Notes: Our Body & Health | GK Olympiad for Class 5 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Sensory System |

|
| Digestive System |

|
| Amazing Facts About the Human Body |

|
| Food and Nutrients |

|
| First Aid and Safety Tips |

|
Introduction
- Our body has different organs that work together to carry out many life processes.
- It’s important to take care of these organs to keep them disease-free.
- Yoga asanas (yoga poses) are one way to help.
- Eating healthy food with all the necessary nutrients is another important way for a healthy life.
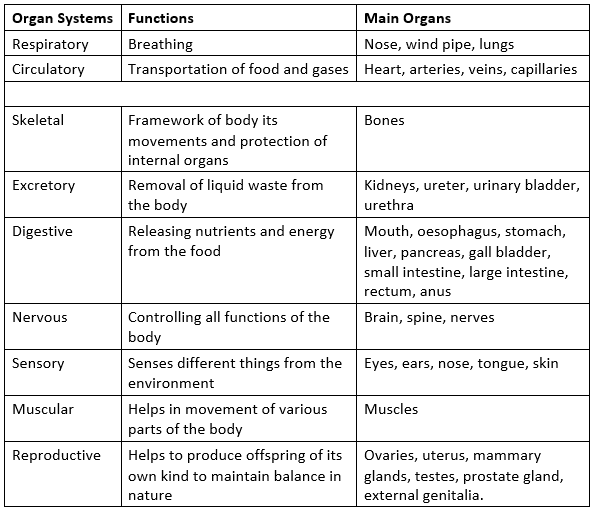
Organ Systems
The structure of our body starts from the smallest unit of life, the cell. It goes like this:- Cells
- Tissues
- Organs
- Organ Systems
- Organisms
Sensory System
- The sensory system helps us understand what is happening around us.
- We have five senses:
1. Sight
2. Hearing
3. Smell
4. Taste
5. Touch
Five Sense Organs
1. Eyes for Sight
- Eyes allow us to see things around us.
- The coloured part of the eye is called the iris, and the small black part inside is the pupil.
- The cornea is the transparent layer covering the front of the eye.
- Light enters through the cornea, travels through the pupil, and helps us see.
- Tears help clean the eyes and keep them moist.
2. Ears for Hearing
- Ears help us hear sounds around us.
- The ear has three main parts: outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear.
- The inner ear contains the eardrum. When sound waves hit the eardrum, it creates nerve impulses that are sent to the brain to understand the sound.
3. Nose for Smell
- The nose helps us smell different things.
- It has two holes called nostrils, where air and smells enter the body.
- The air temperature is adjusted to match our body's internal temperature.
- There are special cells inside the nose that can recognize different smells.
4. Tongue for Taste
- The tongue is a pink muscle located inside the mouth.
- It is attached to the back of the mouth and helps roll food and mix it with saliva.
- The surface of the tongue has small sense pores called taste buds that allow us to enjoy different tastes.
- The tongue identifies five main tastes:
1. Sweet
2. Sour
3. Bitter
4. Umami (savory)
5. Salty - When we accidentally bite our tongue, it heals quickly because the tongue is the fastest healing part of the body.
5. Skin for Touch
- Skin is the largest organ of our body.
- It helps maintain our body’s temperature and allows us to feel different types of touch, such as:
1. Hot
2. Cold
3. Pressure
4. Vibration
5. Roughness
6. Smoothness
Living Things Need Food
All living things need food to:
- Stay alive
- Grow
- Get energy
Food provides nutrients that are digested and absorbed by the body.
Digestive System
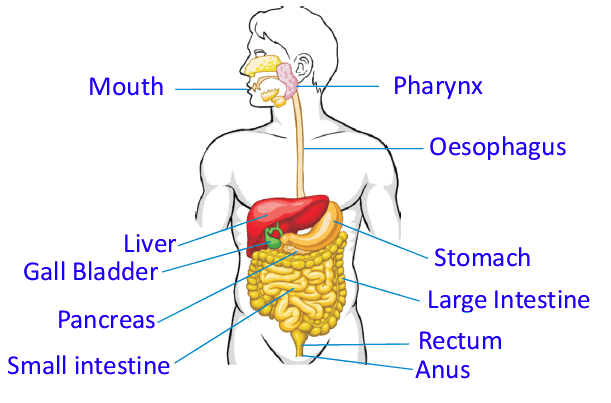
Parts of the Digestive System:
1. Mouth
- Contains the tongue, teeth, and salivary glands.
- Digestion starts here; teeth cut and chew food into small pieces.
- Salivary glands produce saliva, and the tongue mixes food to form a paste.
2. Pharynx
- Helps in swallowing solids and liquids.
3. Oesophagus
- The chewed food moves to the oesophagus (food pipe).
- It is a thin pipe that uses muscle contractions to push food to the stomach.
4. Stomach
- A J-shaped organ made of muscles.
- It has a capacity of about 2 liters and is where part of digestion occurs.
- After partial digestion, food moves to the small intestine.
5. Liver
- Breaks down and builds many biological molecules.
- Stores vitamins and iron.
- Destroys old blood cells, detoxifies poisons, and produces bile juice for digestion.
6. Gall Bladder
- Stores and concentrates bile juice from the liver to help with digestion.
7. Pancreas
- Secretes insulin to regulate blood glucose levels.
- Produces bicarbonates to neutralize stomach acid and hormones like trypsin and chymotrypsin to digest proteins.
8. Small Intestine
- A long, coiled tube about 7.5 m long.
- Most of the digestion takes place here, and undigested food moves to the large intestine in paste form.
9. Large Intestine
- A thick tube about 1.5 m long.
- Absorbs most of the water from undigested food and moves waste to the rectum.
10. Rectum
- Stores waste until it is removed from the body through the anus.
- The waste is called faeces.
Amazing Facts About the Human Body
- Blood Circulation Discovery: William Harvey discovered how blood circulates in the body.
- Length of Blood Vessels: If all our blood vessels were laid out in a straight line, they would stretch from Earth to the Moon.
- Skin Shedding: We lose about 4 kilograms of skin cells each year.
- Lung Size Difference: The right lung is larger than the left, as the heart tilts slightly to the left.
