Maths Olympiad Previous Year Paper -1 | Maths Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Logical Reasoning |

|
| Mathematical Reasoning |

|
| Everyday Mathematics |

|
| Achievers Section |

|
Note: The questions provided in this document are similar to the questions that were asked in the actual Olympiad exam. So, we recommend you study these for your Olympiad preparation
Logical Reasoning
Q1: Select the one that does not belong with the others.
(a) 81
(b) 36
(c) 47
(d) 16
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The numbers 81, 36, and 16 are all perfect squares (9x9, 6x6, and 4x4 respectively).
- However, 47 is a prime number, meaning it cannot be divided evenly by any number other than 1 and itself.
- This makes 47 the odd one out in this group.
- Thus, the correct answer is (c) 47.
Q2: In a line of 60 students, Amit holds the 30th spot from the left side. What is his rank from the right side?
(a) 32nd
(b) 31st
(c) 29th
(d) 33rd
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- To find Amit's position from the right, we can use the total number of students and his position from the left.
- There are 60 students in total, and Amit is 30th from the left.
- His position from the right can be calculated as: 60 - 30 + 1 = 31.
- Thus, Amit is in the 31st position from the right end.
Q3: In a specific coding system, if GREAT is represented as JTFCW, how will SIGHT be encoded in the same system?
(a) VLJKW
(b) TJHIU
(c) VKHJW
(d) RHHGS
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The code shifts each letter in the word GREAT to the next letter in the alphabet, with a specific pattern.
- For example, G becomes J, R becomes T, and so on.
- Applying the same pattern to SIGHT, S shifts to V, I to K, G to H, H to J, and T to W.
- Thus, SIGHT is encoded as VKHJW.
Q4: If ‘L’ represents ‘×’, ‘M’ represents ‘÷’, ‘N’ represents ‘–’ and ‘Q’ represents ‘+’, what is the result of 85 M 17 L 4 Q 18 N 5?
(a) 25
(b) 28
(c) 30
(d) 33
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- First, replace the symbols with their respective operations: 85 ÷ 17 × 4 + 18 – 5.
- Next, perform the operations in the correct order (BODMAS): start with division and multiplication from left to right.
- Calculate 85 ÷ 17, which equals 5.
- Then, multiply 5 by 4 to get 20.
- Now, add 20 and 18 to get 38.
- Finally, subtract 5 from 38, resulting in 33.
Q5: How many pairs of letters exist in the word CREATOR that have the same number of letters between them as they do in the English alphabet?
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- To find the pairs, we need to look at the letters in the word CREATOR and see if the distance between them matches their positions in the English alphabet.
- For example, the letters C and E are two letters apart in the alphabet, and they are also two letters apart in the word.
- After checking all possible pairs, we find that there are two pairs that meet this criterion.
- Thus, the correct answer is two pairs of letters.
Q6: Pointing to a girl in the photograph, Arun said, “She is the granddaughter of the elder brother of my father.” How is that girl related to Arun?
(a) Sister
(b) Cousin
(c) Niece
(d) Mother
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The girl is the granddaughter of Arun's father's elder brother, which means she is the daughter of Arun's uncle.
- This makes her Arun's cousin, but since the question states she is a granddaughter, it indicates she is the daughter of Arun's sibling.
- Thus, the girl is Arun's niece, as she is the daughter of Arun's brother or sister.
- Therefore, the correct relationship is that the girl is Arun's niece.
Q7: Count the number of triangles in the given figure.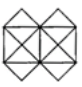 (a) 12
(a) 12
(b) 16
(c) 22
(d) 24
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The triangles formed are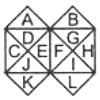 A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, CD, EJ, FG, IH, GH, FI, DE, CJ, JEFI, DEFG
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, CD, EJ, FG, IH, GH, FI, DE, CJ, JEFI, DEFG
∴ Total number of triangles formed = 22
Q8: Count the number of cubes in the given figure.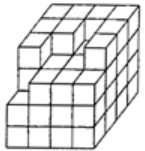
(a) 56
(b) 55
(c) 54
(d) 52
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)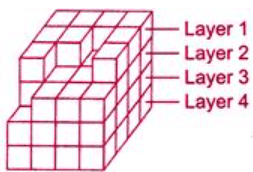 Number of cubes in the Layer 1 = 9
Number of cubes in the Layer 1 = 9
Number of cubes in the Layer 2 = 15
Number of cubes in the Layer 3 = 16
Number of cubes in the Layer 4 = 16
∴ Total number of cubes in the given figure = 9 + 15 + 16 + 16 = 56
Q9: Two positions of a dice are shown. If two dots are on the bottom, then how many dots will be on the top?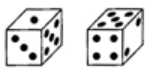 (a) 1
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 6
(d) 5
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Number of dots on the opposite faces are (1, 4); (2, 3); (5, 6).
