Unit Test (Solutions): Combustion and Flame | Science Class 8 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: Which of the following is not a combustible substance?
(i) Wood
(ii) Paper
(iii) Iron nails
(iv) Charcoal
Ans: (iii) Iron nails
Iron nails are not a combustible substance because they do not catch fire or burn easily, unlike wood, paper, and charcoal, which can easily ignite and burn.
Q2: Which of the following substances has the highest calorific value?
(i) Wood
(ii) Coal
(iii) LPG
(iv) Petrol
Ans: (iii) LPG
LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) has the highest calorific value among the options given, meaning it produces the most energy per unit when burned compared to wood, coal, and petrol.
Q3: The substance which catches fire easily and has a very low ignition temperature is called __________.
Ans: Inflammable substance
The substance which catches fire easily and has a very low ignition temperature is called an inflammable substance.
Q4: The lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire is called __________.
Ans: Ignition temperature
The lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire is called the ignition temperature. This is the minimum temperature needed for a substance to begin burning when exposed to an open flame or spark.
Q5: Water is not suitable for extinguishing fires involving __________.
Ans: Electrical equipment
Water is not suitable for extinguishing fires involving electrical equipment because it can conduct electricity, posing a risk of electric shock to the person trying to extinguish the fire, and may also cause further short circuits or damage.
Q6: What is spontaneous combustion? Give an example.
Ans: Spontaneous combustion is the type of combustion where a material suddenly bursts into flames without the application of any apparent external cause. An example is the spontaneous combustion of coal dust in coal mines.
Q7: Why is carbon dioxide considered a good fire extinguisher?
Ans: Carbon dioxide is a good fire extinguisher because it is heavier than oxygen, forms a blanket over the fire, cutting off the oxygen supply, and thus, extinguishing the fire. Additionally, it cools down the temperature of the burning material. Fire ExtinguisherQ8: Explain why water is not used to extinguish fires involving oil or petrol.
Fire ExtinguisherQ8: Explain why water is not used to extinguish fires involving oil or petrol.
Ans: Water is not used for oil or petrol fires because oil and water do not mix, and water being heavier, sinks below the oil. This causes the oil to continue burning on top, potentially spreading the fire further.
Q9: Describe the three different zones of a candle flame.
Ans: The three zones of a candle flame are:
i) Innermost zone: It is black due to the presence of unburnt wax vapors. It is the least hot zone.
ii) Middle zone: It is yellow due to partial combustion and is moderately hot.
iii) Outermost zone: It is blue due to complete combustion and is the hottest part of the flame.
Q10: Why is LPG considered a better domestic fuel compared to wood?
Ans: LPG is a better domestic fuel because:
i) It has a higher calorific value, providing more energy per kilogram.
ii) It burns cleanly without producing smoke, reducing air pollution.
iii) It is easier to store and transport compared to wood.
Q11: What is an explosion? How is it different from rapid combustion?
Ans: An explosion is a sudden reaction involving a rapid release of heat, light, and sound with a large amount of gas.
It differs from rapid combustion as it involves a violent reaction and is often triggered by a pressure increase, while rapid combustion is a fast but controlled process.
Q12: Explain the environmental impact of using fossil fuels like coal and petroleum.
Ans: The use of fossil fuels like coal and petroleum has significant environmental impacts:
i) Global Warming: Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, contributing to global warming. This increase in atmospheric CO2 traps more heat, leading to rising global temperatures and altering weather patterns.
ii) Air Pollution: Emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides cause acid rain, which harms ecosystems and buildings. These pollutants also degrade air quality, posing risks to human health and the environment.
iii) Health Hazards: The release of unburnt carbon particles can cause respiratory issues like asthma. Prolonged exposure to polluted air can lead to chronic health problems, particularly in vulnerable populations such as children and the elderly.
iv) Oil Spills: Extraction and transportation of petroleum can lead to oil spills, damaging marine life. Oil spills can take years to clean up, with long-lasting effects on marine ecosystems and coastal economies.
v) Resource Depletion: Overuse of finite fossil fuels may lead to depletion, stressing the need for alternative energy sources. As these resources become scarcer, energy prices may rise, and economic stability could be threatened.
Q13: Differentiate between complete and incomplete combustion.
Ans: 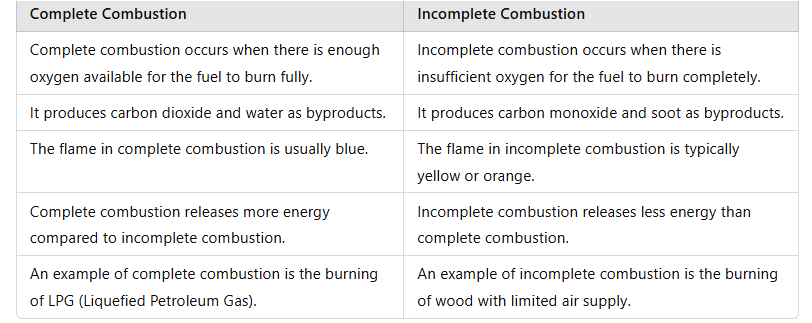
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Combustion and Flame - Science Class 8
| 1. What is combustion and how does it occur? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of flames? |  |
| 3. What is the role of oxygen in combustion? |  |
| 4. What are the products of combustion? |  |
| 5. How can we prevent fire accidents during combustion? |  |
















