Maths Olympiad Previous Year Paper -2 | Maths Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Logical Reasoning |

|
| Mathematical Reasoning |

|
| Everyday Mathematics |

|
| Achievers Section |

|
Note: The questions provided in this document are similar to the questions that were asked in the actual Olympiad exam. So, we recommend you study these for your Olympiad preparation
Logical Reasoning
Q1: Pointing at Ankit, a woman stated, “His mother is the sole daughter of my mother.” What is the relationship of that woman to Ankit?
(a) Mother-in-law
(b) Daughter
(c) Mother
(d) Sister-in-law
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The woman refers to Ankit's mother as the only daughter of her own mother, which means she is Ankit's mother.
- This indicates that the woman is Ankit's mother herself, as she is talking about her own child.
- Thus, the correct answer is that the lady is Ankit's mother.
Q2: Select a term from the options that will complete the following series:
B4M, D7L, F11K, H16J, ?
(a) J22I
(b) I20H
(c) J20C
(d) K19I
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- The series consists of three parts: letters, numbers, and letters again.
- The first letters are increasing by 2: B, D, F, H, and the next is J.
- The numbers are increasing by 3: 4, 7, 11, 16, leading to 22.
- The last letters are decreasing by 1: M, L, K, J, so the next is I.
Q3: Some letters are given which are numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. Find the combination of numbers from the options so that the letters are arranged accordingly to form a meaningful English word. 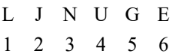 (a) 2, 4, 3, 5, 1, 6
(a) 2, 4, 3, 5, 1, 6
(b) 2, 1, 3, 5, 4, 6
(c) 3, 1, 4, 2, 6, 5
(d) 4, 1, 2, 5, 3, 6
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- The letters given are L, J, N, U, G, E.
- By following the combination 2, 4, 3, 5, 1, 6, we get the arrangement: J, U, N, G, L, E.
- This spells the meaningful word "JUNGLE".
- Thus, the correct option is (a) as it forms a valid English word.
Q4: In a specific coding system, if the word CREDIT is represented as CDEIRT, what will be the coded form of SAFEST in the same system?
(a) TBGFTU
(b) AEFSST
(c) ASEFTSD
(d) TSSFEA
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The coding system rearranges the letters of the word.
- In the example, CREDIT is transformed into CDEIRT by sorting the letters.
- Applying the same method to SAFEST, we sort the letters to get AEFSST.
- Thus, the correct coded form of SAFEST is AEFSST.
Q5: If ‘+’ represents division, ‘÷’ indicates multiplication, ‘×’ means subtraction, and ‘–’ signifies addition, what is the result of 14 ÷ 6 – 8 + 4 × 10?
(a) 70
(b) 150
(c) 76
(d) 86
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- First, replace the symbols according to the given definitions: 14 ÷ 6 becomes 14 × 6, 8 remains 8, 4 × 10 becomes 4 – 10, and 6 – 8 becomes 6 + 8.
- Now, calculate: 14 × 6 = 84, then 84 – 8 = 76, and finally 76 + 4 = 76.
- The final result is 76, which corresponds to option (c).
- Thus, the answer is 76.
Q6: In a joint family, there are father, mother, 4 married sons and three unmarried daughters. Of the sons, two have 2 daughters each, and two have a son and a daughter each. How many female members are there in the family?
(a) 15
(b) 12
(c) 14
(d) 11
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Total female members in the family = 1 + 4 + 3 + 2 × 2 + 2 × 1 = 14
Q7: Which of the following set of letters will complete the given letter series?
WFB, TGD, QHG, ?
(a) NU
(b) NIK
(c) NJK
(d) PJK
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The pattern followed is,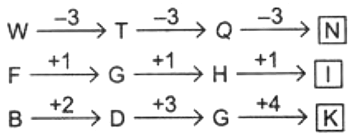
Q8: While going to his office P meets a man Q who is related to P, because P has R, a son, who is married to T. T is the daughter of Q. T has a daughter a. How is P related to A?
(a) Grandfather
(b) Grandmother
(c) Uncle
(d) Father-in-law
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Q9: Count the number of unit cubes in the given solid.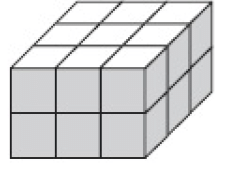 (a) 10
(a) 10
(b) 15
(c) 18
(d) 22
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Each level has 9 cubes and there are two levels. Total is 18
Q10: If the English alphabets are written in reverse order after interchanging alphabets from 'C to M' with those from 'P to Z' respectively, which letter would be midway between F and T in the new order?
