Definition of Administrative Law | Administrative Law - CLAT PG PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Growth of Administrative Law |

|
| Reasons for Growth of Administrative Law |

|
| Emergence of Global Administrative Law |

|
| Definitions of Administrative Law |

|
Growth of Administrative Law
Administrative law is considered one of the most significant legal developments of the 20th century. Although present before the 20th century, it has become more defined and distinct in democratic countries during this time.

- Administrative law has grown in response to the increasing powers and functions of the state, moving from a minimal role focused on law and order to a welfare state involved in various aspects of social and economic life.
- The shift from alaissez-faireapproach to a welfare state has expanded the role of the government, leading to a rise in administrative functions.
- Administrative law has evolved to address the changing needs of society, including urbanization, emergency situations, and the demand for speedy dispute resolution.
- The growth of administrative law reflects the need for efficient governance in a complex and rapidly changing society.
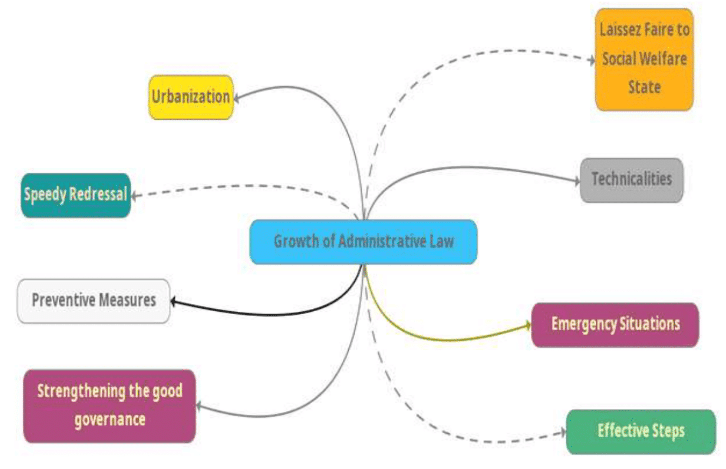
Reasons for Growth of Administrative Law
- Laissez Faire to Social Welfare: The role of the State has shifted from a negative policy of maintaining 'law and order' and 'laissez faire' to a positive policy of welfare. The State now performs a variety of functions beyond traditional roles such as defense and administration of justice.
- Urbanization: Industrialization and the factory system have led to mass migration from rural to urban areas, necessitating the provision of housing, roads, parks, and effective drainage systems. This has resulted in the enactment of legislation and the establishment of administrative authorities to oversee these developments.
- Emergency Situations: In times of emergency, the process of enacting legislation and obtaining presidential assent can be lengthy. Administrative authorities can quickly frame schemes and rules to address local exigencies, contributing to the growth of administrative law.
- Speedy Disposal: The judicial system is often inadequate for resolving all types of disputes, being slow, costly, and complex. Specialized bodies like Industrial Tribunals and Labor Courts have been established to handle disputes such as strikes and lockouts more efficiently.
- Pressure on Legislature: The legislative process may lack the capacity to deal with all details and complexities. Delegating powers to administrative authorities allows for more detailed and effective rule-making.
- Experimental Nature: The administrative process allows for experimentation. Unlike legislation, rules can be made and modified quickly based on practical experience, making the administrative process more flexible.
- Avoiding Technicalities: Administrative authorities can take a functional approach, avoiding the formalities and technicalities that traditional courts must adhere to. This allows for more practical decision-making in complex cases.
- Preventive Measures: Administrative authorities can take preventive actions such as licensing and rate fixing without waiting for disputes to arise, making these measures potentially more effective than punitive actions.
- Effective Steps: Administrative authorities have the power to enforce preventive measures through actions like suspending licenses, destroying contaminated goods, etc., which are not typically available through regular courts.
- In India today, the administrative process has expanded significantly, leading to a system where people are more governed by administration than by traditional legal processes. The importance of the Rule of Law and Judicial Review has increased in this context, ensuring that the executive does not overstep its bounds and infringe upon the liberties guaranteed to citizens by the Constitution.
Emergence of Global Administrative Law
With India's shift towards liberalization, privatization, and globalization, administrative law has gained international dimensions. Despite the state stepping back from direct business involvement, its roles as a facilitator, enabler, and regulator are expanding. New centers of economic power often overlook the fundamental rights of disadvantaged groups, prompting the need for new norms of the rule of law and judicial review to balance economic growth with social justice.
Global Administrative Law
Global Administrative Law is emerging as a new branch within administrative law. This concept highlights the influence of international bodies like the WTO, which sets guidelines for various aspects of governance, including banking. As global administrative law evolves, it may necessitate a reevaluation of the foundations and growth of administrative law.
Definitions of Administrative Law
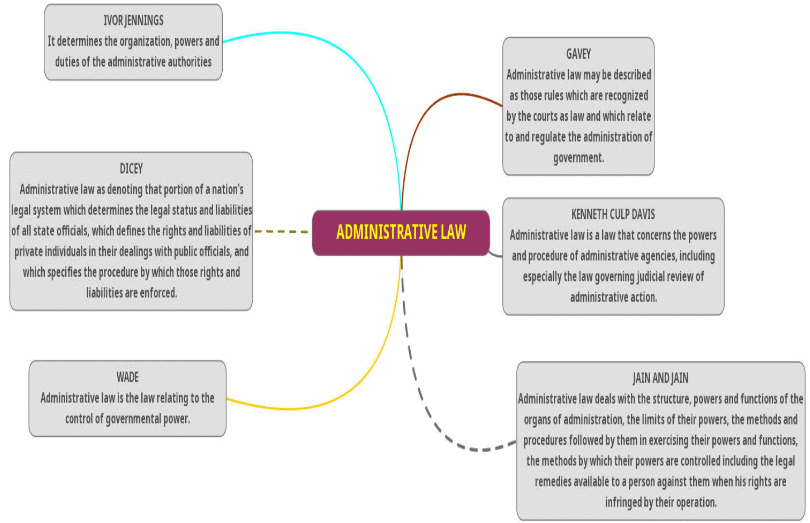
Ivor Jennings' Definition- Administrative law is seen as relating to the administration and focuses on the organization, powers, and duties of administrative authorities.
