Ans: Biodiversity refers to the variety of plants, animals, and other living organisms found in a particular region or ecosystem.
Q2: Fill in the blank: Plants that have soft and green stems are called ________. (1 Mark)Ans: Herbs.
Q3: Which of the following is a feature of monocot plants? (1 Mark)(i) Taproot system
(ii) Reticulate venation
(iii) Parallel venation
(iv) Two cotyledons
Ans: (iii)
Monocot plants are characterized by having parallel venation, which means that the veins in their leaves run parallel to each other. This is a key feature that distinguishes them from dicot plants, which have reticulate venation (a network of veins). Monocots also typically have a fibrous root system, one cotyledon in their seeds, and floral parts usually in multiples of three. Therefore, the correct feature of monocot plants is parallel venation.
Q4: From the members of the various groups given below, find the odd one out. (1Mark)
(a) Coriander (dhania), mint (pudina), jamun, grass.
(b) Rose, mehndi, guava, morepankh.
Ans:
(a) Jamun (Jamun is a tree while others are herbs).
(b) Guava (Guava is a tree while others are shrubs).
Ans: The change in specific features or certain habits, which enables a plant or an animal to live in its surroundings is called adaptation.
Q6: Write the adaptation in aquatic plants due to which (2 Marks)
(a) Submerged leaves can bend in the flowing water.
(b) Leaves can float on the surface of water.
Ans:
(a) Leaves are narrow and ribbon like.
(b) Stems/stalks of leaves are long, hollow and light.
Q7: Some desert plants have very small leaves whereas some others have only spines. How does this benefit the plants? (2 Marks)
Ans: Some desert plants have very small leaves whereas some others have only spines. These are adaptations to dry conditions. As a result of these modifications the surface of lamina is reduced thereby reducing water loss by transpiration.
Q8: What are the specific features present in a deer that helps it to detect the presence of predators like lion? (2 Marks)
Ans:
The specific features present in a deer that helps it to detect the presence of predators like lion are:
(a) Long ears to hear movement of predators.
(b) Eyes on the sides of its head which allow it to look in all directions
Q9: List six characteristics that can be used to classify plants.(3 Marks)
Ans:
- Height – Tall, medium, or short.
- Stem type – Hard or soft.
- Leaf venation – Reticulate or parallel.
- Root system – Taproot or fibrous root.
- Presence of flowers – Flowering or non-flowering.
- Type of habitat – Terrestrial or aquatic.
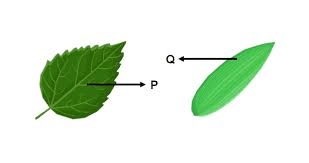
Ans: P:- Reticulate veination and Q:- Parallel Veination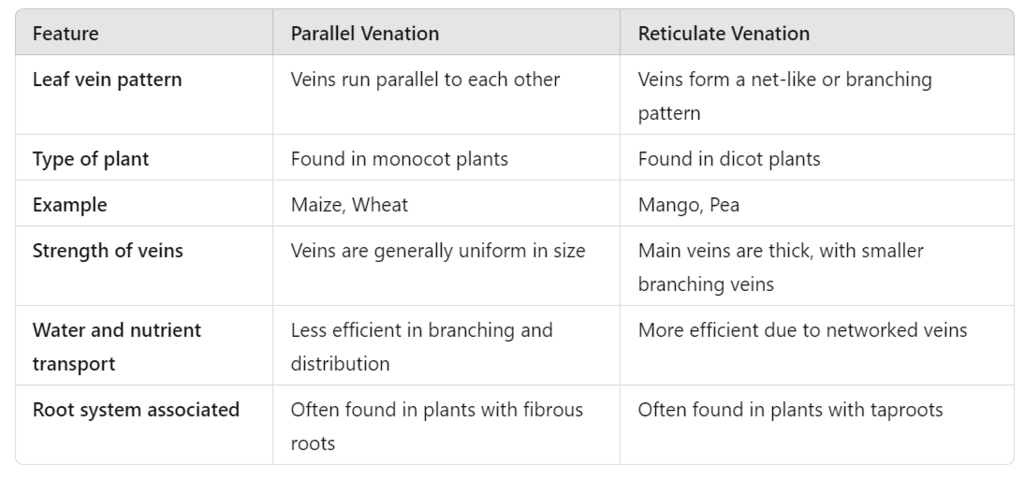

Ans: (a) Taproot system in a mustard plant (b) Fibrous root system in common grass
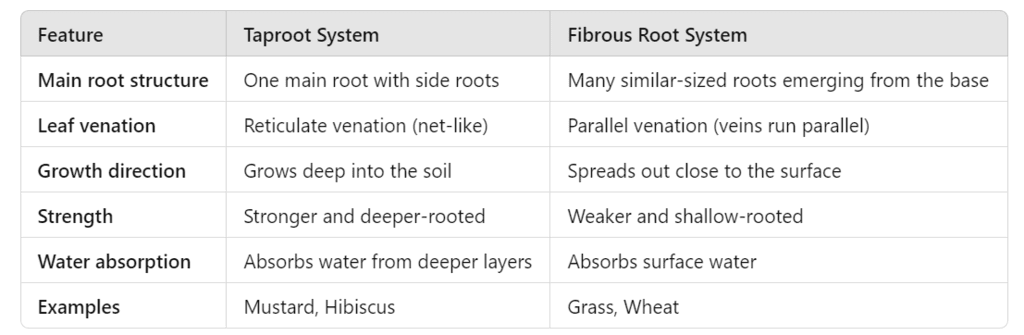
Q12: (a) Identify and give two characterstics of each respectively. (5 Marks)
Ans: 
(b) What are climbers and creepers? Give some examples.
Ans: In some plants like grape vines, money plant, bean stalk, gourd plants, etc., the stem is so weak that it cannot hold it straight. They either stand up with some support or they just spread on the ground. The ones which climb up are called climbers. For example grape vines, money plant. The ones which spread on the ground are called creepers or runners. For example gourd plants.
Q13: Answer the following questions( 5 Marks)
(a) Mention one adaptation present in the following animals:
(i) In camels to keep their bodies away from the heat of sand.
(ii) In frogs to enable them to swim.
(iii) In dolphins and whales to breathe in air when they swim near the surface of water.
Ans:
(a) Long legs
(b) Webbed feet
(c) Blow holes
(b) Classify the following habitats into terrestrial and aquatic types. Grassland, Pond, Ocean, Rice field
Ans:
Terrestrial habitats-Grassland, Rice field
Aquatic habitats – Pond, Ocean
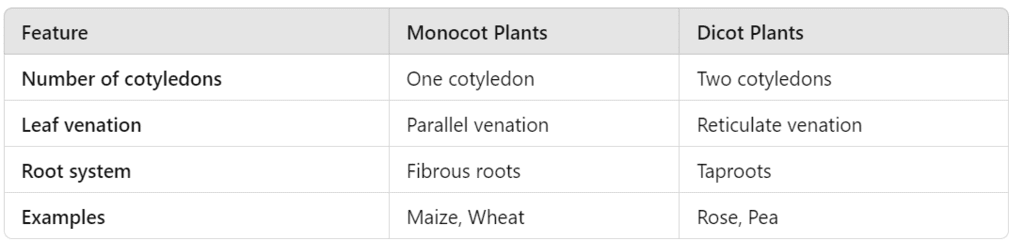
(c) Write the differences between Monocot and Dicot Plants.
Ans: