NCERT Solution: Recording of Transactions-I - Commerce PDF Download
Short Question Answers
Q1: State the three fundamental steps in the accounting process.
Ans: The three fundamental steps in the process of accounting are:
- Collection of data – The first step requires the collection of the data in the form of collecting data of financial transactions in a particular month in the form of all the vouchers and the bills.
- Processing of data – After when the process of identification of the transactions is complete, the process of accounting requires the due recording of these very transactions in the book of accounts. Hence the accountants are expected to journalise these transactions and classify them into the respective ledger accounts and to lastly summarise them through Trial Balance.
- Reporting – After when all the accounts are tallied, the trail balance of the financial statements are prepared. Financial statement is the Profit and loss account and Balance sheet. These reports are made available to users. Once the financial statement for a period is reported it is said to be the completion of the cycle. A new accounting cycle begins thereafter. Previous year closing balances becomes the opening balance for the current cycle.
Q2: Why is the evidence provided by source documents important to accounting?
Ans: The evidence provided by the source document is important because the source document is the initial document which contains of the details of the transactions that have taken place in the business. Thus the source document is important for any organization as:
- It provides confirmation to the transactions that have taken place in the organization.
- It provides a valid evidence of the transaction in the cases when the dispute may likely arise and the matters are taken into courts.
- It contains all the relevant details of the transactions such as date of the transactiona, amount involved in the transaction, parties involved in the transaction, particulars of the transaction etc.
- It acts as a check during the process of auditing.
Q3: Should a transaction be first recorded in the journal or ledger? Why?
Ans: All the transactions should be recorded in the journal first and then in the ledger. Journal entries of all the transactions have to be passed as and when they occur in the chronological order in the course of the business and for the very reason the journal book is also referred to as day book. Journal is also referred to as the book of the original entry as it encompasses of all the details of the transactions such as the date of the transactions, the parties involved, the amount of the transactions which is directly made from the source documents. The postings in the ledger account are made after when the entries are made in the journal book. Journal is the first book in which the transactions are recorded from the source documents Journal gives complete details about a transaction.
Q4: Are debits or credits listed first in journal entries? Are debits or credits indented?
Ans: Accounting follows the double entry system as per which there are two sides namely "Debit‟ and "Credit‟. In the journal entries, the column of "Debit Amount" comes prior to the column of the "Credit Amount‟. Thus the side which indented and posted lately is the credit side.
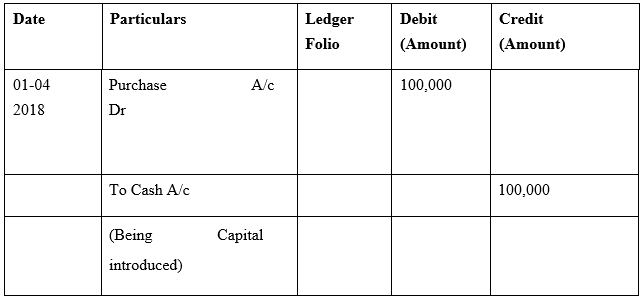
Q5: Why are some accounting systems called double accounting systems?
Ans: The double accounting system refers to the system of accounting in which the transaction is recorded in the two side of the account, namely Debit and Credit. Under the double entry system of accounting, the effect made on the one side of the account is made in simultaneous manner to the other side of the account. This is hence the widely recognized system of accounting which systematically records the transactions and gives the actual financial position of the business. The other method of accounting is the single entry system in which the transactions are recorded in the single side of the account only.
Q6: Give a specimen of an account.
Ans: 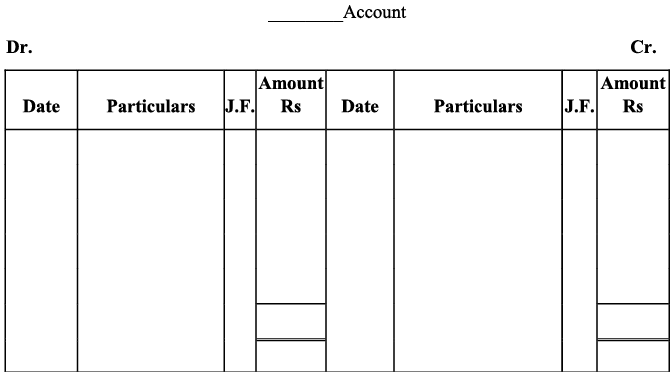
Q7: Why are the rules of debit and credit the same for both liability and capital?
Ans: As per the business entity concept, business is considered to be a legal entity which has its own individual existence which is apart from the existence of the owner. Any business has a number of the sources to fund itself which can be both internal as well as external. He amount invested by the owner of the business is known as capital which is hence regarded to be the internal source of the business fund. Thus the amount invested by the owner of the business is a liability for the business as it is liable o repay the invested amount back in the case when the business is about to close. In a similar manner the amount withdrawn by the owner of the business and the net loss incurred by the business is debited from the capital as it reduces the liability of the business. Hence, the treatment given to the creditor of the business is the same treatment given to the owner of the business and hence rules of the debit and credit are same for both liability and capital.
Q8: What is the purpose of posting J.F. numbers in the journal at the time entries are posted to the accounts?
Ans: The Journal Folio numbers are used as reference to denote the page numbers of the journal entry book in which the particular transactions is recorded. This hence allows the users to directly take the reference of the transaction in the journal entry book from the ledger account. This hence allows the users to track the information in the corresponding manner and verify the details of the transactions in a corresponding manner from the book of journal entries.
Q9: What entry (debit or credit) would you make to:
(a) increase revenue
(b) decrease in expense,
(c) record drawings
(d) record the fresh capital introduced by the owner.
Ans:
(a) Increase in revenue: For this case, Income / Gain should be credited as it increases the revenue of the business making the rise in the amount of the capital.
(b) Decrease in expense: The expenses are usually debited in the books of account. But in this case, the expenses are decreasing implying that reverse treatment should be given and hence the expenses have to be credited.
(c) Record drawings: Drawings refer to the withdrawal of a certain amount from the amount of capital which thereby reduces the amount of the capital. Hence this should be debited in the books of accounts.
(d) Record the fresh capital introduced: Whenever the fresh capital is reduced in the business it must be credited as it increases the liability of the business by giving rise of the capital in the business.
Q10: If a transaction has the effect of decreasing an asset, is the decrease recorded as a debit or as a credit? If the transaction has the effect of decreasing a liability, is the decrease recorded as a debit or as a credit?
Ans: The purchase of the asset is recorded as the debit in the books of account and hence the effects that cause the decrease in the value of the asset will be credited in the books of account. For example, the sale of the asset of the business causes a decrease in the value of the asset and hence such a sale will be credited.
The decrease in the liabilities of the business is debited in the books of accounts as the liabilities are recorded on the credit side of the book. For example, the drawings made by the owner of the business decrease the liability of the capital invested by the organization and hence such transactions will be shown on the debit side.
Long Question Answers
Q1: Describe the events recorded in an accounting system and the importance of source documents in those systems.
Ans: Any business goes through a large number of voluminous transactions on a day-to-day basis and hence is not possible for anyone to remember the details of the transactions. Thus the accounting system allows the organization to record the transactions and keep track of them. These transactions are made on the basis of the source documents which are used as support documents to account and record the transactions.
Only the monetary events are recorded in the books of accounts with the help of supporting documents. These transactions include:
- Credit sale recorded using invoice.
- Purchases are recorded using bill/invoice.
- Cash Sale recorded using Cash memo.
- Bank deposits made and recorded using bank pay-in-slips
- Expenses paid through bank are supported by cheques.
- Purchase returns and Sales returns were recorded using debit notes and credit notes respectively.
The importance of the source document in accounting is as follows:
- It confirms the occurrence of the transactions which has taken place.
- It is valid evidence that can be presented during court proceedings in case of any kind of dispute related to the transaction.
- It contains the necessary details of the transactions such as the parties involved, the amount involved, the date of the transaction, particulars of the transaction etc.
- It acts as a check during the process of auditing.
Q2: Describe how debits and credits are used to analyze transactions.
Ans: As per the dual concept of accounting all the recorded transactions in the books of accounts have two aspects – debit and credit. With the effect on the aspect of the transaction, there is a simultaneous and corresponding effect on the other side of the account. An example of such a transaction is as follows:
A business sells goods of worth Rs. 500 on the 1st April 2018. Thus the books of account will debit the cash received from such transaction and credit the sales in a simultaneous manner in this transaction. In this example, there is sale of the goods that the business deals with cash coming into the business.
There are three kinds of accounts in accountancy which are:
- Personal Account: These are the accounts that deal with persons. The rule of the personal account is that the receiver must be debited and the giver must be credited. Example: Bank A/c represents a bank, an organisation.
- Real Account: These are accounts that deal with assets of a material nature. The rule for the real account is: Debit what comes in and credit what goes out. Example: Furniture A/c, Machinery, Goodwill A/c etc.
- Nominal accounts: These are the accounts that deal with all kinds of expenses/ incomes. The rule of accounting for the real account is: Debit is all the expenses/ losses and all income/gains should be credited.
Example: Salary A/c, Telephone charges A/c, Interest earned, etc.
Q3: Describe how accounts are used to record information about the effects of transactions.
Ans: The journal entry gives a clear picture of particular transactions but it is difficult to asses information about any particular account when there is a chain of transactions related to it. Hence in such a case, the ledger accounts become important as they maintain systematic accounts in tabular format which helps the user to determine the details of the transaction for the particular account. This can be better understood with an example.
01.01.17- Credit Sale is made to Ram for Rs.10000
05.01.17- Goods worth Rs.2000 is returned from Ram
08.01.17- Cheque received Rs.5000 on account from Ram
10.01.17- Cash received Rs.1000 on account from Ram
Now this is posted in the Journal on various dates. A clear picture can be seen only when the entries are posted in the ledger account of Ram. The balance amount receivable from Ram is clearly shown in the ledger below.
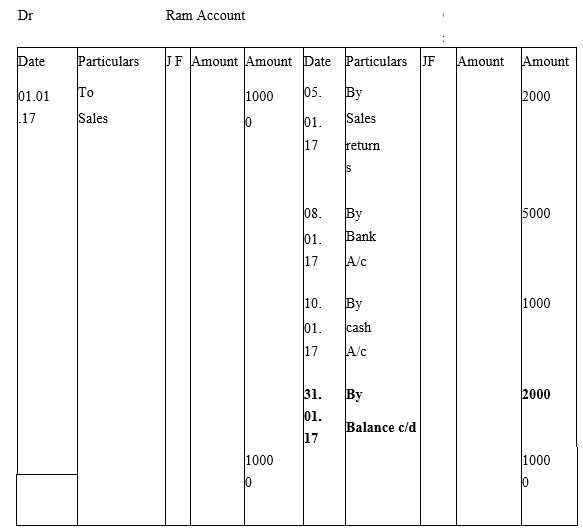
Q4: What is a journal? Give a specimen of a journal showing at least five entries.
Ans: Journal is derived from the French word “Jour”, the meaning of which is “daily records”. Journal thus records the day-to-day transactions of the business in a chronological manner and hence is also called as the “Day Book”. The format of the journal is given below.
The format of the journal is shown below:
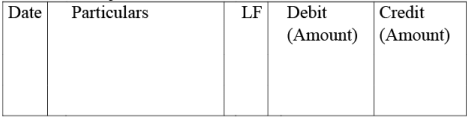 Date: The date of the transaction in which the transaction has occurred so that the journal could be made and maintained in the chronological manner from the source document.
Date: The date of the transaction in which the transaction has occurred so that the journal could be made and maintained in the chronological manner from the source document.
Particulars: The accounts which have to be debited/ credited.
LF: Ledger Folio– It is the reference to the Ledger Page for the particular account.
Debit: The amount which has to be debited is recorded here.
Credit: The amount which has to be credited is recorded here.
Example:
Journalise the below-mentioned transactions in the books of Geeta:
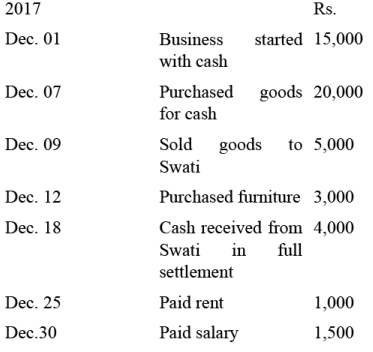
Q5: Differentiate between source documents and vouchers.
Ans: 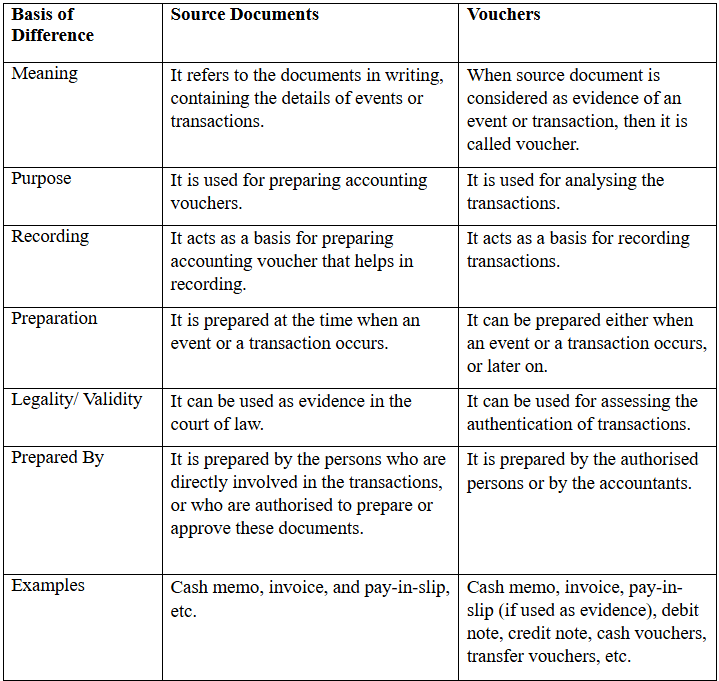
Q6: The accounting equation remains intact under all circumstances. Justify the statement with the help of an example.
Ans: The double-entry accounting system states that or every debit there is an equal amount of credit. However, there is unlikely to be the equality of the total assets with the total claims of the business and the accounting equation will persist to be Assets = Liabilities+ Capital. Hence this equation will remain intact under all the circumstances. The examples for the same are as follows:
a. Mr A started a business with cash Rs.100000
Assets = Liabilities+ Capital
Cash increases by 100000
And Capital 100000
100000 = 0+100000
b. Purchased goods on credit for Rs.30000
Assets (Inventory) =30000
Creditors = 30000
Assets = Liabilities +Capital
30000= 30000+0
Q7: Explain the double entry mechanism with an illustrative example.
Ans: As per the double entry system of accounting, every transaction has two aspects debit and credit. Hence the double-entry accounting system states that for every debit there is an equal amount of credit. Thus the ledger account always shows the debit on one side and the credit on the other side to abide by the dual aspect concept.
The three golden rules of accounting must be known in passing an entry:
1. Personal Account- Debit the receiver
Credit the giver
2. Real Account - Debit what comes in
Credit what goes out
3. Nominal accounts- Debit the expenses/ losses
Credit the income/gain
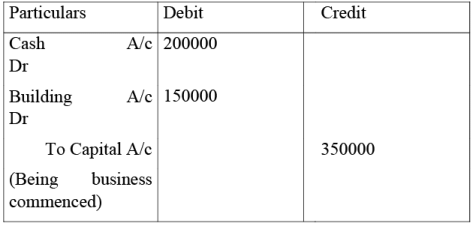
Example: Mr Shyam commenced business with Cash Rs. 200000 and building Rs.150000.
Analysis: In the above transaction Cash comes in Rs. 200000 and building comes in Rs. 150000. On the other hand liability to be paid to the proprietor i.e. Capital increase is Rs. 350000.
Journal Entry in the books of Shyam
Numerical Questions
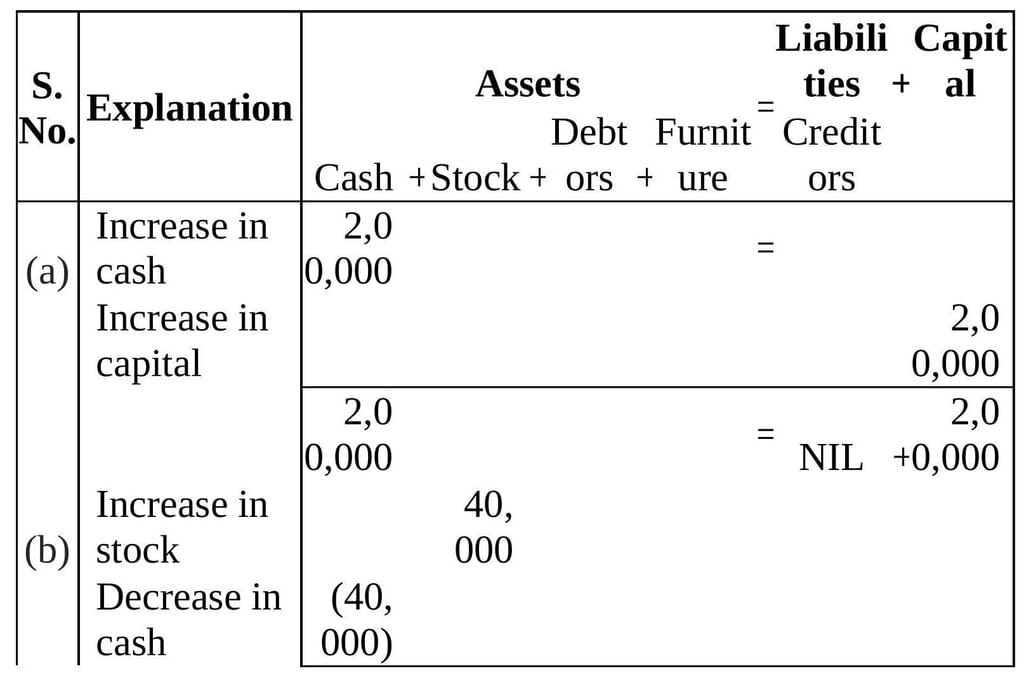
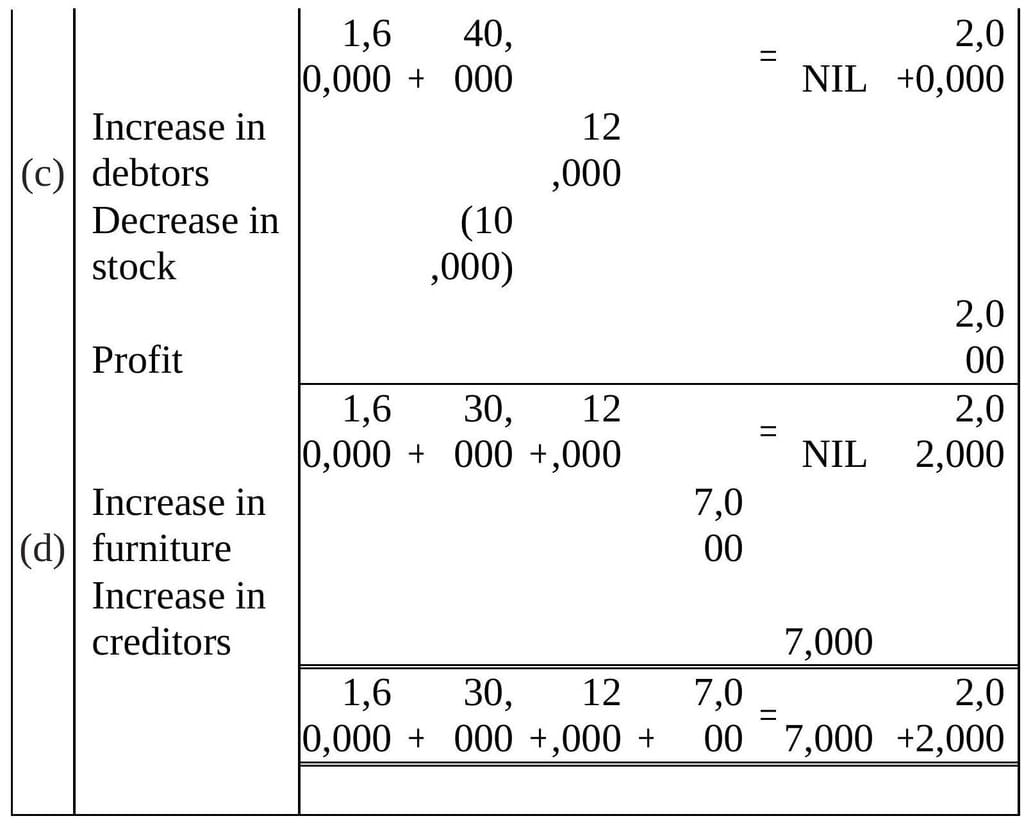
Q1: Prepare accounting equation on the basis of the following:
(a) Harsha started business with cash Rs 2,00,000
(b) Purchased goods from Naman for cash Rs 40,000
(c) Sold goods to Bhanu costing Rs 10,000 for Rs 12,000
(d) Bought furniture on credit Rs 7,000
Ans: The accounting equation is given by:
Assets = Capital + Liabilities
Accounting Equation Calculation:
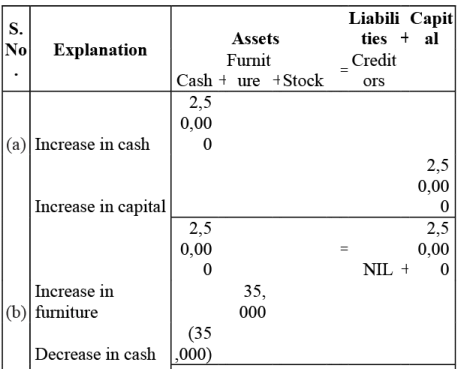
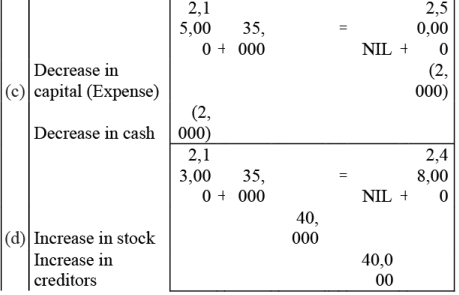
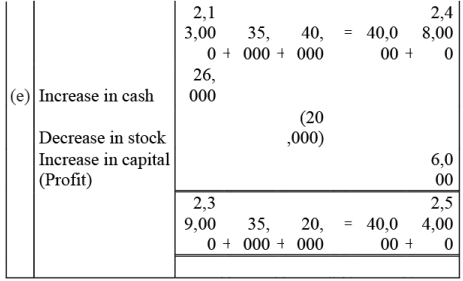
Q2: Prepare accounting equation from the following:
(a) Kunal started business with ₹2,50,000 cash
(b) He purchased furniture for ₹35,000 cash
(c) He paid commission ₹2,000
(d) He purchases goods on credit ₹40,000
(e) He sold goods (costing ₹ 26,000) for cash ₹20,000
Ans:
Q3: Mohit has the following transactions, prepare accounting equation:
(a) Business started with cash - Rs. 1,75,000
(b) Purchased goods from Rohit - Rs. 50,000
(c) Sales goods on credit to Manish (Costing Rs 17,500) - Rs.20,000
(d) Purchased furniture for office use - Rs.10,000
(e) Cash paid to Rohit in full settlement - Rs.48,500
(f) Cash received from Manish - Rs.20,000
(g) Rent paid - Rs.1,000
(h) Cash withdrew for personal use - Rs.3,000
Ans: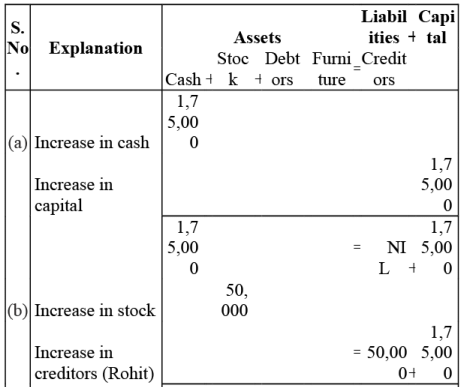

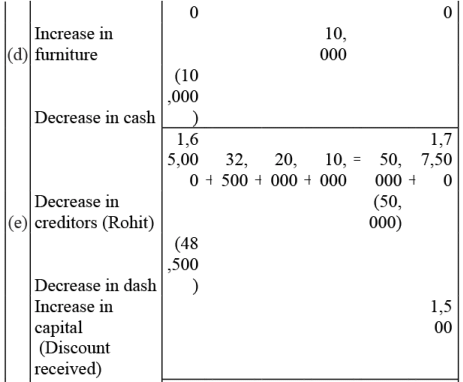
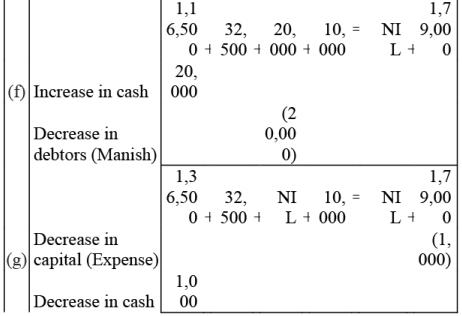
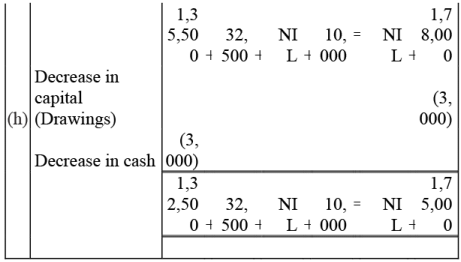
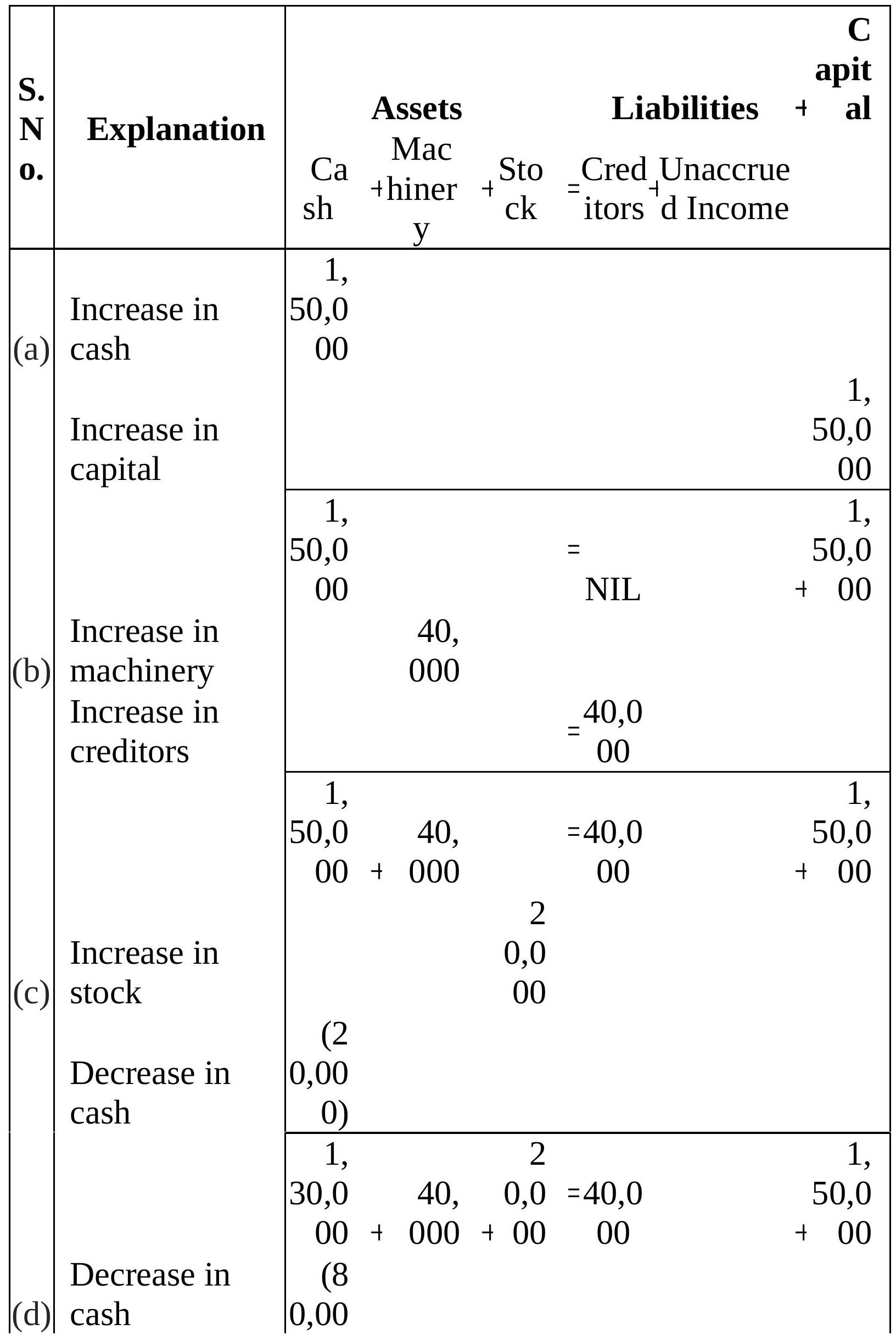
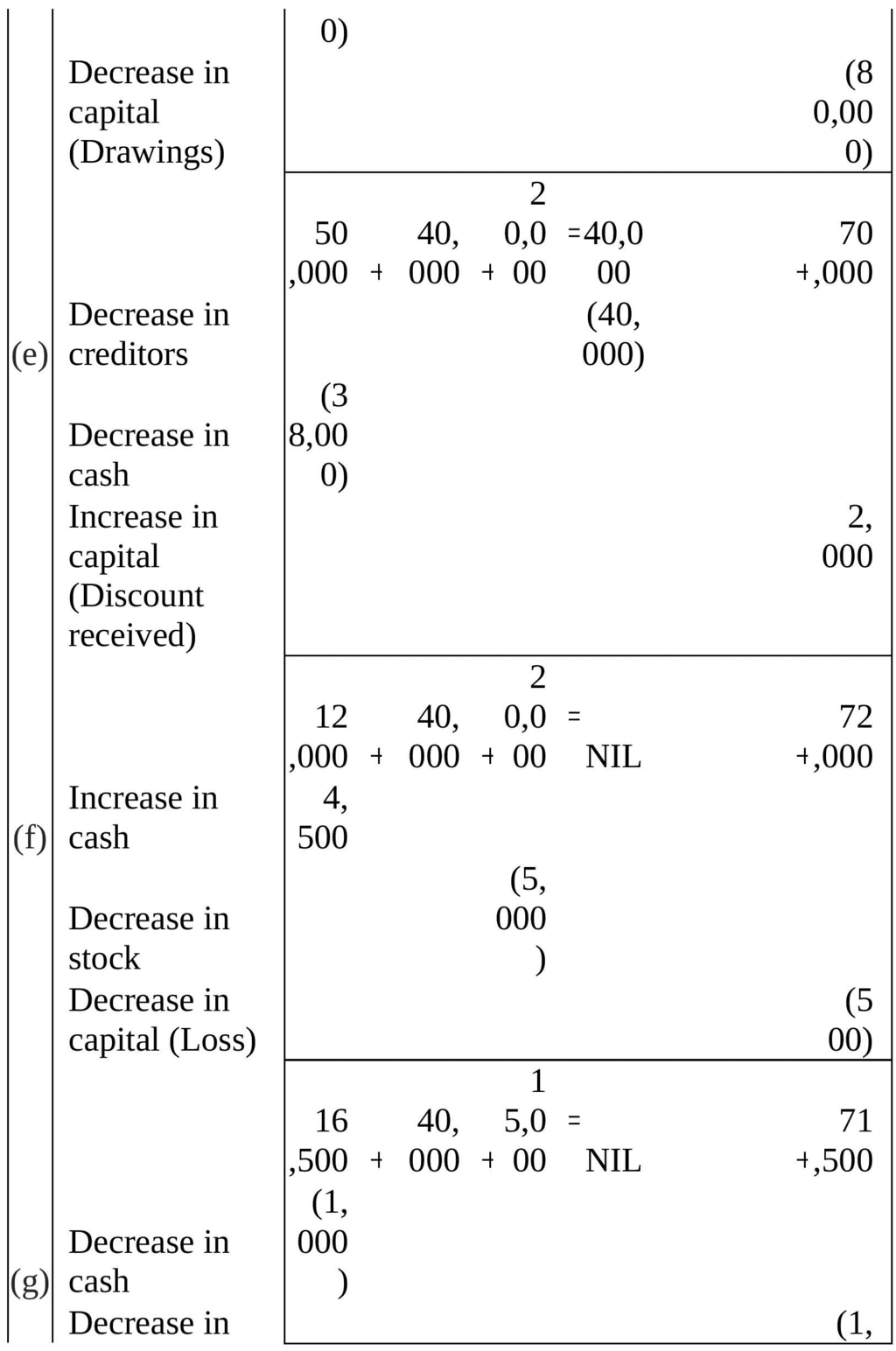
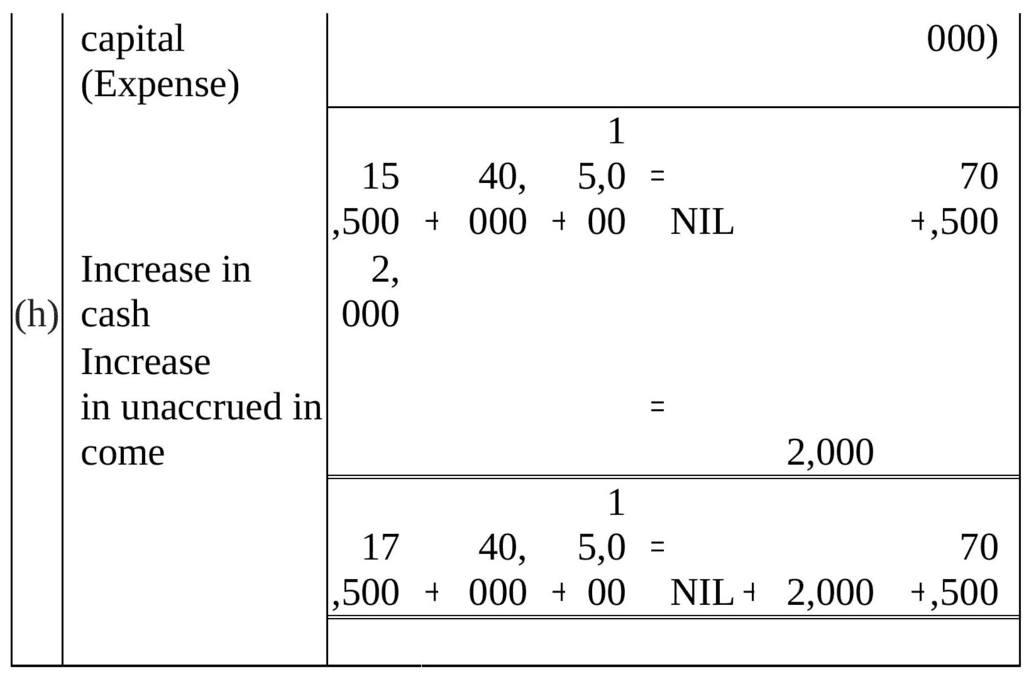
Q4: Rohit has the following transactions :
(a) Commenced business with cash - ₹1,50,000
(b) Purchased machinery on credit - ₹ 40,000
(c) Purchased goods for cash - ₹ 20,000
(d) Purchased car for personal use - ₹ 80,000
(e) Paid to creditors in full settlement - ₹ 38,000
(f) Sold goods for cash costing ₹ 5,000 - ₹ 4,500
(g) Paid rent - ₹ 1,000
(h) Commission received in advance - ₹ 2,000
Prepare the Accounting Equation to show the effect of the above transactions on the assets, liabilities and capital.