- Heart Activity: A healthy heart beats around 100,000 times per day, pumping between 6,000 to 8,000 liters of blood.
- Blood Weight: Blood makes up about 8% of our body weight.
- Baby Bones: At birth, a baby has approximately 300 bones.
- Muscle Count: There are about 650 muscles in the human body.
- Saliva Production: We produce over 350 liters of saliva each year.
- Water Loss: We must drink water regularly, as the body loses it through urine, sweat, and feces.
- Fast-Healing Tongue: The tongue, which has no bones, is the fastest-healing part of the body.
- Bone Joints: Bones connect and meet at joints.
- Adrenal Glands: These glands, which produce essential hormones, are located above the kidneys.
- AIDS: AIDS is a disease that impacts the human immune system.
- Blood Vessel-Free Areas: Certain areas lack blood vessels, including the cornea, nails, outer skin layers, tooth enamel, and hair.
Food and Nutrients
All raw and cooked food items contain nutrients, which are important for growth and development of our body.
The main types of nutrients found in food are:
Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates are a source of energy for the body.
- They are divided into two main types: Starch and Sugar.
- Important sources of carbohydrates include:
1. Glucose
2. Fruits
3. Honey
4. Beans
5. Rice
6. Wheat
7. Pulses
8. Potato
9. Milk
Fats
- Fats act as an energy storehouse for the body.
- They accumulate under the skin and release energy when we don't eat for a long time or do physical work.
- Important sources of fats include:
1. Butter
2. Ghee
3. Cheese
4. Chicken
5. Fish
6. Nuts
7. Ice cream
8. Rice
9. Potato
10. Junk food
Proteins
- Proteins are essential for body cells to function properly.
- They are found in every cell and help repair damaged cells and tissues, as well as strengthen our teeth and bones.
- Important sources of proteins include:
1. Milk
2. Cheese
3. Curd
4. Eggs
5. Seafood
6. Soya
7. Pistachios
8. Chicken - A deficiency of protein can lead to the disease called Kwashiorkor.
Vitamins
- Vitamins are needed in small quantities for the body.
- They are labeled using English alphabets and play different roles in growth and development.
Minerals
- Like vitamins, minerals are also needed in small amounts.
- These are essential elements required for various body functions.
- Vitamins and minerals together are called micro-nutrients because they are needed in small quantities.
Deficiency Diseases
- Deficiency diseases occur when we do not consume a specific nutrient for a long time.
- These diseases are different from communicable diseases, which can spread from one person to another through air, water, or insects (e.g., measles, malaria, bird flu).
Nutrient Deficiencies
- The table below lists various vitamins and minerals, their benefits, sources, and the diseases caused by their deficiency.
First Aid and Safety Tips
- First Aid is immediate help given to a wounded person or accident victim before a doctor arrives.
- The three aims of first aid are known as ‘the 3 P’s of First Aid’:
1. Preserve Life: The primary aim is to save the victim's life.
2. Prevent Worsening: Avoid making the situation worse.
3. Promote Recovery: Help the victim recover as much as possible. - It’s important to keep a first aid box at home and work for emergencies.
Some Important Safety Tips
At Home
- Write emergency contact numbers where they can be easily seen.
- Keep gas and electric connections off when not in use.
- Do not play with sharp objects or toys.
- Avoid using electric switches if your hands are wet.
At School
- Follow the school rules.
- Walk in queues; do not run or push others.
- If someone is hurt, give them space to breathe and get help from the nearest class.
- When traveling in school cabs and buses, keep all body parts inside the vehicle.
On the Road
- Always cross the road at zebra crossings.
- Avoid walking in a zig-zag manner.
- Keep away from strangers and stay alert.
Did You Know?
- Smoking tobacco is harmful to health and can cause lung cancer. It should be avoided.
Yoga and Lifestyle
- An Asana is a comfortable sitting posture that can be maintained.
- Hold the final position of asanas for as long as you are comfortable.
- Some beneficial asanas for good health include:
1. Surya Namaskar
2. Naukasana
3. Padmasana
|
8 videos|19 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Our Body & Health - GK Olympiad for Class 5
| 1. What is the main function of the digestive system? |  |
| 2. How does food travel through the digestive system? |  |
| 3. What are some interesting facts about the human digestive system? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to maintain a healthy digestive system? |  |
| 5. What foods are good for digestive health? |  |















