Nature and Definition of Torts | Daily GK & Current Affairs Tests - Bank Exams PDF Download
Introduction
Law is a set of rules that governs how people behave in society. The Law of Torts is a branch of law that focuses on regulating people's behavior and defining individual rights and duties based on what is considered reasonable and in the interest of public welfare. It aims to provide financial compensation for violations of individual rights. The foundation of the Law of Torts is the principle that no one has the right to harm another person, whether intentionally or unintentionally.
What is a Tort?
A tort is a type of wrong done to someone that the law recognizes as unfair. It’s not a crime or a broken promise, but a civil (private) issue where one person harms another, and the law steps in to help fix it, usually by making the wrongdoer pay money (called damages).
Meaning of a Tort
In simple terms, a tort happens when someone does something (or fails to do something) that causes harm or loss to another person. For example, if someone spreads lies about you and ruins your reputation, that’s a tort. The law says the person who caused the harm must make up for it, usually by paying money to the victim.
Definitions by Famous Scholars
Some important legal experts have explained what a tort is in their own words. Here’s what they say in simple language:
1. Winfield’s : A tort is when someone breaks a rule (or duty) that the law says everyone must follow, and this causes harm. This rule isn’t part of a contract (like a promise), and the person harmed can ask the court for help, usually to get money as compensation.
Example: If a driver carelessly hits your car, they broke a duty to drive safely. That’s a tort, and you can ask for money to fix your car.
2. Salmond’s: A tort is a civil (private) wrong where the person harmed can go to court and ask for money to make up for their loss. This money isn’t fixed in advance (called unliquidated damages), and the wrong isn’t just about breaking a contract or a trust.
Example: If someone locks you in a room without reason (false imprisonment), that’s a tort. You can ask the court for money to make up for the harm.
3. Fraser’s: A tort is when someone violates your legal rights (like your right to be safe or your reputation) in a way that affects you personally, and you can ask the court for money to compensate for the harm.
Key Elements of a Tort
 For something to be called a tort, it must have these four things:
For something to be called a tort, it must have these four things:- Civil Wrong: It’s a private wrong between two people, not a crime against society. For example, if someone damages your property, it’s a tort, not a crime like theft.
- Breach of Duty: The person who caused the harm didn’t follow a rule or duty that the law expects them to follow. For example, everyone has a duty to drive carefully.
- Harm or Injury: The victim must have suffered some kind of loss or harm, like physical injury, emotional distress, or damage to property or reputation.
- Remedy: The law provides a way to fix the harm, usually by making the wrongdoer pay money (damages) to the victim.
Quick Tip: Think of a tort as a situation where someone’s actions (or inaction) unfairly hurt another person, and the law steps in to make things right by giving the victim compensation.
Nature of Torts
The "nature" of torts tells us what torts are, how they differ from other wrongs, and why they exist. Torts are about fixing harm caused by one person to another in a private dispute. They focus on helping the victim, not punishing the person who caused the harm.
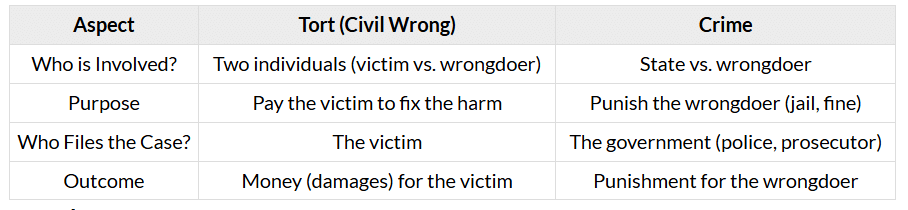
Civil Wrong vs. Criminal Wrong
Torts are civil wrongs, meaning they are private issues between individuals (like you and your neighbor). Crimes, on the other hand, are wrongs against society, and the government steps in to handle them.
Key Differences
Unliquidated Damages
In torts, the victim gets money called damages to make up for their loss. These are unliquidated damages, meaning the amount isn’t fixed in advance. The court looks at the harm (like medical bills or emotional pain) and decides how much money is fair.
Torts as a Developing Area of Law
Tort law keeps growing to handle new kinds of harm as the world changes. For example, new technology brought cyber torts (like online bullying or hacking), and environmental issues led to environmental torts (like pollution harming people or property).
