Enviornment: Meaning and Scope | Environmental Law - CLAT PG PDF Download
Introduction
The environment has everything to meet the needs of the individual and not the desire, first unit under the Environmental law helps us to understand the concept of the environment. Since from the ancient times efforts for protection of the environment are found now and then, as an evidence for such efforts there are writings in the Vedas and Upanishads clearly depicts the idea of environment. Change of times did make an impact on environment; the efforts in modern times do follow the golden thread with a change in the perspectives. Environment and development are two paradoxical situations which needs a balance from both the sides.
Sustainable development is the core concept in modern times for protection of environment and keeps up the pace of development. Environment in broader terms includes each and everything in the ecosystem and their relationship between each other. Development signifies change in the way of life without affecting the ambience around. Sustainable Development speaks the essence of balancing the needs of present and future generations, national and international perspectives clearly helps us to understand the idea of protection of the environment and to give preference on development without altering the purpose and essence of which it is built.
Idea of Environment
- Environment denotes totality of all extrinsic, physical and biotic factors affecting the life and behavior of all living things. It is important that the environment of which land, water, air, human beings plants and animals are the components be preserved and protected from degradation to enable maintenance of the ecological balance. The word "Environment" is derived from the French word "Environmer", means encircle and encompasses within it the land, water, flora, fauna, living creatures, forests and everything on the earth.
- Environment or ecology plays a crucial part in men 's life as well as in the growth and progress of civilization. Industrialization and ever-growing technological development has caused damage to the environment to an alarming extent. The protection of environment is now so fundamental that it must be answered before it is too late it is now pertinent to take some concrete step in order to protect the very existence of mankind and other forms of life on planet earth, the question of protection of environment is so important that it is regarded as a Human Right around the world.
- The term "Environment" is very broad and comprehensive. It is sum of various phenomenons the dynamism of this term defines its scope. On one hand, it is taken to mean that everything in our surrounding on the other hand the entire huge planet. A lot of attempt has been made to define Environment through various national and International instruments. Generally, environment comprises of natural resources, external conditions, stimuli etc., with which a living creature interrelates. The Preamble of the UN Declaration on Human Environment states that: "Man is both creature and moulder of his environment, which gives him physical substance and affords him the opportunity for intellectual, moral, social and spiritual growth"
Environment is clearly Defined under Section 2 (a) of the Environment (Protection) Act 1986 defines:
- Environment:"Environment includes water, air and land and the inter-relationship which exists among and between water, air and land and human beings, other living creatures, plants, micro-organism and property".
- "Environmental Pollution"means the presence in the environment of any environmental pollution'. "Environmental pollutant"means any solid, liquid or gaseous substance present in such concentration as may be, or tend to be, injurious to environment.
Ancient & Medieval Writings
- Environment protection is not a new concept for Indians. It has been 6000 years old tradition for us; it was the "Dhrama" for each individual in the society for protection of nature. The five important elements of nature called "Panchabhootas" were the divine incarnation for us. Natural resources management was given major importance in ancient India like conservation of water bodies, Protection of forests,& wildlife were considered to be the important aspects of governance by the rulers and local people. Punishments were prescribed for causing injury to plants.
- According to evidences in Vedas and Kautilya's Arthasasthra, different dynasties accorded top priority to environmental protection and sustainable use of its components. All of the tree parts were considered important and sacred and Kautilya fixed punishments based on the destruction of the specific part of the tree, some of the important trees were even elevated to the position of God. The Rig-Veda establishes the symbolism of this close kinship when it says: 'Heaven is my father; my mother is this vast earth, my close kin. Atharva-Veda contains the hymn - Bhumi Sukta — in praise of the earth and invokes a balance: upon the immutable, vast earth supported by the law, the universal mother of the plants, peaceful and kind, may we ever walk for ever.
- In Mahabharata, in the Bhisma Parva, refers to the earth as an 'ever-yielding cow' provided its resources are developed and managed with balance and control: 'if Earth is well looked after, it becomes the father, mother, children, firmament and heaven, of all creatures.
- The Rig Veda does mandates about Cow slaughter is a heinous crime equivalent to a human murder and those who commit this crime should be punished. Protection of animals and plants are clearly depicted in the ancient times, following image clearly depicts what was the effort then and how to comply with the same.
The history of environmental protection in India can be studied under the following headings, the efforts made for protection of environment and the punishment so emphasized.
- In Ancient Period
- In Medieval Period
- The Post-Independence period
Environmental Protection in Ancient Period
- Forests, Wildlife and more particularly trees were held in high esteem and held a place of special reverence in Hindu theology. The vedas, Puranas, Upanishads and other scriptures of the Hindu religion gave a detailed description of trees, plants and wildlife and their importance to the people.
- The Rig Veda highlighted the potentialities of nature in controlling the climate, increasing fertility and improvement of human life emphasizing for intimate kinship with nature.
- During the Vedic period,cutting of live trees was prohibited and punishment was prescribed for such acts. In Srimad Bhagavatam, it has been rightly pointed out that a man who with exclusive devotion offers respect to sky, water, earth, heavenly bodies, living beings, trees, rivers and seas and all created beings and considers them as a part of the body of the Lord attaints the state of supreme peace and God's grace. Yajnavalkya smriti has declared cutting of trees and forests as a punishable offence.