(a) Z
(b) M
(c) N
(d) X
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)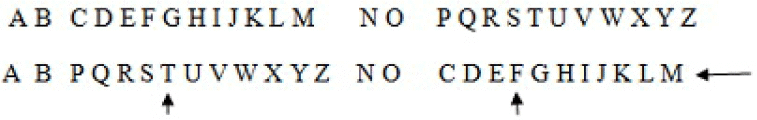
Q11: If in a certain code language, 'CROWNED' is written as 'PSDVEFO', then how will 'STREAMS' be written in that language?
(a) SUTDBNT
(b) TUSDTNB
(c) SUTDTNB
(d) QSRDTNB
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Q12: How many meaningful English words can be formed from the letters ADRW, using each letter only once in each word?
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Q13: How many such letters are there in the word 'CATEGORY' each of which is as far away from the beginning of the words when they are arranged in alphabetical order?
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Q14: Complete the series 1, 6, 13, 22, 33,..
(a) 46
(b) 48
(c) 49
(d) 51
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Pattern is +5, +7, +9, +11
So next number will be +13
=> 33+13 = 46
Q15: Find the odd one out of the options given below:
(a) ACDE
(b) FHIJ
(c) KMNO
(d) PQRS
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Mathematical Reasoning
Q16: What is the ratio of vowels to total letters in the word "MATHEMATICS"?
(a) 5/11
(b) 7/11
(c) 6/11
(d) 4/11
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- The word "MATHEMATICS" has a total of 11 letters.
- It contains 4 vowels: A, E, A, I.
- The fraction of vowels is calculated as number of vowels divided by total letters, which is 4/11.
- Thus, the correct answer is 4/11.
Q17: What is the distinction between the place value and face value of 3 in the number 637258?
(a) 29997
(b) 15980
(c) 30003
(d) None of these
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- The face value of a digit is the value of the digit itself, which for 3 is simply 3.
- The place value of a digit depends on its position in the number. In 637258, the 3 is in the thousands place, so its place value is 3000.
- To find the difference, subtract the face value from the place value: 3000 - 3 = 2997.
- Thus, the difference between the place value and face value of 3 in 637258 is 2997.
Q18: Determine the total count of prime factors in the number 7350.
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 3
(d) 5
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- To find the prime factors of 7350, we start by dividing it by the smallest prime number, which is 2. This gives us 3675.
- Next, we continue factoring 3675 by dividing by 3, resulting in 1225.
- Then, we factor 1225 by dividing by 5, leading to 245, and again by 5 to get 49.
- Finally, we factor 49 as 7 multiplied by 7. Thus, the prime factors of 7350 are 2, 3, 5, and 7.
- Counting these, we find there are 4 distinct prime factors: 2, 3, 5, and 7.
Q19: Vicky is 5 years older than his cousin. If Vicky's age is x years, what is the age of his cousin (in years)?
(a) x + 5
(b) x × 5
(c) x ÷ 5
(d) x – 5
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- Vicky is 5 years older than his cousin.
- If Vicky's age is x years, then to find his cousin's age, we need to subtract 5 from x.
- This gives us the formula: cousin's age = x - 5.
- Thus, the correct answer is (d) x – 5.
Q20: The result of 0.90 + 34.77 – 23.03 is _______.
(a) 21.63
(b) 12.64
(c) 16.67
(d) 18.59
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- First, we add 0.90 and 34.77, which gives us 35.67.
- Next, we subtract 23.03 from 35.67.
- The calculation is 35.67 - 23.03 = 12.64.
- Thus, the final answer is 12.64, which corresponds to option (b).
Q21: The decimal representation of 75 divided by 491/1000 is:
(a) 7504.91
(b) 7500.491
(c) 75.491
(d) 75.0491
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The expression 75 divided by 491/1000 can be simplified by multiplying 75 by the reciprocal of 491/1000, which is 1000/491.
- This calculation results in approximately 75.491, which is the correct decimal form.
- Understanding how to convert fractions to decimals is key here, as it involves basic division.
- Thus, the correct answer is 75.491.
Q22: Which of the following shapes possesses precisely two lines of symmetry?
(a) Equilateral triangle
(b) Isosceles triangle
(c) Rectangle
(d) Square
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The rectangle has two lines of symmetry: one vertical and one horizontal.
- In contrast, an equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry, while an isosceles triangle has one.
- A square has four lines of symmetry, which is more than two.