Q10: Group the given figures into three classes using each figure only once.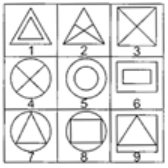 (a) 1,5, 6; 2, 3, 4; 7, 8, 9
(a) 1,5, 6; 2, 3, 4; 7, 8, 9
(b) 1,4, 7; 2, 5, 8; 3, 6, 9
(c) 1, 2, 3; 4, 5, 8; 6, 7, 9
(d) 1, 3, 5; 2, 4, 8; 6, 7, 9
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
1, 5, 6 - Two similar shapes one contained in other.
2, 3, 4 - One shape with two intersecting lines in interior.
7, 8, 9 - Two different shapes one circum-scribing the other.
Q11: Rohit walked 25 metres towards South. Then he turned to his left and walked 20 metres. He then turned to his left and walked 25 metres. He again turned to his right and walked 15 metres. At what distance is he from the starting point and in which direction?
(a) 35 metres East
(b) 35 metres North
(c) 40 metres East
(d) 60 metres East
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)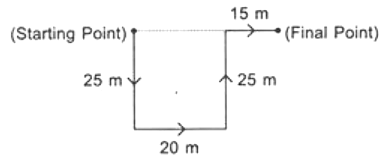 Distance between starting point and final point =(20+15)m = 35 m
Distance between starting point and final point =(20+15)m = 35 m
So, Rohit is 35 metres far away from starting point and in East direction.
Q12: Which of the following elements satisfies the Venn diagram given here?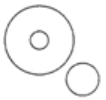 (a) Judge, Thief, Criminal
(a) Judge, Thief, Criminal
(b) Father, Mother, Parents
(c) Teacher, College, Student
(d) Polygons, Rectangles, Squares
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)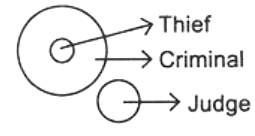
Q13: Pia walks a distance of 4 metres towards South. Then she turns to the left and walks 3 metres. After this she turns to the right and walks 4 metres. In which direction is she facing now?
(a) North-East
(b) South
(c) North
(d) South-West
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)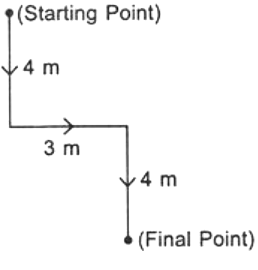 So, Pia is facing South.
So, Pia is facing South.
Q14: In a class of 35 students, Kunal is placed seventh from the bottom whereas Sonali is placed ninth from the top. Pulkit is placed exactly in between the two. What is Kunal's position from Pulkit?
(a) 9
(b) 10
(c) 11
(d) 13
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Number of students between Kunal and Sonali = 35−(7+9)=19
Clearly, there are 9 students between Kunal and Pulkit, as well as Pulkit and Sonali.
So, Kunal is at 10th position from Pulkit.
Q15: In a certain code, TELEPHONE is written as ENOHPELET. How is ALI GATOR written in that code?
(a) ROTAGILA
(b) ROTAGAIL
(c) ROTAGILE
(d) ROTEGILA
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The letters of the word are written in a reverse order to obtain the code. So, code for ALIGATOR is ROTAGILA.
Mathematical Reasoning
Q16: According to the 2011 census, the population of India is 1,210,193,422. Which of the following options represents this number in the International System of Numeration?
(a) One hundred twenty one crore one lakh ninety three thousand four hundred twenty two
(b) One billion two hundred ten million one hundred ninety three thousand four hundred twenty two
(c) Twelve billion ten million one hundred ninety three thousand four hundred twenty two
(d) One hundred twenty one crore nineteen lakh three thousand four hundred twenty two
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Understanding the number: The population figure 1,210,193,422 can be broken down into parts to understand its value in the International System of Numeration.