- The Sages and Saints of India lived in forest. In the history, people attitude towards plants, trees, sky, air, water, and animals was to keep a sympathetic attitude towards them. Hindu religion instructed man to show reverence for presence of spirituality in nature. The flora and fauna, hills, mountains, rivers are worshiped as symbols of veneration. The cutting of trees, polluting air, water, and land were regarded as sins and they were to be respected as associated with gods and goddesses. India possesses a great-diversified ecosystem including forests, wetlands, islands, estuaries, parks, landscapes, oceans and rich blend of variety of natural surroundings. Many customary or community practices were evolved by the ancestors to protect the environment. The efforts of the people in local community in conservation of natural resources quite deserve to eulogize.
- In consequence to rapid industrialization, sophisticated science and technological advancement, increased population, urbanization, deforestation, indiscriminate utilization of natural resources etc., the traditional practices to preserve and conserve natural resources have not been taken seriously by the people in modern times which have resulted in environmental degradation. The phenomenon of environmental protection is not a new concept to the human civilization. The efforts of people in ancient times for improving the environment can be traced out from early Indian history. Indians have understood the complete significance of environment for their survival on earth. It was considered that the primary duty of the individual is to protect the nature. The people used to worship the gods and goddesses associated with their objects of birds and animals. Hinduism said to be dealt with various aspects of nature and ways of worshipping the nature.
- It appears that the civilization of Mohenjodaro, Harappa and Dravidian civilization lived in consonance with its ecosystem and their small population and their needs maintained the harmony with the environment. The Mauryan period was perhaps the most glorious chapter of the India. It was in this period that we find detailed and perceptive legal provisions found in kautalaya's Arthashastra written between 321 B.C. and 300 B.C.
Hindu Mythology on Environment Protection
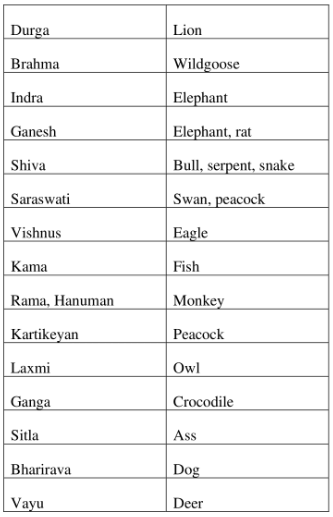
Hindu religion is one of the oldest religions of the world. Ever since Vedic times, the main motto of social life was to have in harmony with the nature. Sages, saints and the great philosophers of India lived in forest and on mountains where they meditate and expressed in to form, of Vedas, Upanishads and Smriti.Accordingly felling of trees, polluting air, water and desert land was regarded as sin as these were to be respected and regarded as God and Goddesses. Some of the trees associated with the Gods and Goddesses.
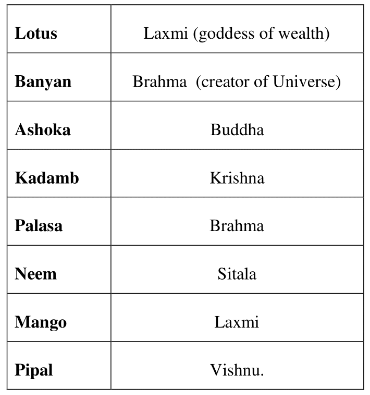
Planting of trees was also treated as sacred religious duty and work of great virtue and regarded one tree to equal ten sons. One who plant one pipal, one neem, one ber, ten flowering plants creepers, two pomegranates, two oranges and five mango trees will not go to hell. Similarly, several Hindu Gods and Goddesses have animals and birds as their associates.
Environmental Protection in Medieval India
- From the point of view of environment conservation, a significant contribution of Moghul emperors has been the establishment of magnificent gardens, fruit orchards and green park, round about their places, central and provincial headquarters, public places, on the banks of rivers and in the valley and dales which they used as holiday resorts or places or temporary headquarters during the summer season.
- Among the officials empowered for administration of justice by the sultans and the emperors of India,Muhtasibs' were vested with the duty of prevention of pollution. Main duty among others was to remove obstructions from the streets and to stop the commission of nuisance in public places.
- The instructions were given to a newly appointed muhtasib by the emperor Aurangazed throws a flood of light on the functions of this officer. In the bazaars and lanes observe if anyone, contrary to the regulations and customs has screened off a part of the street, or closed the path or thrown dirt and sweepings on the traffic and opened his shops, there you should in such cases urge them to remove the violation of regulations.
Environmental Protection During the Post-Independence Era
- The post-independence era witnessed a lot of changes in the policies and attitudes of the Governments with respect to environmental protection.
- Under the constitution various provisions directly or indirectly deals with environmental protection.
|
39 docs|15 tests
|
FAQs on Enviornment: Meaning and Scope - Environmental Law - CLAT PG
| 1. What is the definition of environment in the context of ancient and medieval writings? |  |
| 2. How did ancient civilizations approach environmental protection? |  |
| 3. What role does Hindu mythology play in environmental protection? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the environmental protection practices in medieval India? |  |
| 5. What are the key components of the environment as discussed in the article? |  |
















