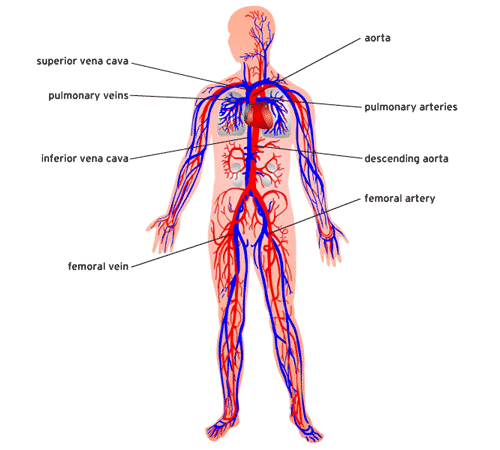
Blood vessels
In humans, three types of blood vessels are present.
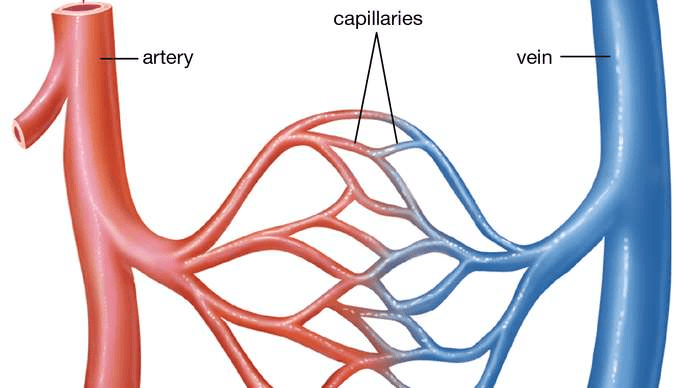
1. Arteries: The vessels which carry blood from the heart to various organs of the body.
2. Veins: They collect the blood from different parts of the body and pour it into the heart.
3. Capillaries: These are the smallest blood vessels and one-cell thick.
The major differences between various blood vessels have been given in Table.
Comparative Study of Blood Vessels
| S. No. | Features | Arteries | Veins | Capillaries |
| 1 | Direction of blood flow | Take the blood away from heart to different parts of body. | Bring the blood towards the heart from various body parts. | Blood flows from arterioles (capillaries) to venules. |
| 2 | Kind of blood | Oxygenated blood except in pulmonary artery. | Deoxygenated blood except in pulmonary vein. | Blood changes from oxygenated to deoxygenated. |
| 3 | Blood pressure | Pressure is high | Pressure is low. | Pressure is extremely low |
| 4 | Blood flow | Blood flows rapidly with jerks. | Blood flows smoothly without jerks. | Blood flows smoothly without jerks. |
| 5 | Lumen | Narrow | Wide | Very small |
| 6 | Semilunar valves | Absent | Present | Absent |
| 7 | Location | Mostly deep seated. | Mostly superficial. | Form a network all over the body and in the organs. |
Lymph
- Lymph, also known as tissue fluid, is a vital part of the circulatory system that works alongside blood to transport essential substances throughout the body.
- Unlike blood, which flows through veins and arteries, lymph is a clear, colorless fluid that forms when plasma, proteins, and a few blood cells escape from capillaries into the spaces between cells.
- This fluid, rich in nutrients but with less protein than plasma, drains into tiny lymphatic capillaries that merge into larger vessels.
- These vessels eventually connect with the veins, allowing the lymph to return to the bloodstream.
- Lymph plays a crucial role in the body's defense mechanisms and the maintenance of fluid balance. It carries digested fats from the intestines to the blood and helps in draining excess fluid from the extracellular spaces, preventing swelling and maintaining a stable internal environment.
FAQs on Transportation in Human Beings: Circulatory System & The Human Heart - Class 10
| 1. What is the primary function of the human circulatory system? |  |
| 2. How does the heart function as a pump in the circulatory system? |  |
| 3. What are the major components of the human circulatory system? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between arteries and veins? |  |
| 5. How does the circulatory system contribute to maintaining homeostasis? |  |