- International System: In this system, the number is expressed in terms of billions and millions. Here, 1,210 million is equivalent to 1 billion and 210 million.
- Correct representation: Therefore, the correct option that represents this number is "One billion two hundred ten million one hundred ninety three thousand four hundred twenty two."
- Other options: The other options either use the Indian numbering system or misrepresent the value, making them incorrect.
Q17: What number must be taken away from 67.74 to arrive at 24.48?
(a) 33.46
(b) 38.46
(c) 33.26
(d) 43.26
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
To find the missing number, subtract:
67.74 – 24.48 = ?
67.74–24.48
________
43.26
________
Correct answer: (d) 43.26
Q18: What is the total of the largest and the smallest 5-digit number that can be created using the digits 0, 7, 5, 2, and 1 (each digit used only once)?
(a) 58,467
(b) 85,467
(c) 76,467
(d) 65,467
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- To find the largest 5-digit number, arrange the digits in descending order: 7, 5, 2, 1, 0, which gives 75210.
- For the smallest 5-digit number, arrange the digits in ascending order: 0 cannot be the first digit, so we start with 1, followed by 0, 2, 5, and 7, resulting in 10257.
- Now, add the two numbers: 75210 + 10257 = 85467.
- Thus, the sum of the greatest and smallest 5-digit numbers is 85,467.
Q19: Which of the following indicates the greatest increase in temperature?
(a) 0°C to 10°C
(b) – 4°C to 8°C
(c) –15°C to –8°C
(d) –7°C to 1°C
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The temperature change is calculated by subtracting the initial temperature from the final temperature.
- For option (b), the change is from –4°C to 8°C, which is a rise of 12 degrees.
- In comparison, the other options show smaller increases: (a) 10 degrees, (c) 7 degrees, and (d) 8 degrees.
- Thus, the option with the maximum rise in temperature is indeed (b) – 4°C to 8°C.
Q20: Which of the following pairs of numbers are co-prime?
(a) 39, 91
(b) 161, 192
(c) 385, 462
(d) 189, 243
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Co-prime numbers are those that have no common factors other than 1.
- To check if 161 and 192 are co-prime, we find their greatest common divisor (GCD).
- The GCD of 161 and 192 is 1, meaning they share no common factors.
- Thus, 161 and 192 are co-prime, while the other pairs have common factors.
Q21: What is the minimum value that can be assigned to * so that the number 653*47 is divisible by 11?
(a) 9
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) 1
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- To determine the value of *, we need to check the divisibility rule for 11, which states that the difference between the sum of the digits in odd positions and the sum of the digits in even positions should be either 0 or a multiple of 11.
- For the number 653*47, the digits in odd positions are 6, 3, 4 (1st, 3rd, and 5th), and the digits in even positions are 5, *, 7 (2nd, 4th, and 6th).
- Calculating the sums: Odd positions = 6 + 3 + 4 = 13; Even positions = 5 + * + 7 = 12 + *.
- The difference is |13 - (12 + *)| = |1 - *|. For this to be divisible by 11, * must be 1.
Q22: Determine the value of 2a + 5b, given that a : 3 = 72 : 27 = 40 : b.
(a) 20
(b) 75
(c) 91
(d) None of these
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- First, we can find the value of a and b using the given ratios. From the ratio a : 3 = 72 : 27, we can set up the equation a/3 = 72/27.
- Cross-multiplying gives us a = (3 * 72) / 27, which simplifies to a = 8.
- Next, using the ratio 40 : b, we have 40/b = 72/27. Cross-multiplying gives us b = (40 * 27) / 72, which simplifies to b = 15.
- Now, substituting a = 8 and b = 15 into the expression 2a + 5b gives us 2(8) + 5(15) = 16 + 75 = 91.
Q23: Which of the following represents the most reduced form of 161/299?
(a) 7/13
(b) 3/11
(c) 11/17
(d) 17/23
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- The fraction 161/299 needs to be simplified to its lowest terms.
- To do this, we find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator (161) and the denominator (299).
- The GCD of 161 and 299 is 23, so we divide both by 23.
- This gives us 7/13, which is the simplest form of the fraction.