CLAT PG Tip: Be ready to give examples of modern torts (like cyber or environmental) in case-based questions.
Objectives of Tort Law
Tort law has three main goals to make things fair:
- Compensate the Victim: Pay money to cover the victim’s losses, like medical bills or broken property.
- Restore Their Position: Help the victim get back to where they were before the harm, as much as possible (e.g., fix their car or reputation).
- Deter Wrongful Conduct: Warn people to be careful by making wrongdoers pay, so others avoid similar mistakes.
Essential Characteristics of Torts
The essential characteristics of torts are the key features that make something a tort. For an incident to be considered a tort, it must have these five elements. These are like the ingredients needed to call something a tort in the eyes of the law.
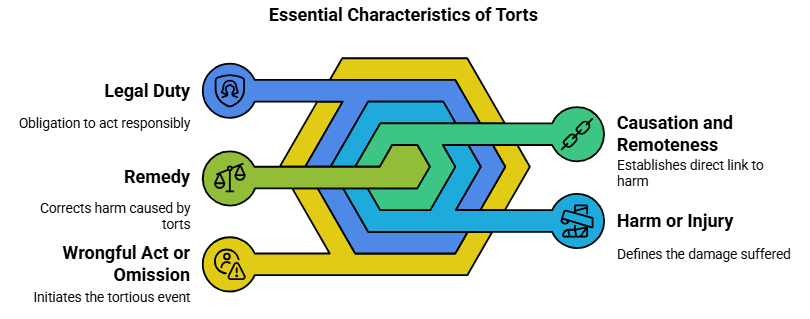
1. Wrongful Act or Omission
A tort starts with a wrongful act (doing something wrong) or omission (failing to do something you should). This act or failure must break a legal rule or duty that the person was supposed to follow.
Example: If a shopkeeper leaves a wet floor without a warning sign and someone slips, that’s an omission (failing to warn). If someone intentionally pushes you, that’s a wrongful act. Both can be torts.
2. Legal Duty
The person who caused the harm (the defendant) must have had a legal duty to act carefully toward the person who was harmed (the plaintiff). This duty is something the law expects, like being careful while driving or keeping your property safe.
Example: A driver has a legal duty to follow traffic rules to keep others safe. If they speed and hit someone, they’ve breached that duty, which can lead to a tort.
3. Harm or Injury
The plaintiff (the person harmed) must suffer some kind of harm or injury. This could be physical (like a broken arm), emotional (like stress or fear), economic (like losing money), or reputational (like harm to your good name).
Example: If someone spreads lies about you and you lose your job, that’s reputational and economic harm. If you fall because of a broken staircase, that’s physical harm. Both can be torts.
4. Causation and Remoteness
The wrongful act must cause the harm, and the harm must not be too remote (too far removed from the act). This means the act must directly lead to the harm, and the harm must be something that could reasonably happen because of the act.
Example: If a driver runs a red light and hits you, causing a broken leg, the act (running the light) caused the harm (broken leg). But if you later catch a cold in the hospital, that’s too remote to be part of the tort.
5. Remedy
The law provides a remedy to fix the harm, usually by making the wrongdoer pay money (damages). Sometimes, the court might order other remedies, like an injunction (stopping the wrongdoer from doing something) or specific restitution (returning something taken).
Example: If someone damages your car, the court might order them to pay for repairs (damages). If a neighbor keeps trespassing on your land, the court might issue an injunction to stop them.
Distinction Between Tort and Other Laws
A tort is a civil wrong, but it’s different from other legal concepts like crimes, contracts, quasi-contracts, and trusts. Understanding these differences helps you identify what kind of legal issue you’re dealing with and what the law can do about it. For CLAT PG, this topic is crucial because questions often ask you to compare torts with other laws or identify the correct legal category for a situation.
Tort vs. Crime
Torts and crimes both involve wrongs, but they are handled differently because they affect different parties and have different goals.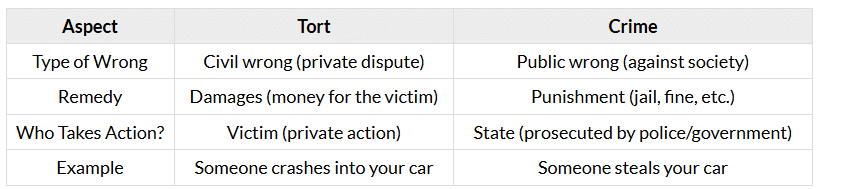
Tort vs. Contract
Torts and contracts both involve duties, but the source of the duty and how they’re enforced are different.
