Unit Test (Solutions): Coal and Petroleum | Science Class 8 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
MM: 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each
Q1: Which of the following is a fossil fuel?
(i) Sunlight
(ii) Water
(iii) Coal
(iv) Wind
Ans: (iii) Coal
Coal is a fossil fuel formed from the remains of dead plants over millions of years.
Q2: The process of conversion of dead vegetation into coal is called ___________.
Ans: Carbonization
Carbonization is a process through which dead vegetation, such as plants and trees, is gradually transformed into coal over millions of years.
Q3: Which of the following is obtained from petroleum?
(i) Naphthalene balls
(ii) Natural gas
(iii) Bitumen
(iv) All of the above
Ans: (iii) Bitumen
Bitumen is obtained from petroleum and is used for road surfacing.
Q4: Natural gas is stored under high pressure as ___________.
Ans: CNG
CNG is a natural gas that is stored under high pressure in order to reduce its volume for easier storage and transportation.
Q5: Fill in the blank: Petroleum is also known as ___________.
Ans: Black gold
Petroleum is referred to as "black gold" due to its immense value and crucial role in the global economy, similar to how gold is treasured for its rarity and worth.
Q6: Why is petroleum called a fossil fuel?
Ans: Petroleum is called a fossil fuel because it is formed from the remains of ancient marine organisms that were buried under sediments and transformed over millions of years under heat and pressure.
Q7: What is coal gas, and how is it used?
Ans: Coal gas is obtained during the processing of coal to get coke. It was historically used for street lighting and is now used as a source of heat in industries.  Coal
Coal
Q8: Explain the importance of natural gas as a fuel.
Ans: Natural gas is important because it is a cleaner fuel compared to other fossil fuels, reducing pollution. It is also versatile, used in power generation, as a domestic fuel (CNG), and in the production of chemicals.
Q9: Describe the process of refining petroleum.
Ans: i) Crude Oil Heating: The crude oil is first heated in a furnace to convert it into vapor.
ii) Fractional Distillation: The heated vapor is passed into a distillation column where it cools as it rises.
iii) Separation by Boiling Points: Components with different boiling points condense at various heights in the column.
a) Lighter fractions (e.g., petrol) condense at higher levels.
b) Heavier fractions (e.g., diesel, kerosene) condense lower down.
iv) Collection: The separated components are collected, purified, and processed for use in various industries.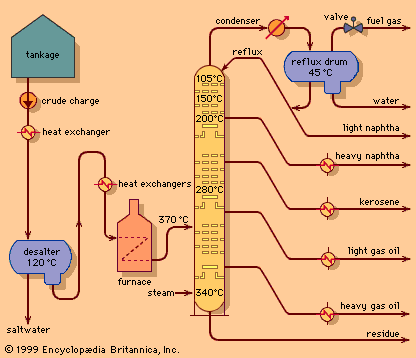
Q10: Explain the formation of coal and its types.
Ans: Formation Process:
i) Plant Decay: Dead plants in swampy areas decay and accumulate.
ii) Burial: Layers of sediment bury this organic material over millions of years.
iii) Carbonization: Heat and pressure transform the buried material into coal through carbonization.
Types of Coal:
i) Peat: The earliest stage with low carbon content.
ii) Lignite: Brown coal with higher carbon content than peat.
iii) Bituminous: Soft coal used for electricity generation, a higher carbon content than lignite.
iv) Anthracite: The hardest type, with the highest carbon content, burns the cleanest and is used in industrial applications.
Q11: Differentiate between CNG and LPG.
Ans: 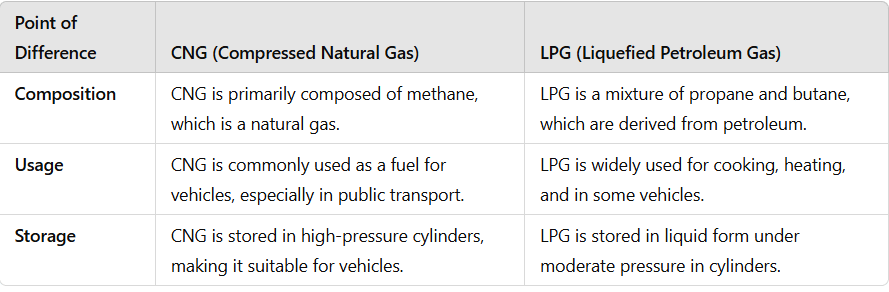
Q12: Explain the environmental impact of using fossil fuels like coal and petroleum.
Ans: The use of fossil fuels like coal and petroleum has significant environmental impacts:
Burning fossil fuels like coal and petroleum releases large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. CO2 is a major greenhouse gas that traps heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to global warming.
Fossil fuels also emit harmful pollutants such as sulphur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) when burned. These gases can react with water vapor in the atmosphere to form sulfuric and nitric acids, which then fall as acid rain.
The extraction of fossil fuels, such as mining for oil, can lead to significant habitat destruction. Forests and wildlife habitats are often cleared or disturbed, leading to a loss of biodiversity. Furthermore, the transportation of fossil fuels, particularly oil, carries the risk of spills, which can devastate marine and coastal ecosystems.
Fossil fuels are non-renewable resources, meaning they exist in limited quantities. Overuse of these resources can lead to their depletion, making them unavailable for future generations.
Leakage from fossil fuel storage facilities and transportation pipelines, as well as spills, can lead to the contamination of soil. This contamination can make the land infertile, affecting agriculture and leading to a loss of productivity.
Q13: Discuss the measures that can be taken to conserve fossil fuels.
Ans: To conserve fossil fuels, the following measures can be taken:
Increasing energy efficiency: Improving energy efficiency in homes, vehicles, and industries means using less energy to perform the same tasks, which directly reduces the demand for fossil fuels. This can be achieved through better insulation, more efficient appliances, and fuel-efficient vehicles.
Promoting alternative energy sources: Encouraging the use of renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power helps reduce dependence on fossil fuels. These alternative energy sources are sustainable and do not deplete the Earth's natural resources, making them vital for long-term energy security.
Encouraging public transportation and carpooling: Promoting public transportation and carpooling reduces the number of individual vehicles on the road, which in turn lowers the overall consumption of fossil fuels.
Reducing wastage, recycling, and using energy-efficient appliances: Reducing energy wastage and recycling materials can significantly cut down the demand for energy derived from fossil fuels.
Educating the public: Educating people about the importance of conserving fossil fuels can foster more sustainable behaviours, such as using energy more wisely and supporting policies that promote conservation.
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Coal and Petroleum - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the main differences between coal and petroleum? |  |
| 2. How is coal formed? |  |
| 3. What are the environmental impacts of using coal and petroleum? |  |
| 4. What are some alternative energy sources to coal and petroleum? |  |
| 5. How do we extract coal and petroleum? |  |

