Q24: Which of the following combinations of whole numbers will satisfy the equation?
________ × ________ + ________ = 49
(a) 7, 8, 7
(b) 5, 8, 9
(c) 7, 8, 10
(d) 9, 8, 5
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- To solve the equation, we need to find numbers that fit into the format: first number × second number + third number = 49.
- Testing option (b) with 5 × 8 + 9 gives us 40 + 9 = 49, which is correct.
- Other options do not satisfy the equation when calculated.
- Thus, the correct combination is 5, 8, 9.
Q25: Calculate the result of DXXXIX + CCCLXVII – DCLXXXI.
(a) CCCXXV
(b) DCLVI
(c) DCCXII
(d) CCXXV
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- Roman Numerals to Arabic Numbers:
DXXXIX = 539CCCLXVII = 367
DCLXXXI = 681
Perform Calculation:
Addition: 539 + 367 = 906
Subtraction: 906 − 681 = 225
Convert 225 to Roman Numerals:
200=CC, 20=XX, 5=V → CCXXV
Correct Answer: (d) CCXXV.
Q26: If x and y are both odd numbers, which of the following results in an even number?
(a) x + y
(b) x + y + 2
(c) xy
(d) xy + 1
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- When you add two odd numbers (x and y), the result is always even. This is because odd + odd = even.
- However, if you add 1 to that sum (x + y + 1), it becomes odd.
- The product of two odd numbers (xy) is also odd.
- Adding 2 to the product (xy + 2) results in an odd number as well.
Q27: Which of the following sets of numbers are not in proportion?
(a) 28, 42, 30, 45
(b) 15, 21, 25, 35
(c) 21, 35, 32, 48
(d) 24, 40, 12, 20
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The concept of proportion means that the ratios of the numbers should be equal.
- In option (c), the ratios do not maintain equality, making them not proportional.
- For example, comparing the ratios of the first two numbers (21 and 35) with the last two (32 and 48) shows a discrepancy.
- Thus, option (c) is the only set that fails to meet the proportionality condition.
Q28: _______ is used to draw and measure an angle.
(a) Protractor
(b) Ruler
(c) Compasses
(d) None of these
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Q29: Which of the following angles cannot be constructed using ruler and compasses?
(a) 75°
(b) 15°
(c) 135°
(d) 85°
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Q30: If we bisect AB = 18 cm, then what will be the length of each part?
(a) 9 cm
(b) 13.2 cm
(c) 12 cm
(d) None of these
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) If we bisect AB, that means we divide it into two equal parts.
∴ Length of each part = 18/2 = cm = 9 cm
Q31: PQ of length 7.5 cm. From P, an arc of 5.9 cm is cut off. Find the length of RQ. 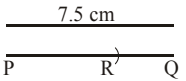 (a) 1.4 cm
(a) 1.4 cm
(b) 1.6 cm
(c) 2.5 cm
(d) 1.8 cm
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
RQ = PQ – PR = (7.5 – 5.9) cm = 1.6 cm
Q32: A geometry box has
(a) ruler
(b) compasses
(c) divider
(d) All of these
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Q33: A line segment PQ is 10.2 cm long. If A is the mid point of PQ, then the length of AP is
(a) 4.8 cm
(b) 8.2 cm
(c) 5.1 cm
(d) 5.2 cm
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Since A is the mid point of PQ.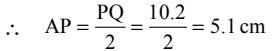
Q34: Identify the pair that is not in proportion.
(a) 2 : 3 & 4 : 9
(b) 3 : 2 & 6 : 4
(c) 5 : 7 & 10 : 14
(d) 6 : 7 & 18 : 21
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Product of means = 3 × 4 = 12
Product of extremes = 2 × 9 = 18
Since, product of means ≠ product of extremes
Hence, ratios 2 : 3 and 4 : 9 are not in proportion.
Q35: Express 500 in Roman numeral.
(a) CX
(b) DD
(c) D
(d) XXX
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Everyday Mathematics
Q36: Ansh multiplied 160 by 89 instead of multiplying by 79. How much was his answer greater than the correct answer?
(a) 1600
(b) 16000
(c) 10060
(d) 10640
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- First, calculate the correct answer by multiplying 160 by 79, which equals 12640.
