UGC NET Exam > UGC NET Notes > V-Model
V-Model - UGC NET PDF Download
The V-Model, also known as the Verification and Validation Model, follows a structured and sequential approach in software development, similar to the Waterfall model. In this model, each phase of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) must be completed before moving on to the next. One distinctive feature is that testing is planned in parallel with each development phase.
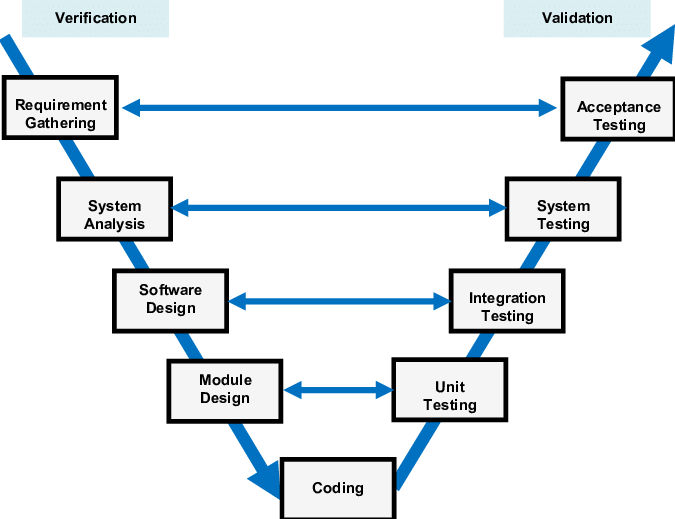
- Verification: This is a static analysis process, where the product is reviewed without running the code. It focuses on assessing whether the product development process meets the specified requirements.
- Validation: This is a dynamic analysis process that involves testing the software by executing code. The goal is to ensure the final product aligns with customer expectations and requirements after development is completed.
The V-Model is structured such that Verification phases are on one side, and Validation phases are on the other, with the coding phase connecting them in the shape of a 'V'. This structure gives the model its name.
Verification Phases in the V-Model:
- Business Requirement Analysis: This is the initial stage where the product’s requirements are understood from the customer's perspective. Detailed communication is key to accurately capturing the customer’s expectations.
- System Design: System engineers analyze the business needs of the proposed system based on the user requirements document.
- Architecture Design: In this phase, the overall system architecture is defined, detailing modules, their functionalities, interfaces, dependencies, database structures, and technology considerations. Integration testing is planned at this stage.
- Module Design: The system is broken down into smaller modules, and detailed designs for each module are created. This phase is often referred to as Low-Level Design.
- Coding Phase: After designing, coding begins. The appropriate programming language is selected, and code is written following specific guidelines and standards. The final build undergoes optimization and multiple reviews for performance before it is finalized.
Validation Phases in the V-Model:
- Unit Testing: Test plans for unit testing are developed during the module design phase. Unit testing checks that individual modules function correctly when isolated.
- Integration Testing: Test plans for integration testing are developed during the architectural design phase to ensure that independently created modules can work together.
- System Testing: System test plans are developed during the system design phase, typically by the client's business team, to verify that the application meets the intended requirements.
- Acceptance Testing: This phase corresponds to the business requirement analysis stage, testing the software in a real user environment. It checks compatibility with other systems and identifies non-functional issues such as performance and load handling.
When is the V-Model appropriate?
The V-Model is best used when the requirements are well-defined and not subject to change. It is suited for small to medium-sized projects with clearly established and fixed requirements. Additionally, the V-Model is ideal when technical resources with the necessary expertise are available.
Advantages of the V-Model:
- Easy to understand.
- Testing phases, including planning and design, occur before coding begins, which can save time and increase the likelihood of success compared to the waterfall model.
- Helps prevent defects from propagating downward.
- Effective for small projects where requirements are clearly understood.
Disadvantages of the V-Model:
- Very rigid and inflexible.
- Not suitable for complex projects.
- Software is developed only during the implementation phase, so no early prototypes are available.
- Any mid-project changes require updates to test documents and other related documents.
FAQs on V-Model - UGC NET
| 1. What is the V-Model in software development? |  |
Ans. The V-Model, or Verification and Validation Model, is a software development methodology that emphasizes a sequential path of execution of processes. It is shaped like a "V," where the left side represents the stages of development (requirements analysis, system design, architecture design, module design, and coding) and the right side represents the corresponding testing phases (unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and acceptance testing). Each development phase has a directly associated testing phase, ensuring that verification and validation are integral parts of the development process.
| 2. When is the V-Model appropriate to use in projects? |  |
Ans. The V-Model is particularly appropriate for projects with well-defined requirements and low risk of changes during the development process. It is suitable for small to medium-sized projects where requirements are clear and unlikely to evolve significantly. Additionally, it is effective in projects requiring high reliability, such as safety-critical systems in aerospace, automotive, and medical applications, where validation and verification are crucial.
| 3. What are the advantages of using the V-Model? |  |
Ans. The V-Model offers several advantages, including:
1. Clear structure: The model provides a clear and systematic approach to software development and testing.
2. Early detection of defects: Since testing phases are planned in parallel with development, defects can be identified and addressed early in the process.
3. Improved quality: The emphasis on verification and validation helps ensure that the final product meets user requirements and quality standards.
4. Easy to manage: The model is straightforward to manage due to its linear structure, making it easier to track progress and handle changes.
| 4. What are the limitations of the V-Model? |  |
Ans. The V-Model has some limitations, including:
1. Inflexibility: It is not well-suited for projects with rapidly changing requirements, as it assumes that all requirements are known upfront.
2. High dependency on initial requirements: The model relies heavily on the accuracy and completeness of initial requirements, which can be challenging to achieve.
3. Not ideal for large projects: For larger and more complex projects, the sequential nature of the V-Model can lead to difficulties in coordination and integration.
4. Limited adaptability: The model does not accommodate iterative or incremental development, making it less suitable for agile environments.
| 5. How does the V-Model ensure quality in software development? |  |
Ans. The V-Model ensures quality through its emphasis on verification and validation at each development stage. Each phase of development corresponds with a testing phase that verifies the functionality and quality of the software. For example, after coding, unit testing checks individual components, while system testing evaluates the entire system's performance. This approach allows for early detection of defects, continuous quality assurance, and ensures that the final product meets user requirements, thus enhancing overall software quality.
Related Searches


