- Thus, the only shape with exactly two lines of symmetry is the rectangle.
Q23: What is the numerical representation of the phrase, “Two hundred fifty-three million five hundred three thousand four hundred two” in the International System of Numeration?
(a) 253,530,402
(b) 253,503,402
(c) 253,503,420
(d) 253,053,402
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The phrase describes a large number broken down into parts: two hundred fifty-three million (253,000,000), five hundred three thousand (503,000), and four hundred two (402).
- When combined, these parts form the number 253,503,402.
- In the International System of Numeration, commas are used to separate groups of three digits, making it easier to read large numbers.
- Thus, the correct numeral form is 253,503,402.
Q24: Which of the following statements is accurate?
(a) The smallest natural number is 0.
(b) Every whole number has a successor.
(c) The predecessor of a two-digit number is always a two-digit number.
(d) The smallest whole number is 1.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The statement that every whole number has a successor is true. A successor is the number that comes right after a given number.
- For example, the successor of 5 is 6, and this applies to all whole numbers.
- In contrast, the smallest natural number is 1, not 0, and the smallest whole number is 0.
- Also, the predecessor of a two-digit number can be a one-digit number, so that statement is incorrect.
Q25: The given data shows the number of goals scored by a player in 24 different football matches. Study the data carefully and answer the following question.
2, 3, 2, 1, 0, 4, 3, 1, 2, 0, 3, 2, 1, 3, 0, 2, 5, 2, 4, 3, 1, 2, 1, 3
How many times did the player score at least 2 goals?
(a) 13
(b) 14
(c) 15
(d) 16
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- To find out how many times the player scored at least 2 goals, we need to count the occurrences of scores that are 2 or higher.
- The scores are: 2, 3, 2, 1, 0, 4, 3, 1, 2, 0, 3, 2, 1, 3, 0, 2, 5, 2, 4, 3, 1, 2, 1, 3.
- Counting the scores of 2, 3, 4, and 5, we find that they appear 16 times in total.
- Thus, the player scored at least 2 goals a total of 16 times.
Q26: What is the value of n if (9 × 4) + (n × 5) = 9 × (4 + 5)?
(a) 9
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) None of these
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
If (9 × 4) + (n × 5) = 9 × (4 + 5) then by distributive property, n = 9
Q27: Whole numbers are not commutative under ________.
(a) Multiplication
(b) Subtraction
(c) Addition
(d) Both multiplication and addition
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Q28: Parallel lines are _______ intersecting lines.
(a) always
(b) never
(c) sometimes
(d) two
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Q29: Find the value of A from the given figure: 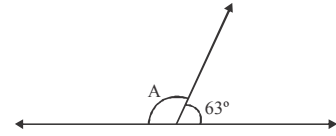
(a) 17º
(b) 117º
(c) 90º
(d) 110º
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Straight angle = 180º
A + 63º = 180º
A = 180º – 63º
A = 117º
Q30: The area of a triangle with each side equals 5.1 metres and the third side 4.6 metres is
(a) 10.47 sq.m
(b) 2.86 sq.m
(c) 11.45 sq.m
(d) None of these
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)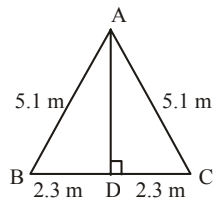
In right angled ΔADC,
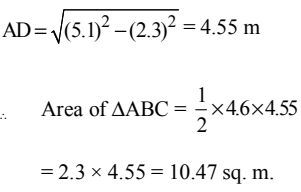
Q31: The successor of –11 is?
(a) –9
(b) –10
(c) –12
(d) 0
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
(–11) + 1 = (–10)
Q32: Temperature at the foot of a mountain is +5°C. It fell down by 10°C at the top of the mountain. The temperature recorded on the top is
(a) +15°C
(b) –15°C
(c) +5°C
(d) –5°C
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
+5°C + (–10°C) = –5°C
Q33: The sum of a number and its additive inverse is:
(a) 1
(b) –1
(c) 0
(d) Number itself
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Q34: What is the reciprocal of shaded parts in the picture given below?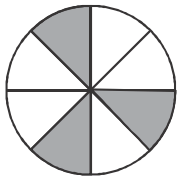 (a) 3/8
(a) 3/8
(b) 8/3
(c) 5/8
(d) 8/5
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Fraction of shaded parts in the picture = 3/8
Reciprocal of shaded parts in the picture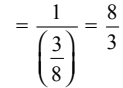
Q35: 324 athletes threw a shotput at a track and field event. If this was 15/100 of all the athletes at the event, then the total number of athletes who competed at the event were _______.