Ans:
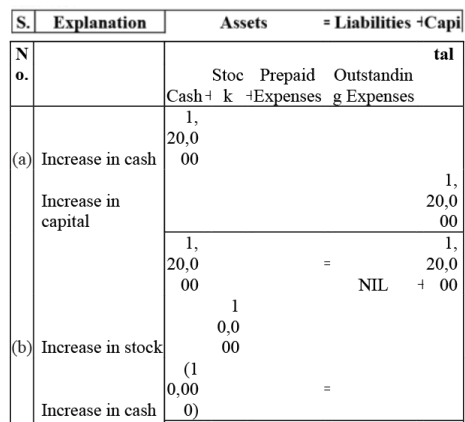
Q5: Use accounting equation to show the effect of the following transactions of M/s Royal Traders:
(a) Started business with cash - ₹1,20,000
(b) Purchased goods for cash - ₹ 10,000
(c) Rent received - ₹ 5,000
(d) Salary outstanding - ₹ 2,000
(e) Prepaid Insurance - ₹ 1,000
(f) Received interest - ₹ 700(g) Sold goods for cash (Costing ₹ 5,000) - ₹ 7,000
(h) Goods destroyed by fire - ₹ 500
Ans:
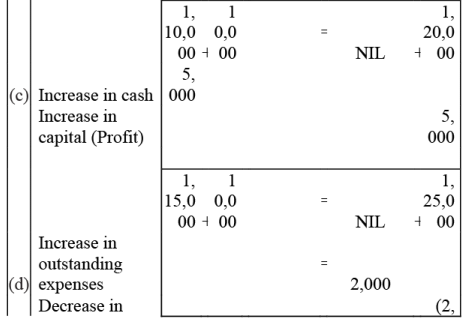


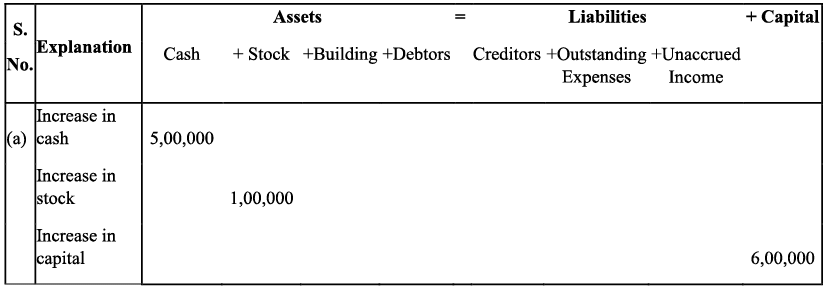
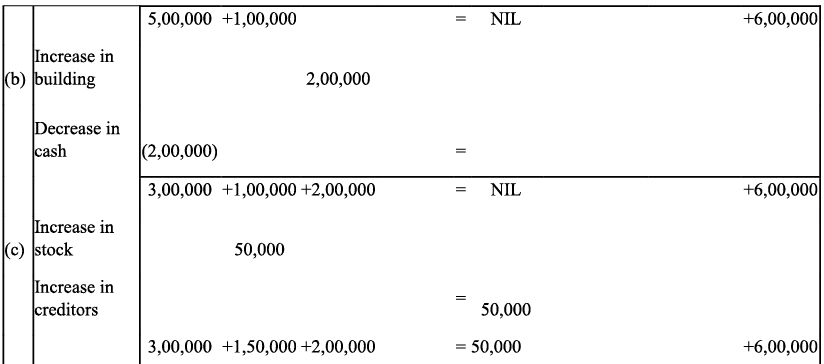
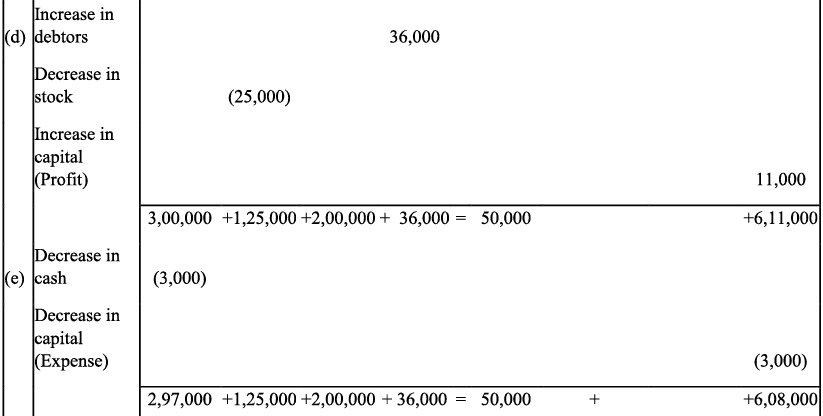
Q6: Show the accounting equation on the basis of the following transaction:
(a) Udit started business with:
(i) Cash - ₹ 5,00,000
(ii) Goods - ₹ 1,00,000
(b) Purchased building for cash - ₹ 2, 00,000
(c) Purchased goods from Himani - ₹ 50,000
(d) Sold goods to Ashu (Cost ₹ 25,000) - ₹ 36, 000
(e) Paid insurance premium - ₹ 3,000
(f) Rent outstanding - ₹ 5,000
(g) Depreciation on building - ₹ 8,000
(h) Cash withdrawn for personal use - ₹ 20,000
(i) Rent received in advance - ₹ 5,000
(j) Cash paid to himani on account - ₹ 20,000
(k) Cash received from Ashu - ₹ 30,000
Ans:


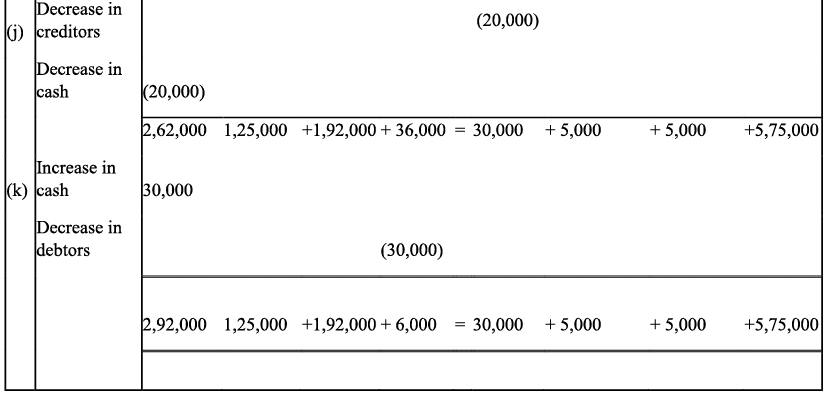
Q7: Show the effect of the following transactions on Assets, Liabilities and Capital through accounting equation:
(a) Started business with cash ₹ 1,20,000
(b) Rent received ₹ 10,000
(c) Invested in shares ₹ 50,000
(d) Received dividend ₹ 5,000
(e) Purchase goods on credit from Ragani ₹ 35,000
(f) Paid cash for household Expenses ₹ 7,000
(g) Sold goods for cash (costing ₹10,000) ₹ 14,000
(h) Cash paid to Ragani ₹ 35,000
(i) Deposited into bank ₹ 20,000
Ans: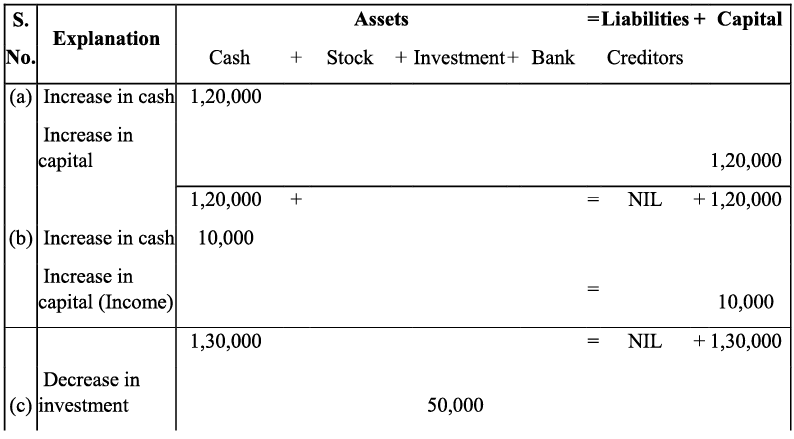

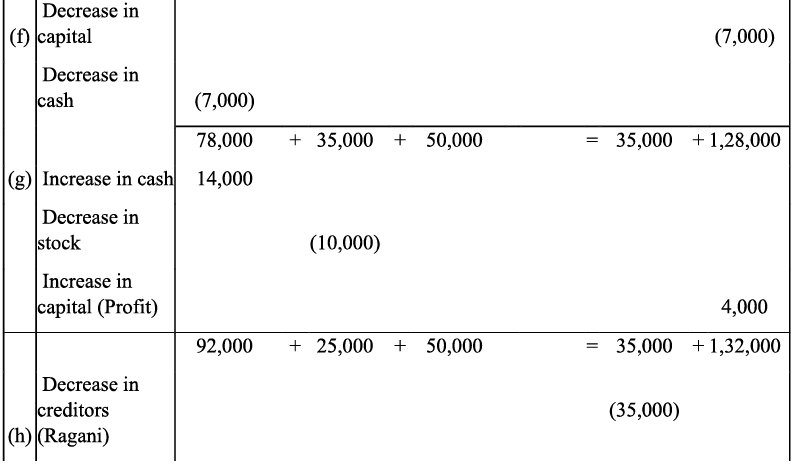
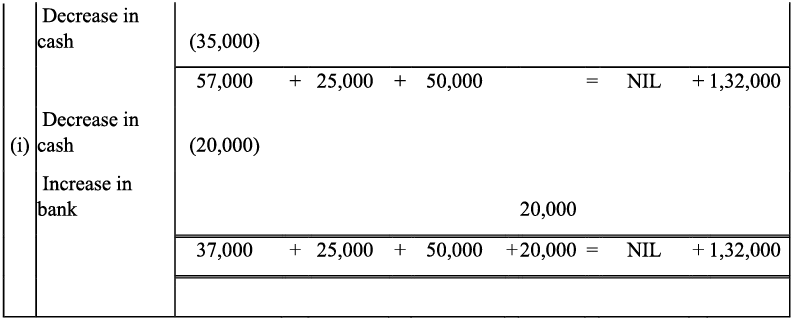
Q8: Show the effect of following transaction on the accounting equation:
(a) Manoj started business with
(i) Cash ₹ 2,30,000
(ii) Goods ₹ 1,00,000
(iii) Building ₹ 2,00,000
(b) He purchased goods for cash ₹ 50,000
(c) He sold goods (costing ₹20,000) ₹ 35,000
(d) He purchased goods from Rahul ₹ 55,000
(e) He sold goods to Varun (Costing ₹ 52,000) ₹ 60,000
(f) He paid cash to Rahul in full settlement ₹ 53,000
(g) Salary paid by him ₹ 20,000
(h) Received cash from Varun in full settlement ₹ 59,000
(i) Rent outstanding ₹ 3,000
(j) Prepaid Insurance ₹ 2,000
(k) Commission received by him ₹ 13, 000
(l) Amount withdrawn by him for personal use ₹ 20,000
(m) Depreciation charge on building ₹ 10,000
(n) Fresh capital invested ₹ 50,000
(o) Purchased goods from Rakhi ₹ 10,000
Ans:
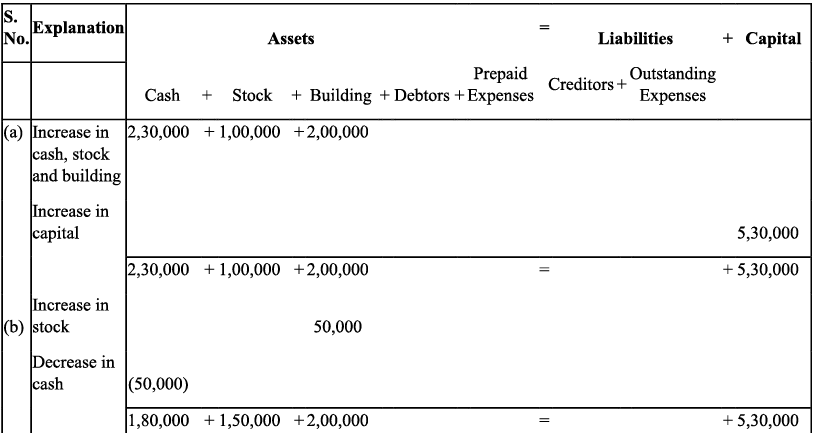

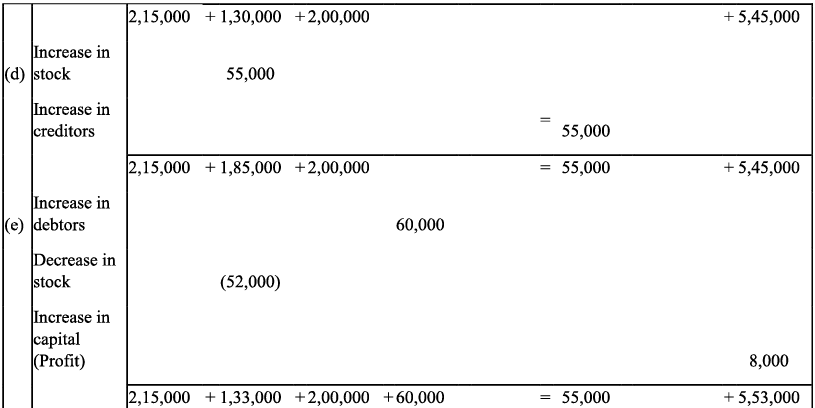
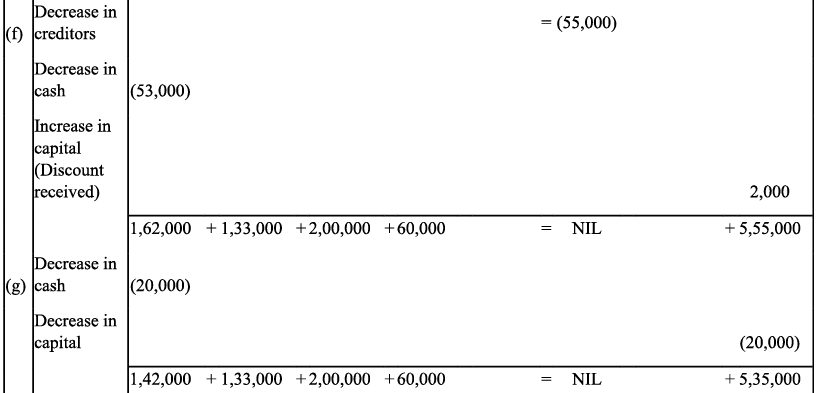

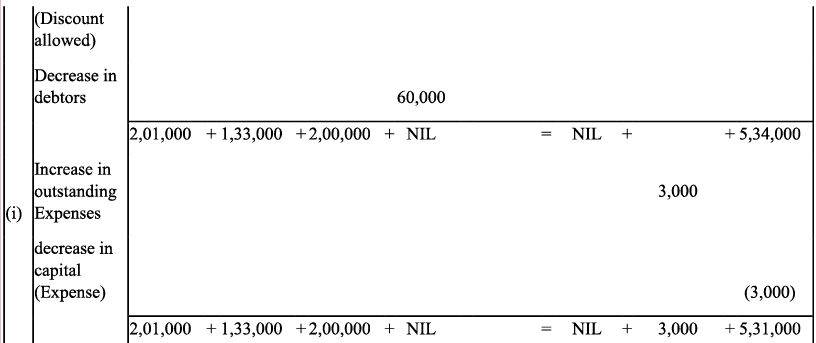
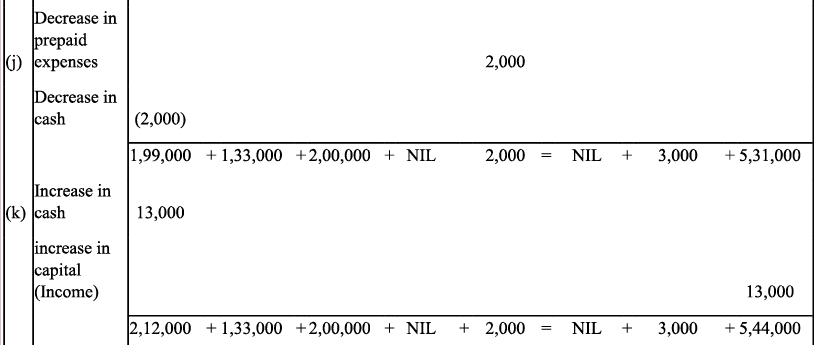
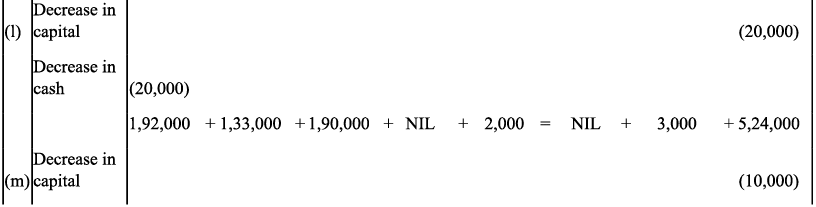
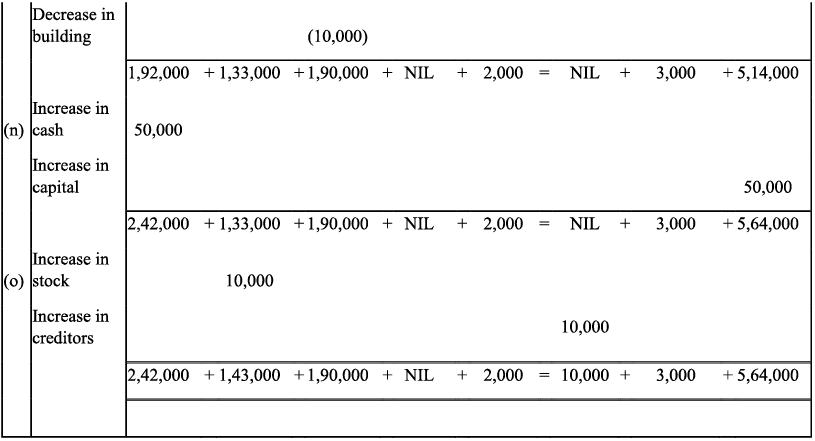
Q9: Transactions of M/s Vipin Traders are given below.
Show the effects on Assets, Liabilities and Capital with the help of accounting Equation.
(a) Business started with cash - ₹ 1,25,000
(b) Purchased goods for cash - ₹ 50,000
(c) Purchase furniture from R.K. Furniture - ₹ 10,000
(d) Sold goods to Parul Traders (Costing ₹ 7,000 vide bill no. 5674) - ₹9,000
(e) Paid cartage - ₹ 100
(f) Cash Paid to R.K. furniture in full settlement - ₹ 9,700
(g) Cash sales (costing ₹10,000) - ₹ 12,000
(h) Rent received - ₹ 4,000
(i) Cash withdrew for personal use - ₹ 3,000
Ans: 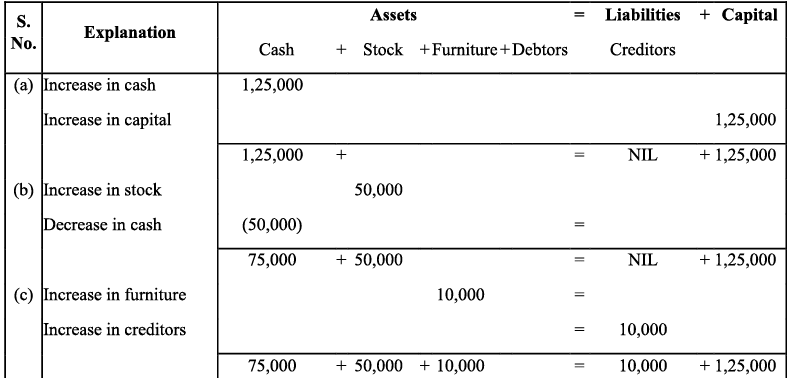


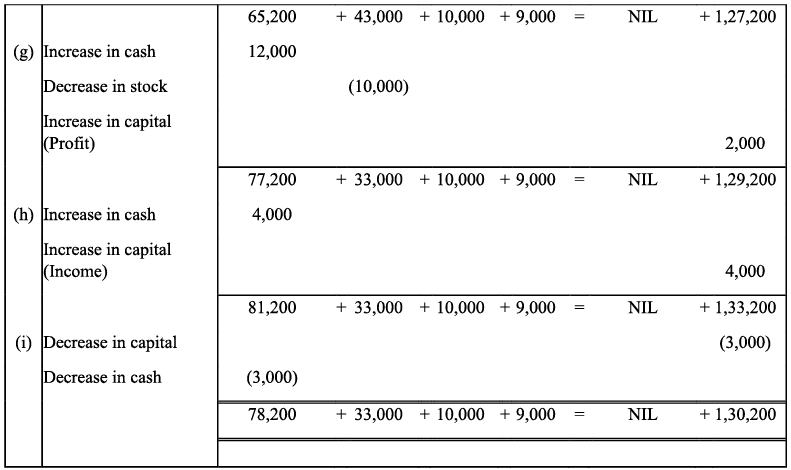
Q10: Bobby opened a consulting firm and completed these transactions during November, 2017:
(a) Invested ₹ 4,00,000 cash and office equipment with ₹ 1,50,000 in a business called Bobbie Consulting.