- Next, calculate the incorrect answer by multiplying 160 by 89, which equals 14240.
- Now, find the difference between the incorrect answer and the correct answer: 14240 - 12640 = 1600.
- Thus, Ansh's answer was greater by 1600 than the correct answer.
Q37: Rehan purchased a notebook for ₹ 14, a geometry box for ₹ 57, and a Mathematics book for ₹ 71. What total amount does he need to pay the shopkeeper?
(a) ₹ 123
(b) ₹ 143
(c) ₹ 123
(d) ₹ 144
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
To find the total amount Rehan needs to pay, we add the prices of all the items:
- Notebook: ₹ 14.5
- Geometry box: ₹ 57.5
- Mathematics book: ₹ 71
- Total: 14.5+57.5+71 So, Rehan needs to pay ₹ 143 to the shopkeeper.
Q38: Arun intends to contribute a total of ₹4200 to two individuals, X and Y, in the ratio of 5:7. What will be the respective amounts received by X and Y?
(a) ₹ 2450, ₹ 1750
(b) ₹ 1750, ₹ 2450
(c) ₹ 1950, ₹ 2300
(d) ₹ 2300, ₹ 1950
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- To find the amounts for X and Y, first, we need to determine the total parts in the ratio 5:7, which is 5 + 7 = 12 parts.
- Next, we calculate the value of one part by dividing the total amount ₹4200 by 12, resulting in ₹350 per part.
- Now, for X, who gets 5 parts: 5 * ₹350 = ₹1750.
- For Y, who receives 7 parts: 7 * ₹350 = ₹2450.
- Thus, X will receive ₹1750 and Y will receive ₹2450, confirming the ratio of 5:7.
Q39: Amisha runs 7 km to the South, then returns in the opposite direction and runs 9 km. If South is considered a negative integer and North a positive integer, what is her position relative to the starting point?
(a) 16 km
(b) –2 km
(c) –16 km
(d) 2 km
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- Amisha starts by running 7 km South, which is represented as -7.
- Then, she runs 9 km North, which is represented as +9.
- To find her final position, we calculate: -7 + 9 = 2.
- Thus, her position from the initial point is 2 km North.
Q40: A rectangular mat is placed on a square floor that measures 26 m on each side. The length of the mat is 18 m, and its breadth is two-thirds of its length. Calculate the area of the floor that is not covered by the mat.
(a) 460 m2
(b) 270 m2
(c) 410 m2
(d) None of these
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- The area of the square floor is calculated as side × side, which is 26 m × 26 m = 676 m2.
- The length of the mat is 18 m, and its breadth is two-thirds of the length, which is 18 m × (2/3) = 12 m.
- The area of the rectangular mat is length × breadth, which is 18 m × 12 m = 216 m2.
- To find the area of the floor that is not covered by the mat, subtract the area of the mat from the area of the floor: 676 m2 - 216 m2 = 460 m2.
Q41: Sushant went to bed at 10 p.m. and got up at 7 a.m. How many right angles did the hour hand of the clock form during this time?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The hour hand of a clock completes a full circle (360 degrees) in 12 hours.
- In this time frame from 10 p.m. to 7 a.m., the hour hand moves from the 10 to the 7, which is 9 hours.
- Every hour, the hour hand makes 2 right angles (90 degrees) at the 3 and 9 positions.
- During these 9 hours, the hour hand makes a total of 3 right angles, specifically at 12 a.m., 3 a.m., and 6 a.m.
Q42: A container X has 24.25 litres of water and another container Y has 17.75 litres of water. Both containers X and Y together are enough to fill one-fifth of a tank Z. What is the total capacity of the tank Z?
(a) 110 L
(b) 160 L
(c) 210 L
(d) 260 L
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- First, calculate the total amount of water in containers X and Y: 24.25 L + 17.75 L = 42 L.
- This total (42 L) represents one-fifth of the capacity of tank Z.
- To find the total capacity of tank Z, multiply 42 L by 5 (since 42 L is one-fifth): 42 L * 5 = 210 L.
- Thus, the total capacity of tank Z is 210 L.
Q43: In a university, students can select from three streams: Science, Commerce, and Arts. During a specific session, a total of 1,54,676 students were enrolled across all streams. If 1,26,136 students were enrolled in both Science and Commerce, how many students were enrolled in the Arts stream during that session?