(a) 160
(b) 200
(c) 240
(d) 150
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Let the total no. of athletes = x 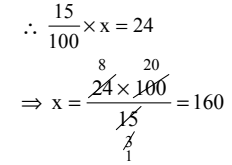
Everyday Mathematics
Q36: Arpita completes 5 laps around a rectangular park, where the length is 7 meters shorter than twice its breadth. If the breadth of the park is 65 meters, what is the total distance Arpita covers?
(a) 1680 m
(b) 1560 m
(c) 1880 m
(d) 1660 m
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- First, calculate the length of the park: Length = 2 * Breadth - 7 = 2 * 65 - 7 = 130 - 7 = 123 m.
- Next, find the perimeter of the rectangular park: Perimeter = 2 * (Length + Breadth) = 2 * (123 + 65) = 2 * 188 = 376 m.
- Now, to find the total distance Arpita travels, multiply the perimeter by the number of rounds: Total Distance = 5 * Perimeter = 5 * 376 = 1880 m.
- Thus, the total distance travelled by Arpita is 1880 meters.
Q37: The students in a class can be divided into groups of 2, 3, 5, and 6. What is the minimum number of students this class can have?
(a) 40
(b) 30
(c) 35
(d) 42
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The problem requires finding the least common multiple (LCM) of the numbers 2, 3, 5, and 6.
- The LCM is the smallest number that can be evenly divided by all these group sizes.
- The LCM of 2, 3, 5, and 6 is 30, which means 30 students can be divided into groups of these sizes without any remainder.
- Thus, the minimum number of students in the class is 30.
Q38: The price of 5 eggs is ₹ 27.50 and the price of 5 omelettes is ₹ 60. What is the ratio of the price of one egg to the price of one omelette?
(a) 12:25
(b) 25:12
(c) 24:11
(d) 11:24
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- To find the cost of one egg, divide the total cost of 5 eggs by 5: 27.50 / 5 = 5.50.
- To find the cost of one omelette, divide the total cost of 5 omelettes by 5: 60 / 5 = 12.
- The ratio of the cost of one egg to the cost of one omelette is 5.50:12.
- To simplify, convert 5.50 to a fraction: 5.50 = 11/2, so the ratio becomes (11/2):12, which simplifies to 11:24.
Q39: Rohit took part in a race that is 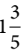 km long. After running
km long. After running 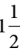 km, what distance does he still need to cover to finish the race?
km, what distance does he still need to cover to finish the race?
(a) 1/10 km
(b) 2/5 km
(c) 3/10 km
(d) 3/5 km
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- First, convert the distances to improper fractions:
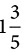 km is 8/5 km and
km is 8/5 km and 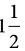 km is 3/2 km.
km is 3/2 km. - Next, find a common denominator to subtract: 8/5 km - 3/2 km = 8/5 km - 15/10 km = 16/10 km - 15/10 km = 1/10 km.
- Thus, the distance Rohit still needs to run is 1/10 km.
Q40: The cost of cultivating a square field at ₹ 17 per sq. m is ₹ 612. Find the side of the field.
(a) 9 m
(b) 8 m
(c) 6 m
(d) 10 m
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- To find the side of the square field, we first need to determine the area of the field. The area can be calculated by dividing the total cost by the cost per square meter.
- The total cost is ₹ 612 and the cost per square meter is ₹ 17. So, the area = 612 / 17 = 36 sq. m.
- Since the field is square, the area (A) is equal to the side length (s) squared: A = s2. Therefore, s2 = 36.
- Taking the square root of both sides gives us s = 6 m. Thus, the side of the field is 6 meters.
Q41: Rohan saved ₹2860 from his pocket money in a certain year. What is the Roman numeral for this saving amount?
(a) MMDCCLX
(b) MDCCCLX
(c) MMDCCCLX
(d) MMDCCCLIX
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The number 2860 in Roman numerals is represented as MMDCCCLX.
- To break it down: 2000 is MM, 800 is DCCC, and 60 is LX.
- When combined, they form MMDCCCLX, which is the correct representation.
- Thus, the answer is option (c).
Q42: Arun has ₹ 125 in his savings account. He withdraws ₹ 117, makes a deposit of ₹ 45 and then withdraws another ₹ 69. What is the remaining balance in his account? (Write the amount as an integer.)