Key Differences
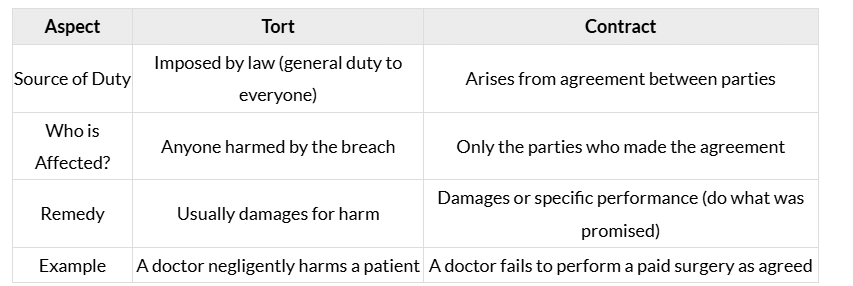
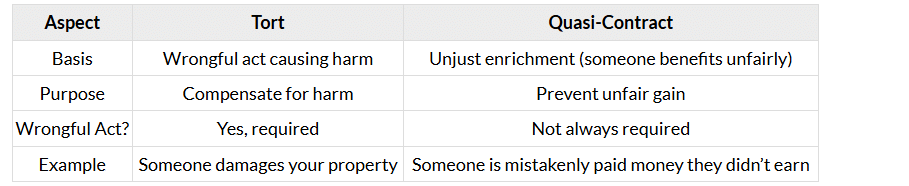
Tort vs. Quasi-Contract
Torts and quasi-contracts both involve civil remedies, but they deal with different kinds of problems.
Key Differences
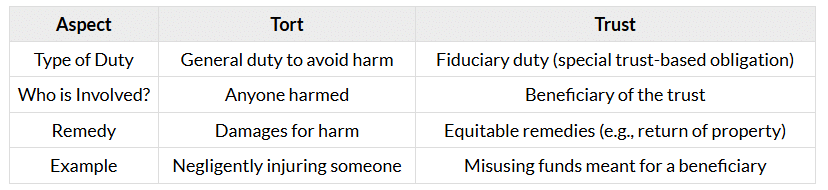
Tort vs. Trust
Torts and trusts both involve duties, but they apply in very different situations.
Key Differences
Foundational Principles of Tort Law
The foundational principles of tort law are the core ideas that explain how tort law works and why it exists. These principles help courts decide when someone deserves compensation for harm and ensure fairness. For CLAT PG, understanding these principles is key because they often appear in case-based questions or theoretical discussions.
Principle 1: Ubi Jus Ibi Remedium

- Example: If someone enters your property without permission (violating your right to privacy), the law can make them pay you money, even if they didn’t cause any damage.
- Case: Ashby v. White (1703)
A voter was wrongfully stopped from voting, violating his legal right. The court awarded him damages even though he suffered no actual loss, showing that a remedy exists for every right violated.
Principle 2: Injuria Sine Damno vs. Damnum Sine Injuria
This principle explains when you can (or cannot) get a remedy in tort law, based on whether a legal wrong or actual damage occurred.
1. Injuria Sine Damno
Injuria Sine Damno means a "legal wrong without damage." If someone violates your legal right but you don’t suffer any actual harm (like loss of money or injury), you can still get a remedy (usually money) because your right was violated.
- Example: If someone walks across your land without permission (trespass), they’ve violated your right to your property. Even if they didn’t damage anything, you can sue them for a small amount of money.
- Case: Ashby v. White (1703)
The voter’s right was violated without any physical or financial harm, but the court gave him a remedy because a legal wrong occurred.
2. Damnum Sine Injuria
Damnum Sine Injuria means "damage without a legal wrong." If you suffer harm (like losing money) but no legal right was violated, you cannot get a remedy in tort law.
- Example: If a new shop opens next to yours and takes your customers, you lose money, but they haven’t broken any legal rule (it’s just competition). You can’t sue them for this loss.