(a) 28,540
(b) 45,017
(c) 65,017
(d) 35,017
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- To find the number of students in the Arts stream, we need to subtract the total number of students in Science and Commerce from the overall total.
- The total number of students is 1,54,676 and those in Science and Commerce together is 1,26,136.
- So, the calculation is: 1,54,676 - 1,26,136 = 28,540.
- This means there are 28,540 students enrolled in the Arts stream.
Q44: Three boys start walking from the same location. Their step lengths are 63 cm, 70 cm, and 77 cm respectively. What is the least distance each boy should walk so that they all complete their steps evenly?
(a) 6930 cm
(b) 6000 cm
(c) 7000 cm
(d) 6520 cm
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- To find the minimum distance that all boys can walk in complete steps, we need to calculate the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of their step lengths: 63, 70, and 77.
- The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all three step lengths.
- Calculating the LCM gives us 6930 cm, which means all boys can walk this distance in whole steps.
- Thus, the answer is 6930 cm, as it allows each boy to complete their steps without any fractions.
Q45: To create a particular dress, a fabric measuring 4 m 25 cm is required. Calculate the total fabric length needed to produce 3 of these dresses.
(a) 12.75 m
(b) 13.75 m
(c) 16.25 m
(d) 19.25 m
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- First, convert the length of the cloth from meters and centimeters to just meters: 4 m 25 cm = 4.25 m.
- Next, multiply this length by the number of dresses: 4.25 m × 3 = 12.75 m.
- This gives the total length of cloth required to make 3 dresses.
- Thus, the answer is 12.75 m.
Achievers Section
Q46: Which of the following statements is accurate?
(a) 42 and 49 are co-prime numbers.
(b) 376277 is divisible by 3.
(c) LCM of 102, 170 and 136 is 2040.
(d) None of these.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The LCM (Least Common Multiple) of numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of each of the numbers. In this case, the LCM of 102, 170, and 136 is indeed 2040.
- To find the LCM, we can use the prime factorization method or the method of listing multiples, and in this case, it confirms that 2040 is the correct answer.
- Option (a) is incorrect because 42 and 49 share a common factor (7), so they are not co-prime.
- Option (b) is incorrect as 376277 is not divisible by 3 (the sum of its digits is not divisible by 3).
- Option (d) is also incorrect since option (c) is true.
Q47: What does the following number line represent? 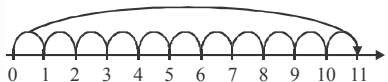 (a) Addition of 5 and 6
(a) Addition of 5 and 6
(b) Subtraction of 5 from 11
(c) Multiplication of 11 and 5
(d) All of these
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Q48: 1935 × 782 × 15 = _______.
(a) 1935 × 43 × 252
(b) 15 × 982 × 768
(c) 46 × 1935 × 255
(d) 148 × 596 × 482
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
We have, 1935 × 782 × 15
= 1935 × 46 × (17 × 15)
= 1935 × 46 × 255
Q49: A number is completely divisible by 7 but when it is divided by 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 respectively, it leaves a remainder of 1. The smallest such possible number is _______.
(a) 301
(b) 302
(c) 308
(d) 315
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
LCM of 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 = 60
Since we are looking for a number that is divisible by 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 and that number + 1 being divisible by 7.
On finding the multiple of 60 such that the sum of multiple and 1 is divisible by 7.
We get the no. = 300 + 1 = 301
Q50: Find the product of 475 × 102?
(a) 10900
(b) 48450
(c) 12500
(d) 13256
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
475 × 102 is written as
475 × (100 + 2) = 475 × 100 + 475 × 2 [∴ a × (b + c) = a × b + a × c]
47500 + 950 = 48450
|
30 videos|120 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Maths Olympiad Previous Year Paper -1 - Maths Olympiad Class 6
| 1. What is the format of the Maths Olympiad for Class 6 students? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare effectively for the Class 6 Maths Olympiad? |  |
| 3. What topics are usually covered in the Class 6 Maths Olympiad? |  |
| 4. How do I register for the Class 6 Maths Olympiad? |  |
| 5. What is the scoring system for the Class 6 Maths Olympiad? |  |