(a) ₹ (–16)
(b) ₹ 16
(c) ₹ 30
(d) ₹ (–30)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Initially, Arun has ₹ 125 in his account.
- After withdrawing ₹ 117, the balance becomes ₹ 8 (125 - 117).
- Then, he deposits ₹ 45, making the new balance ₹ 53 (8 + 45).
- Finally, after withdrawing ₹ 69, the balance is ₹ (16) (53 - 69).
- Since the amount is negative, it is represented as ₹ (–16).
Q43: A company X manufactures two varieties of laptops, namely P and Q. The combined output of both laptop types in a specific year is 8,75,677. If the total output of P type laptops is 3,37,563, what is the total output of Q type laptops?
(a) 4,48,224
(b) 4,38,114
(c) 5,48,224
(d) 5,38,114
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- To find the total production of Q type laptops, we need to subtract the production of P type laptops from the total production.
- The total production is 8,75,677 and the production of P type laptops is 3,37,563.
- So, the calculation is: 8,75,677 - 3,37,563 = 5,38,114.
- Thus, the total production of Q type laptops is 5,38,114.
Q44: Prerna had a total of ₹5000. She purchased 2 boxes of chocolates at ₹52.98 each, 3 packets of chips at ₹12.98 each, and 2 books at ₹ 300.05 each. What amount remains with her?
(a) ₹ 4255
(b) ₹ 4750
(c) ₹ 4000
(d) ₹ 3875
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- First, calculate the total spent on chocolates: 2 boxes × ₹ 52.98 = ₹ 105.96.
- Next, calculate the total for chips: 3 packets × ₹ 12.98 = ₹ 38.94.
- Then, calculate the total for books: 2 books × ₹ 300.05 = ₹ 600.10.
- Add all the expenses: ₹ 105.96 + ₹ 38.94 + ₹ 600.10 = ₹ 744.00.
- Finally, subtract the total expenses from the initial amount: ₹ 5000 - ₹ 744.00 = ₹ 4256.00.
Thus, Prerna has ₹ 4255 left after her purchases.
Q45: Kanika’s teacher instructed her to round the numbers 1248, 3127, and 4105 to the nearest tens. What will be the estimated sum after rounding these numbers?
(a) 7500
(b) 8000
(c) 8480
(d) None of these
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- First, we round each number to the nearest ten:
- 1248 rounds to 1250 (since 8 is 5 or more).
- 3127 rounds to 3130 (since 7 is 5 or more).
- 4105 rounds to 4110 (since 5 is 5 or more).
- Now, we add these rounded numbers: 1250 + 3130 + 4110 = 8490.
- Since 8490 is not listed in the options, the correct answer is None of these.
Achievers Section
Q46: The sum of 46.009 and 146 is
(a) 192.009
(b) 129.9
(c) 182.99
(d) 179.09
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Q47: Mean of a set of observations is the value which
(a) occurs most frequently
(b) divides observation into two equal parts
(c) is a representative of the whole group
(b) is the sum of observations
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Q48: Data obtained in the original form is called ______.
(a) Bar graph
(b) Pie chart
(c) Raw data
(d) Observation
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Data obtained in original form is called Raw data.
49: Pictorial representation of data by a number of bars of uniform width is called ______.
(a) Bar graph
(b) Pictograph
(c) Pie chart
(d) Tally marks
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Q50: Average age of five children is 8 yrs. 4 months. If the average age of four children is 7 yrs. 10 months, the age of fifth child is__________.
(a) 9 yrs. 8 months
(b) 7 yrs. 5 months
(c) 8 yrs. 6 months
(d) 10 yrs. 4 months
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Average age of 5 children = 8 yrs 4 months
Total age of 5 children
= 5 x (8 yrs 4 months)
= 40 yrs 20 months
= 41 yrs 8 months
Average age of 4 children = 7 yrs. 10 months
Total age of 4 children =4 x (7 yrs 10 months) = 31 yrs 4 months
∴ Age of fifth child
= 41 yrs 8 months - 31 yrs 4 months
= 10 yrs 4 months
|
30 videos|120 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Maths Olympiad Previous Year Paper -2 - Maths Olympiad Class 6
| 1. What types of questions can I expect in the Maths Olympiad for Class 6? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare effectively for the Maths Olympiad? |  |
| 3. Are there any specific topics I should focus on for Class 6 Maths Olympiad? |  |
| 4. How is the marking scheme structured in the Maths Olympiad for Class 6? |  |
| 5. What are the benefits of participating in the Maths Olympiad? |  |