- Jennings' formulation does not differentiate between administrative and constitutional law.
- It emphasizes the organization and powers without addressing the manner of their exercise.
- For instance, administrative law concerns how a minister discharges functions, like approving a scheme for a new township, rather than how the minister is appointed.
- Jennings' definition leaves some aspects of administrative law, such as control mechanisms, unaddressed.
DICEY'S Definition
- Dicey did not recognize administrative law as independent. He viewed it as part of a nation's legal system that determines the legal status and liabilities of state officials.
- His definition focuses on the rights and liabilities of private individuals in dealings with public officials and the procedures for enforcing these rights and liabilities.
- Dicey's approach is narrow as it excludes various aspects of administrative law and emphasizes judicial remedies against state officials.
- His definition contrasts with the French concept of droit administratiff and primarily concentrates on judicial aspects, leaving out other important facets of administrative law.
American Approach to Administrative Law
- The American perspective, particularly as articulated by Kenneth Culp Davis, recognizes administrative law as a distinct branch of legal discipline.
- Davis defines administrative law as concerning the powers and procedures of administrative agencies, with a focus on judicial review of administrative actions.
- His definition includes the study of administrative rulemaking and rule adjudication but excludes rule application, which he attributes to public administration.
- While emphasizing the procedures followed by administrative agencies, Davis's definition overlooks the substantive law generated by these agencies.
- Davis views an administrative agency as a governmental authority, excluding courts and legislative bodies, that impacts the rights of private parties through adjudication or rulemaking.
- Critics argue that Davis's definition fails to encompass non-adjudicative administrative functions and places too much emphasis on judicial control while neglecting other forms of oversight, such as parliamentary control and administrative appeals.
Garner's Definition
- Garner aligns with the American perspective, defining administrative law as rules recognized by courts that govern the administration of government.
Wade's Definition
- Wade defines administrative law as the regulation of governmental power, aiming to keep government actions within legal bounds to protect citizens from abuse.
- Wade's definition emphasizes the objective of administrative law but does not clearly define the subject or address the powers, duties, and procedures of administrative authorities.
Griffith and Street's Perspective
- Griffith and Street focus on the operation and control of administrative authorities in administrative law.
- Their approach involves three key aspects: the nature of powers exercised by the administration, the limits of those powers, and the methods of containing the administration within those limits.
Indian Law Institute's Contribution
- The Indian Law Institute suggests two additional aspects for a comprehensive understanding of contemporary administrative law: the procedures followed by administrative authorities and the remedies available to individuals affected by administrative actions.
Jain and Jain's Definition
- Jain and Jain define administrative law as dealing with the structure, powers, functions, limits, methods, and procedures of administrative organs, along with the legal remedies available against them when their actions infringe individual rights.
- Their definition encompasses four aspects: composition and powers of administrative authorities, limits of their powers, procedures for exercising these powers, and control mechanisms over these authorities.
Professor Upendra Bakshi's Perspective
- Professor Upendra Bakshi emphasizes the protection of individuals from arbitrary public power in administrative law.
- He defines administrative law as the study of power pathology in a developing society, focusing on controlling abuse of power by administrative authorities to safeguard individual rights.
- There is no clear and widely accepted definition of administrative law.
- For our discussion, we can describe administrative lawas a part of public law that focuses on:
- How administrative and quasi-administrative agencies are organized.
- The powers they hold.
- The principles and rules that guide their actions.
- It looks at how official actions relate to individual rights and freedom.
- Administrative lawaims to manage both local and international administrative matters to:
- Ensure fairness.
- Enhance accountability.
- This regulation is important for achieving equity and inclusiveness in both domestic and global systems.
- In essence, administrative lawdefines:
- The structure of administrative authorities.
- The powers and responsibilities of administrative agencies.
- The rules governing how administrative actions can be reviewed by the courts.
|
35 docs|9 tests
|




