- Case: Gloucester Grammar School Case
A school lost students because a rival school opened nearby. The court said there was no tort because no legal right was violated, even though the school suffered financial harm.
Principle 3: Fault-Based Liability
Most torts require proof of fault, meaning the person who caused the harm acted intentionally, negligently, or recklessly. However, some torts don’t need fault and are based on strict liability (liable even without fault) or absolute liability (liable with no exceptions).
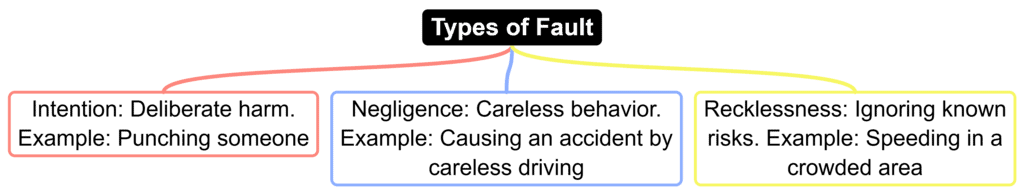
Exceptions: Strict and Absolute Liability
- Strict Liability: The person is liable for harm even if they weren’t at fault, as long as certain conditions are met (e.g., keeping dangerous things like explosives).
- Absolute Liability: The person is liable no matter what, with no defenses allowed (e.g., hazardous industries in India).
A man was held liable for water escaping from his reservoir and damaging a neighbor’s property, even without fault, under the rule of strict liability.
In India, a company was held liable for a gas leak under absolute liability because it was a hazardous activity, with no defenses allowed.
Types of Torts
Torts are civil wrongs that cause harm, and they can be grouped into different types based on how the harm happens and who is responsible. Understanding these types helps you identify what kind of tort is involved in a situation and what rules apply. For CLAT PG, this topic is important because questions often ask you to classify a tort or apply a specific type to a case.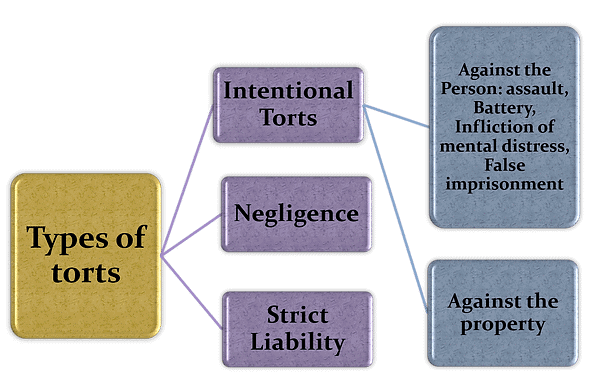
1. Intentional Torts
Intentional torts happen when someone deliberately does something to harm another person or their property. The person meant to cause the harm or knew it was likely to happen.
Common Examples of Intentional Torts
- Assault: Threatening to harm someone, making them fear for their safety (e.g., raising a fist to scare someone).
- Battery: Physically harming someone by touching them without consent (e.g., hitting someone).
- False Imprisonment: Locking someone up or restricting their freedom without a legal reason (e.g., locking someone in a room).
- Defamation: Spreading lies about someone that harm their reputation (e.g., falsely saying someone is a thief).
- Trespass: Interfering with someone’s person, land, or goods without permission (e.g., entering someone’s house or taking their phone).
2. Negligence-Based Torts
Negligence-based torts happen when someone fails to be careful enough (exercise reasonable care) and accidentally causes harm. They didn’t mean to hurt anyone, but their carelessness led to the harm.
Key Elements of Negligence
- A duty to be careful (e.g., drivers must drive safely).
- Breaching that duty (e.g., texting while driving).
- Causing harm because of the breach (e.g., hitting someone’s car).
A woman got sick after drinking a bottle with a snail in it. The court said the manufacturer was negligent for not ensuring the product was safe, establishing the modern law of negligence.
3. Strict Liability Torts
Strict liability torts hold someone responsible for harm even if they weren’t careless or didn’t mean to cause it. This applies to dangerous activities or things where the risk is high, and the law says the person must take full responsibility.
Common Examples
- Keeping dangerous animals (e.g., a lion that escapes and attacks someone).
- Storing dangerous things (e.g., explosives or water that escapes and causes damage).
