Attorney General of India | Constitutional Law - CLAT PG PDF Download
Article 76 of the Indian Constitution delineates the vital role of the Attorney General for India, who holds the apex position in the country's legal hierarchy. This individual, often hailed as the highest-ranking legal officer, embodies unparalleled authority and expertise, guiding the nation's legal course and standing as a pillar of constitutional interpretation and advisory. Let's explore the profound significance and multifaceted responsibilities encapsulated within this eminent office.
 Attorney General of India
Attorney General of India
Appointment and Term
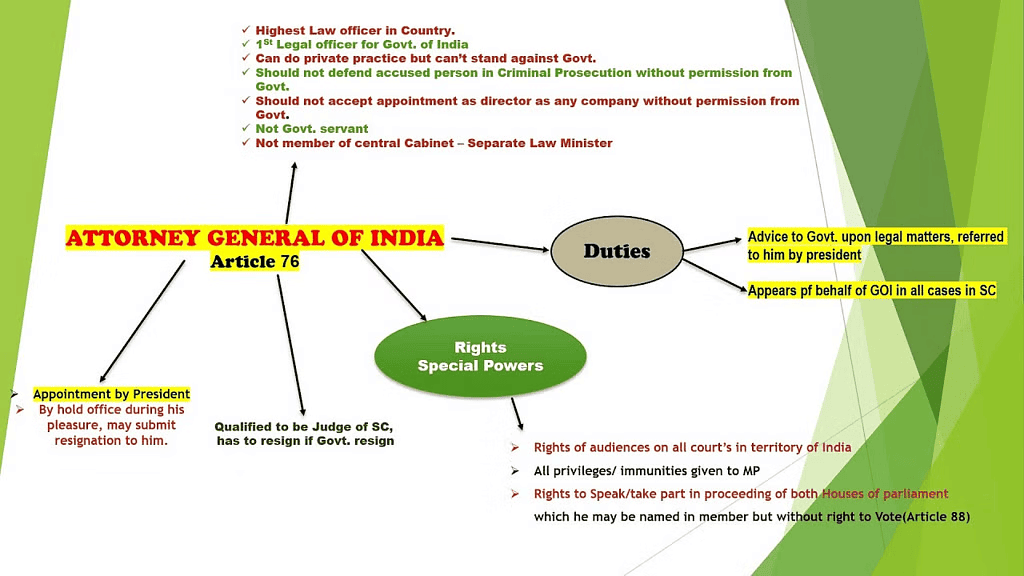
- Attorney General Appointment: Chosen by the President of India.
- Qualifications: Must be eligible to serve as a Supreme Court judge, a citizen of India, with either five years' experience as a high court judge, ten years' experience as a high court advocate, or recognised as an eminent jurist by the President.
- Tenure: Not fixed by the Constitution.
- Removal: No specified procedure or grounds for removal. Serves at the pleasure of the President and can be removed or may resign voluntarily. Often resigns when the government changes, as they're appointed based on government advice.
- Remuneration: Not constitutionally fixed; determined by the President.
Article 76 of Chapter I (The Executive) in Part V (The Union) of the Constitution deals with the office of the Attorney Genera l of India.
Duties and Functions
AG's Duties as Chief Law Officer
- Provide legal advice to the Government on referred matters.
- Execute other legal duties assigned by the President.
- Carry out functions specified by the Constitution or other laws.
Duties Assigned by the President
- Represent the Government in Supreme Court cases involving national interests.
- Act on behalf of the Government in references made by the President to the Supreme Court under Article 143 of the Constitution.
- Appear in high court cases concerning the Government's interests when required.
Rights and Limitations
AG's Rights and Privileges
- Has the right of audience in all courts across India.
- Can speak and participate in Parliament without voting rights, enjoying parliamentary privileges.
- Enjoys immunities and privileges similar to a Member of Parliament.
Limitations and Responsibilities
- Cannot advise or represent against the Government of India.
- Avoids cases where involvement with the Government of India might arise.
- Cannot defend accused persons in criminal prosecutions without government permission.
- Needs approval before taking up a directorial role in any company.
- Advice can be given only when proposals come through the Ministry of Law and Justice.
Role Clarification:
- Not a full-time government employee.
- Retains the right to engage in private legal practice.
Solicitor General of India
 Solicitor General of India
Solicitor General of India
Law Officers in the Government of India
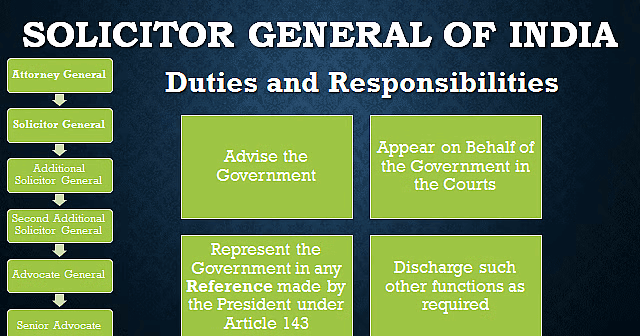
- Apart from the AG, there are the solicitor general and additional solicitor general.
- These officials assist the AG in fulfilling official responsibilities.
Constitutional Establishment
- The AG's office is the only one specifically created by the Constitution.
- The Constitution doesn't explicitly mention the solicitor general and additional solicitor general.
AG's Position in the Central Cabinet
- The AG isn't a member of the Central cabinet.
- The Central cabinet has a separate law minister who manages legal matters at the government level.
During the prime ministership of JawaharJal Nehru, a proposal was put forward by the Central government that the office of the Attorney General be merged with the office of the law minister. It did not materialise.
|
115 docs|26 tests
|
FAQs on Attorney General of India - Constitutional Law - CLAT PG
| 1. What is the role of the Solicitor General of India? |  |
| 2. How does the Attorney General of India differ from the Solicitor General? |  |
| 3. What are the qualifications required to become the Solicitor General of India? |  |
| 4. Can the Solicitor General of India represent private clients? |  |
| 5. What are the limitations of the powers of the Attorney General of India? |  |





