(b) Purchased land and a small office building. The land was worth ₹ 1,50,000 and the building worth ₹ 3, 50,000. The purchase price was paid with ₹ 2,00,000 cash and a long term note payable for ₹ 3,00,000.
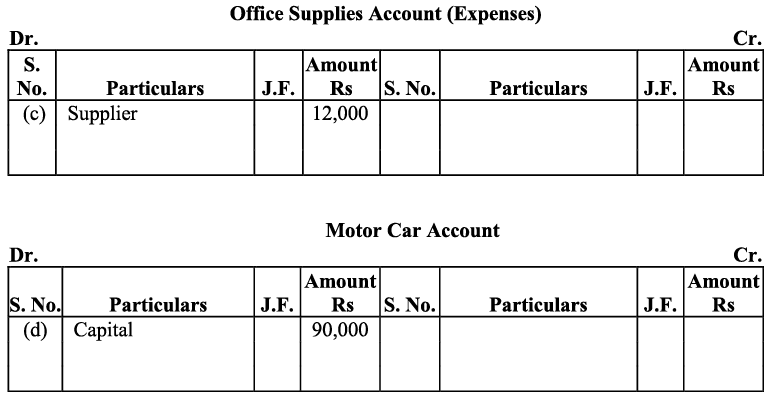
(c) Purchased office supplies on credit for ₹ 12,000.
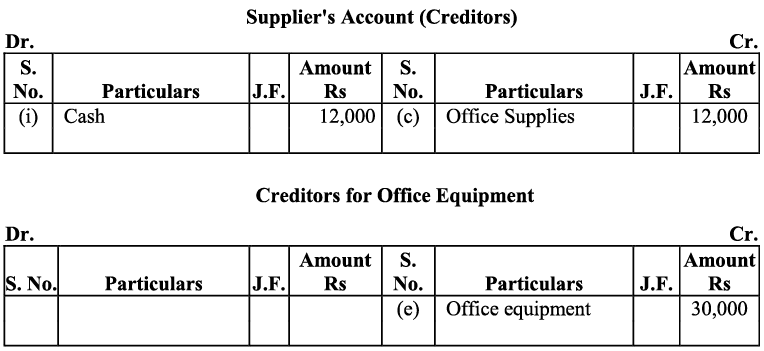
(d) Bobbie transferred title of motor car to the business. The motor car was worth ₹ 90,000.
(e) Purchased for ₹ 30,000 additional office equipment on credit.
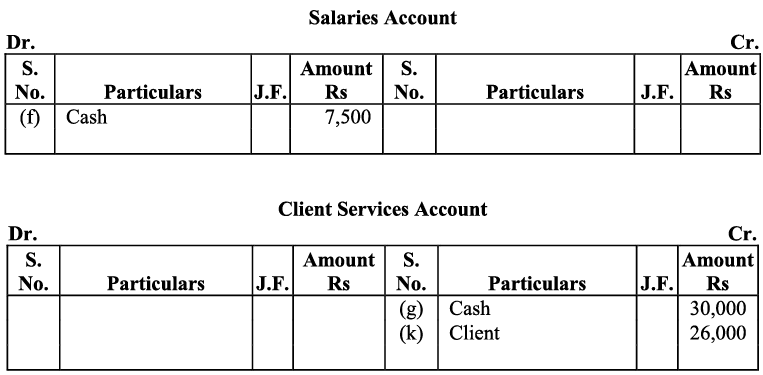
(f) Paid ₹ 75,00 salary to the office manager.
(g) Provided services to a client and collected ₹ 30,000
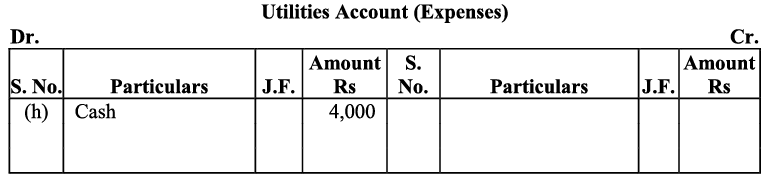
(h) Paid ₹ 4,000 for the month’s utilities.
(i) Paid supplier created in transaction c.
(j) Purchase new office equipment by paying ₹ 93,000 cash and trading in old equipment with a recorded cost of ₹ 7,000.
(k) Completed services of a client for ₹ 26,000. This amount is to be paid within 30 days.
(l) Received ₹ 19,000 payment from the client created in transaction k.
(m) Bobby withdrew ₹ 20,000 from the business.
Analyse the above stated transactions and open the following T-accounts: Cash, client, office supplies, motor car, building, land, long term payables, capital, withdrawals, salary, expense and utilities expense.
Ans:
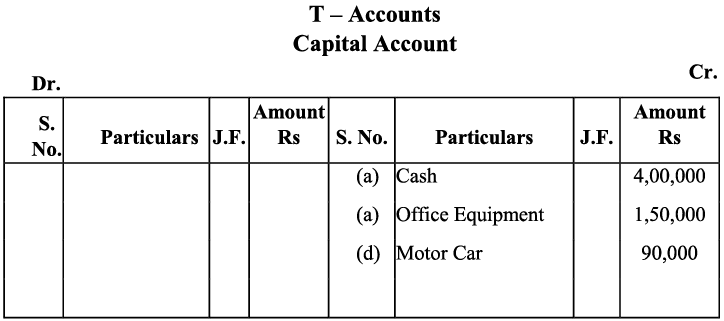
a) The transaction (a) increases assets by Rs 5,50,000 (cash Rs 4,00,000 and office equipment Rs 1,5,000) it will be debited and on the other hand it will increase the capital by Rs 5,50,000, so it will be credited in capital account.
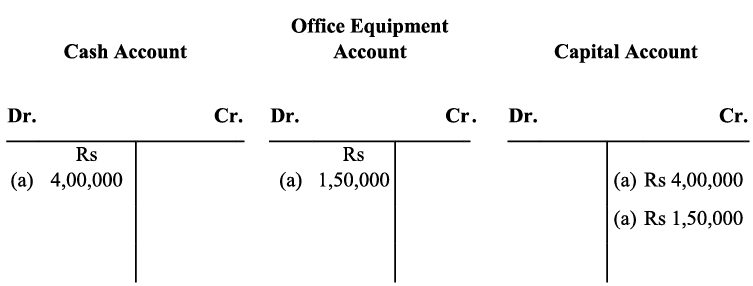
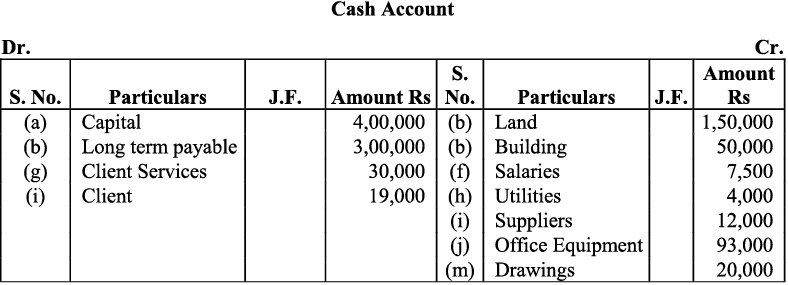
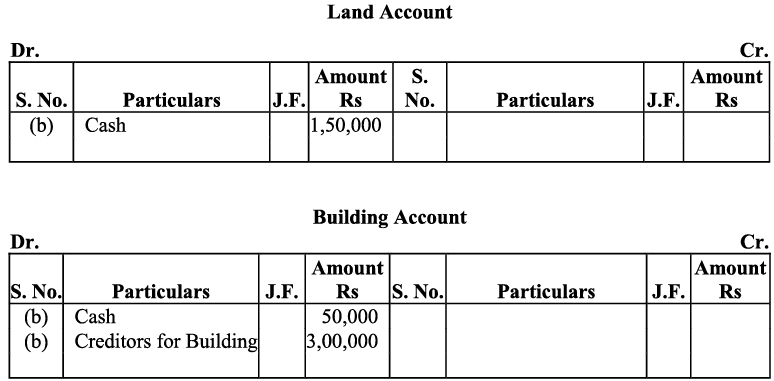
b) Purchase of land and small office buildings are assets. On one hand, the purchase of these items will increase their individual accounts and this will increase the total amount of the assets in the business; so, both the accounts will be debited. On the other hand, payment in cash on the purchase of these assets will decrease the cash balance, so the cash account will be credited to the extent of the amount paid. After payment for the building in cash, the balance of the building account will be transferred to creditors for the building account. This will increase the amount of the creditors, which in turn will increase the total liabilities of the business. Long-term payables are regarded as loan to the business that will increase both cash balance (due to intake of loan) as well as liabilities of the business.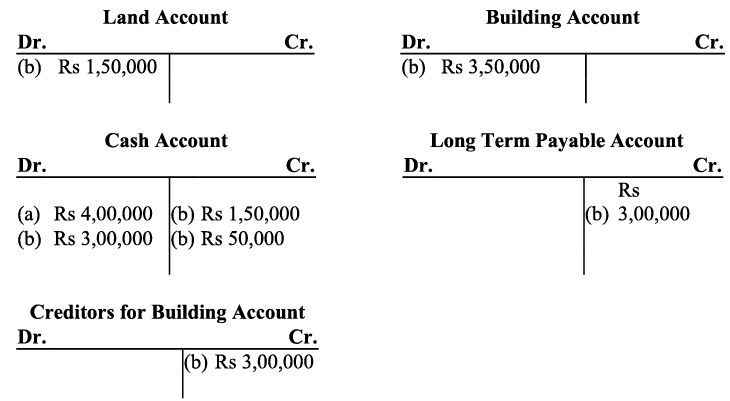 c) Here ‘office supplies’ is an expense. So, according to the golden rule, ‘All expenses are debited’, it will be debited on one hand while on the other hand, office supplies has been purchased on credit, so it will increase the liability, on account of which, supplier’s account will be credited.
c) Here ‘office supplies’ is an expense. So, according to the golden rule, ‘All expenses are debited’, it will be debited on one hand while on the other hand, office supplies has been purchased on credit, so it will increase the liability, on account of which, supplier’s account will be credited.
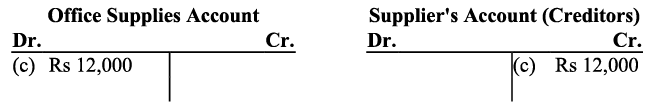 d) Amount invested (motor car) by the proprietor in the business would increase both the capital and assets.