Water escaped from a reservoir and damaged a neighbor’s property. The owner was held liable under strict liability because storing water was a dangerous activity.
4. Absolute Liability
Absolute liability is like strict liability but stricter. It applies to extremely hazardous activities, especially in India, where the person is liable for any harm caused, with no defenses allowed (not even if they took all precautions).
A gas leak from a factory harmed people. The court said the factory was liable under absolute liability because it was a hazardous activity, with no defenses allowed.
Key Case Laws in Tort Law

International Case Laws
1. Ashby v. White (1703)
- Facts: A voter was wrongfully prevented from voting by an official. He didn’t suffer any actual harm (like losing money), but his legal right to vote was violated.
- Principle: Established Injuria Sine Damno (legal wrong without damage). If a legal right is violated, the victim can get a remedy (usually money) even if no actual harm occurred.
- Outcome: The court awarded damages to the voter because his right was violated, even without any loss.
2. Gloucester Grammar School Case
- Facts: A school lost students and money because a rival school opened nearby, offering better services. The first school suffered financial harm but no legal right was violated.
- Principle: Established Damnum Sine Injuria (damage without legal wrong). If you suffer harm but no legal right is broken, you can’t get a remedy in tort law.
- Outcome: The court refused to award damages because the rival school’s actions were lawful competition.
3. Rylands v. Fletcher (1868)
- Facts: A man built a reservoir on his land, but water escaped and flooded a neighbor’s property, causing damage. He wasn’t careless, but the activity was dangerous.
- Principle: Introduced the rule of strict liability. If you keep something dangerous (like water or chemicals) on your land and it escapes, causing harm, you’re liable even if you weren’t at fault.
- Outcome: The court held the man liable because the reservoir was a risky activity.
4. Donoghue v. Stevenson (1932)
- Facts: A woman drank ginger beer from a bottle with a dead snail inside, which made her sick. She hadn’t bought the bottle herself, so there was no contract, but the manufacturer was careless.
- Principle: Established the modern law of negligence and the neighbor principle: You owe a duty of care to anyone who might be harmed by your actions (your “neighbor”).
- Outcome: The court held the manufacturer liable for negligence because they failed to ensure the product was safe.
Indian Case Laws
1. M.C. Mehta v. Union of India (1987)
- Facts: A factory in Delhi leaked harmful gas, injuring people and causing environmental damage. The factory was engaged in a hazardous activity.
- Principle: Introduced absolute liability in India. For extremely dangerous activities (like handling toxic chemicals), the person is liable for any harm caused, with no defenses allowed, even if they were careful.
- Outcome: The court held the factory liable and ordered compensation, emphasizing that hazardous industries bear full responsibility.
2. Indian Medical Association v. V.P. Shantha (1995)
- Facts: A patient suffered due to a doctor’s negligence in a medical procedure. The question was whether medical services could be covered under tort law and consumer protection laws.
- Principle: Established that medical negligence is a tort and that doctors can be held liable for failing to meet the standard of care. It also brought medical services under the Consumer Protection Act.
- Outcome: The court ruled that patients could sue doctors for negligence and seek compensation under tort law or consumer laws.
Conclusion
The Law of Torts is essential for ensuring fairness in society by addressing wrongs that individuals commit against one another. It provides a mechanism for victims to seek compensation for harm caused by wrongful acts, whether intentional or negligent. The principles of tort law, such as Ubi Jus Ibi Remedium (where there is a right, there is a remedy) and the differentiation between Injuria Sine Damno (legal wrong without damage) and Damnum Sine Injuria (damage without a legal wrong), highlight the importance of legal rights and the need for remedies. As society evolves, tort law continues to adapt to new challenges, ensuring that justice is accessible and that individuals are held accountable for their actions. Understanding these concepts is crucial for navigating legal disputes and upholding individual rights.
|
57 docs|861 tests
|
FAQs on Nature and Definition of Torts - Daily GK & Current Affairs Tests - Bank Exams
| 1. What is the statutory definition of 'Tort' in India? |  |
| 2. How do torts differ from crimes in legal terms? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between a tort and a breach of trust? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the distinction between tort and quasi-contract? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of torts commonly recognized in law? |  |





