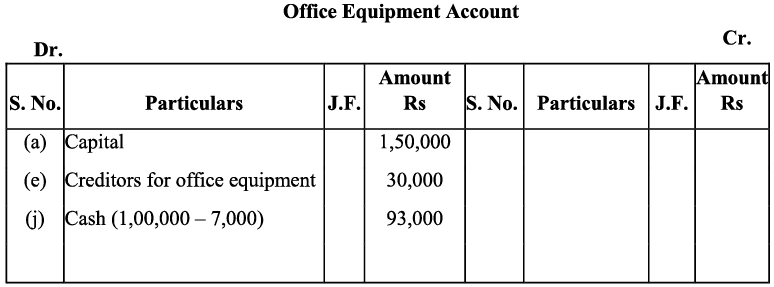
d) Amount invested (motor car) by the proprietor in the business would increase both the capital and assets.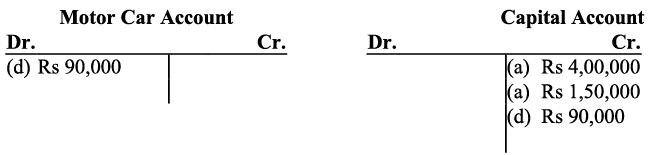 e) Purchase of additional equipment increases the assets; hence, offices equipment account will be debited.
e) Purchase of additional equipment increases the assets; hence, offices equipment account will be debited.
Further as the office equipment was purchased on credit, it increases the amount of the creditors for office equipment and the creditors account will be credited. f) Salary is an expense and as all the expenses are debited, so the payment of salary to the manager will be debited to the salary account. And on the other hand the payment of the salary in cash decreases the cash balance (Assets) so the cash account would be credited (as decrease in assets is credited).
f) Salary is an expense and as all the expenses are debited, so the payment of salary to the manager will be debited to the salary account. And on the other hand the payment of the salary in cash decreases the cash balance (Assets) so the cash account would be credited (as decrease in assets is credited).
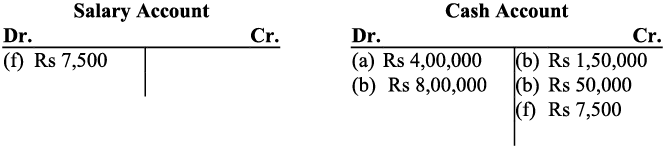
g) Amount received or receivable from services rendered to the client is revenue for the business. All revenues are to be credited so client service account will be credited.
On the other hand, cash received in exchange of services would increase the cash balance. It would be debited to the cash account.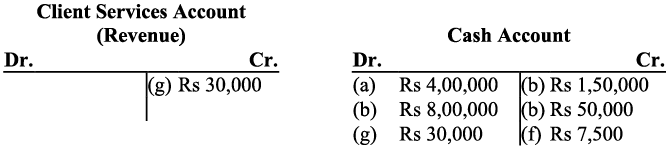 h) The ‘utilities’ has been treated as a revenue expense. All expenses are to be debited. Amount paid for utilities would be debited to Utilities account.
h) The ‘utilities’ has been treated as a revenue expense. All expenses are to be debited. Amount paid for utilities would be debited to Utilities account.
Utilities have been paid in cash so the cash account will be credited (as this decreases assets).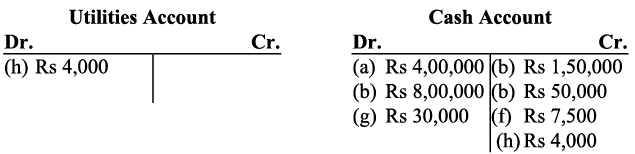
i) Payment to the supplier (creditors) will be debited. It results in the decrease in liabilities. Further as the payment has been made in cash, so it results in decrease in the cash balance (assets) and hence the cash account will be credited.
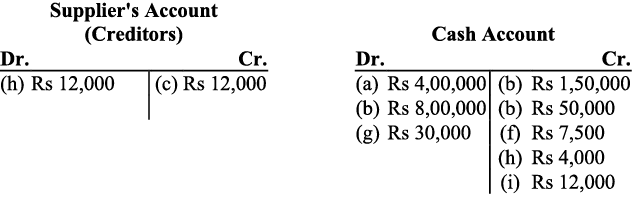 j) Purchase of the equipments will be debited in the Equipment Account (as there is increase in the assets). Also as the equipments of worth Rs. 1,00,000 and Rs. 93,000 have been purchased for cash and old equipments of worth Rs. 7,000 have been exchanged so the purchase of the equipments will be debited in the Office Equipment account and equipment of Rs. 7,000 will be credited in the same account.
j) Purchase of the equipments will be debited in the Equipment Account (as there is increase in the assets). Also as the equipments of worth Rs. 1,00,000 and Rs. 93,000 have been purchased for cash and old equipments of worth Rs. 7,000 have been exchanged so the purchase of the equipments will be debited in the Office Equipment account and equipment of Rs. 7,000 will be credited in the same account.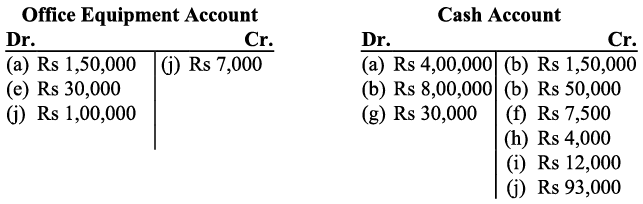
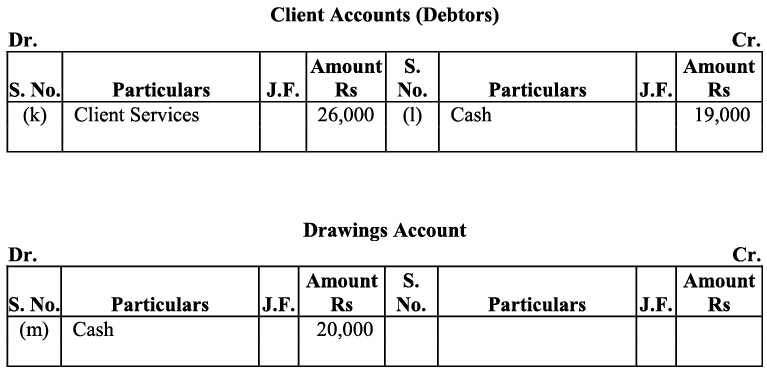
k) Receipt from ‘Client services’ is revenue. All revenues are credited. The client services account will be credited and the client is considered as debtor, so the client account will be debited. I) The client has been considered as Debtors. The amount received from the client will lead to the decrease in the debtor’s balance and the client account will be credited. Receipts from the client will increase the cash balance (asset), and hence the cash account will be debited.
I) The client has been considered as Debtors. The amount received from the client will lead to the decrease in the debtor’s balance and the client account will be credited. Receipts from the client will increase the cash balance (asset), and hence the cash account will be debited.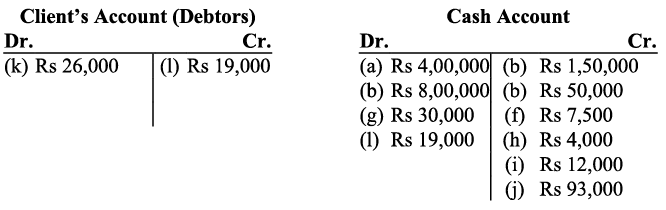 m) The amount withdrawn by the proprietor is considered as ‘drawings’. According to the Business Entity Concept, drawings decrease the owner’s capital,) Thus the drawings account will be debited (as decrease in capital is debited). On the other hand, as drawings have been made in cash, decrease in cash means cash account will be credited with the amount of drawings.
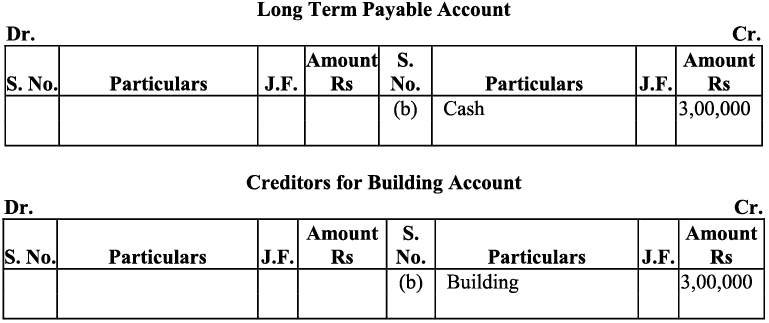
m) The amount withdrawn by the proprietor is considered as ‘drawings’. According to the Business Entity Concept, drawings decrease the owner’s capital,) Thus the drawings account will be debited (as decrease in capital is debited). On the other hand, as drawings have been made in cash, decrease in cash means cash account will be credited with the amount of drawings.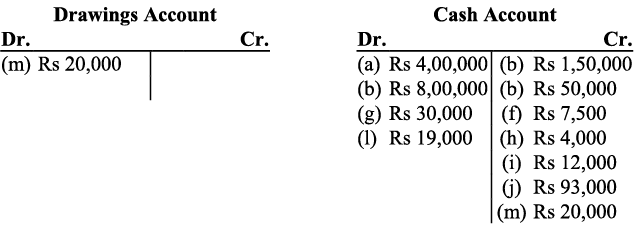
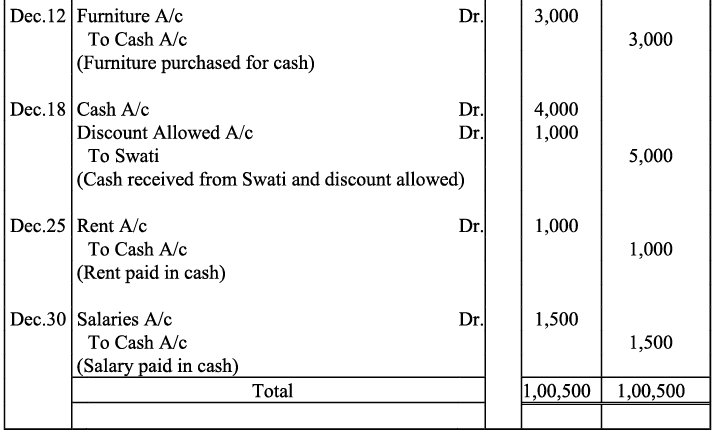
Q11: Journalise the following transactions in the books of Himanshu:
 Ans:
Ans: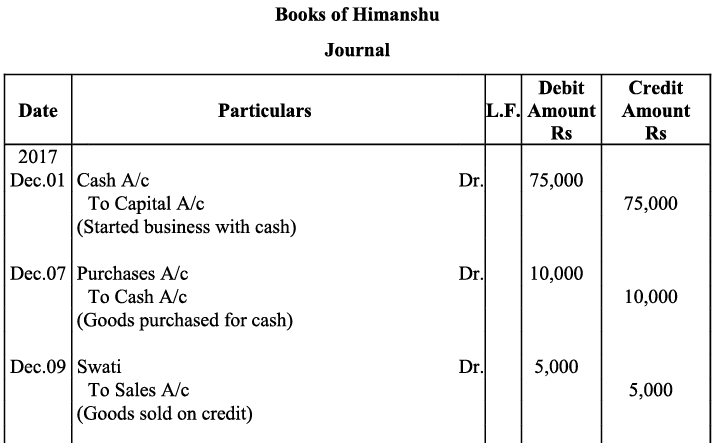
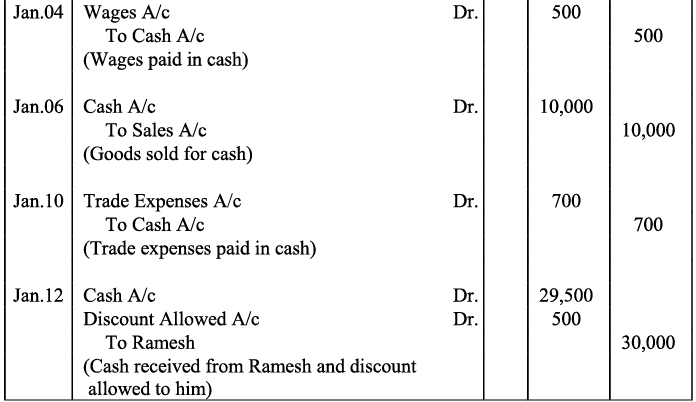
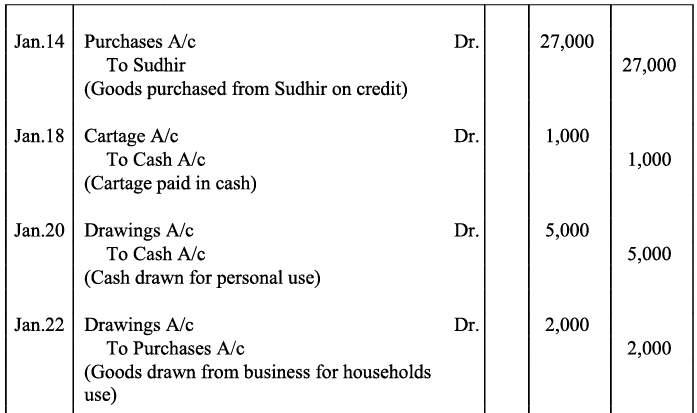
Q12: Enter the following Transactions in the Journal of Mudit :

 Ans:
Ans: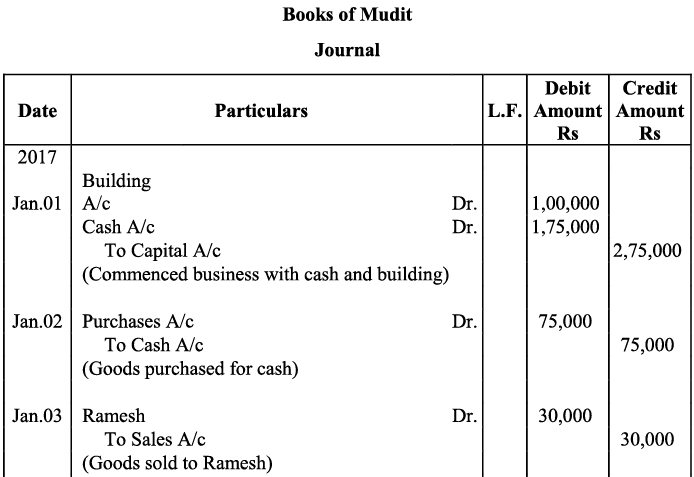

Q13: Journalise the following transactions: Ans:
Ans: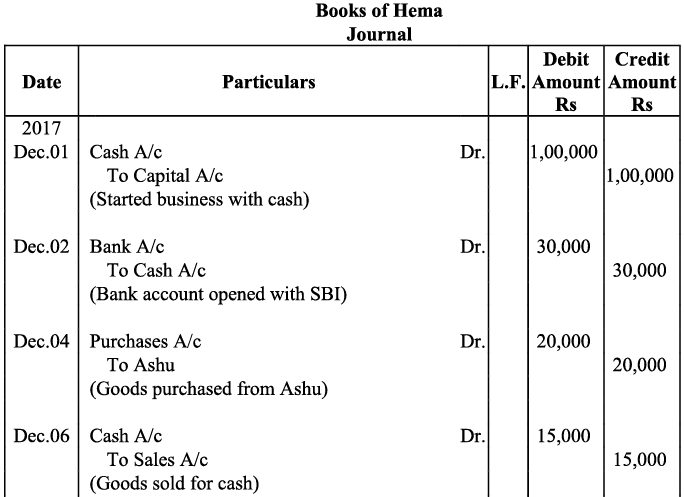
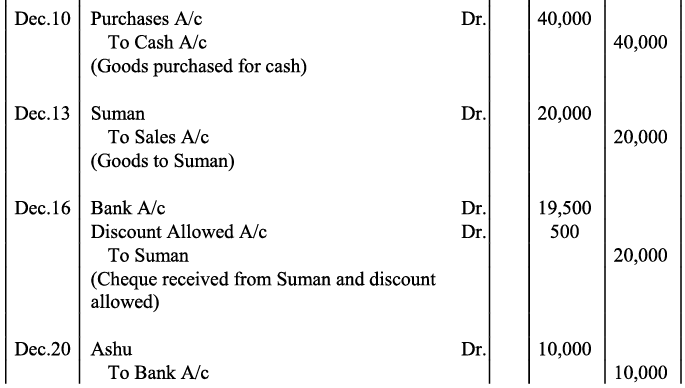
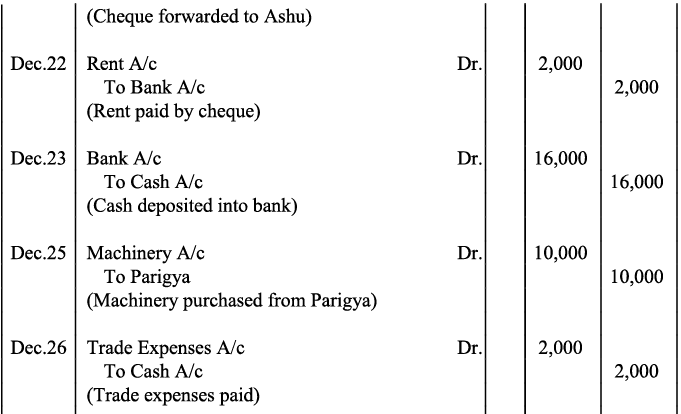
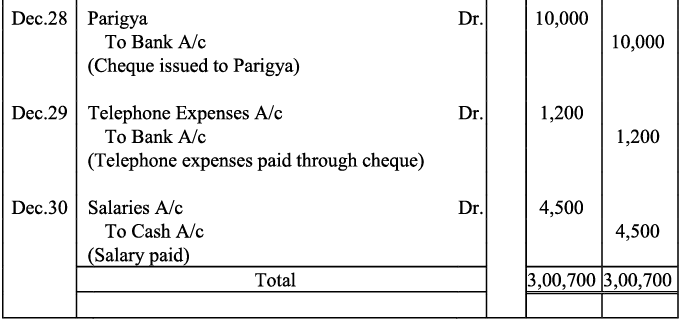
Q14: Jouranlise the following transactions in the books of Harpreet Bros.:
(a) ₹1,000 due from Rohit are now bad debts.
(b) Goods worth ₹2,000 were used by the proprietor.
(c) Charge depreciation @ 10% p.a for two month on machine costing ₹30,000.
(d) Provide interest on capital of ₹ 1,50,000 at 6% p.a. for 9 months.
(e) Rahul become insolvent, who owed is ₹ 2,000 a final dividend of 60 paise in a rupee is received from his estate.
Ans:

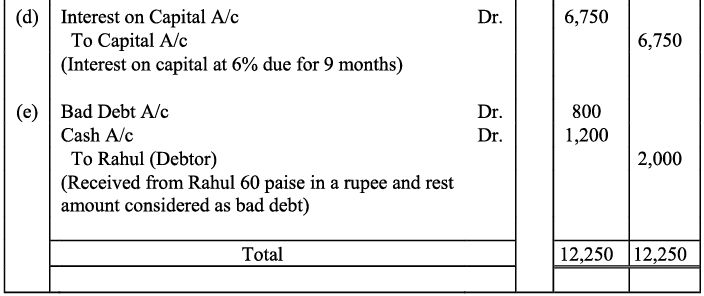
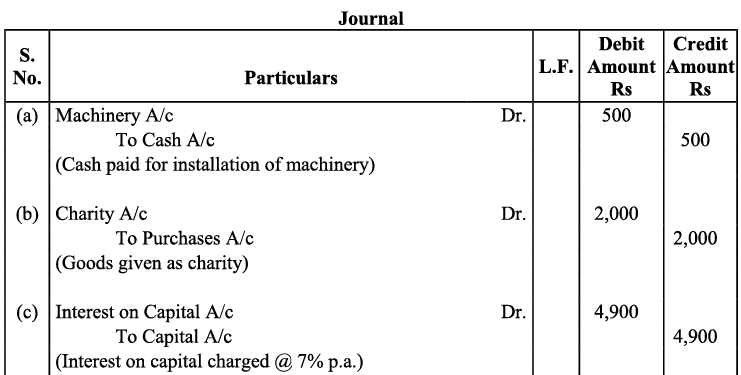
Q15: Prepare Journal from the transactions given below :
(a) Cash paid for installation of machine ₹ 500
(b) Goods given as charity - ₹ 2,000
(c) Interest charge on capital @7% p.a. when total capital were-₹ 70,000
(d) Received ₹1,200 of a bad debts written-off last year.
(e) Goods destroyed by fire - ₹ 2,000
(f) Rent outstanding - ₹ 1,000
(g) Interest on drawings - ₹ 900
(h) Sudhir Kumar who owed me ₹ 3,000 has failed to pay the amount. He pays me a compensation of 45 paise in a rupee.
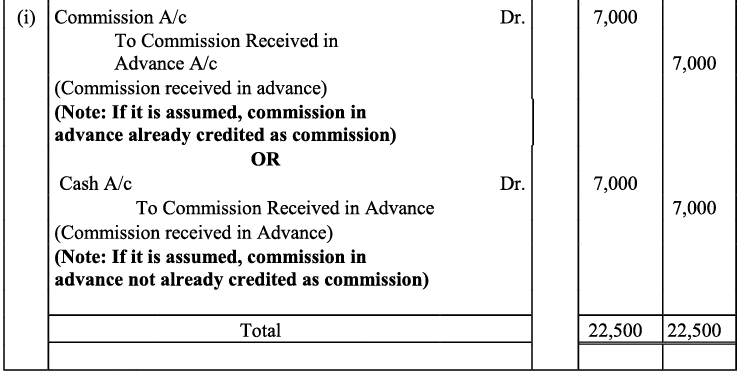
(i) Commission received in advance - ₹ 7,000
Ans:


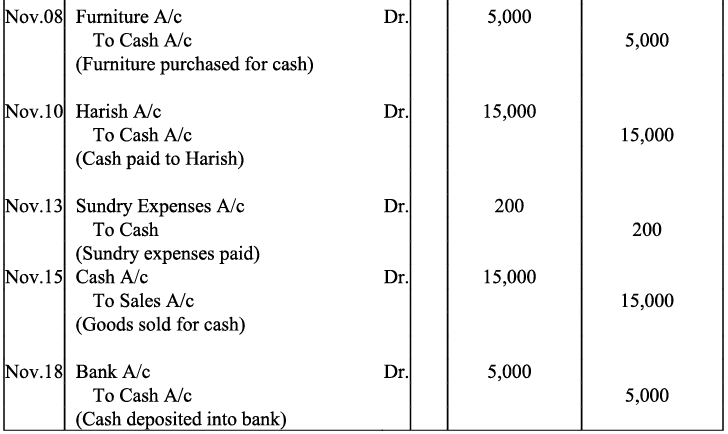
Q16: Journalise the following transactions, post to the ledger: Ans:
Ans: 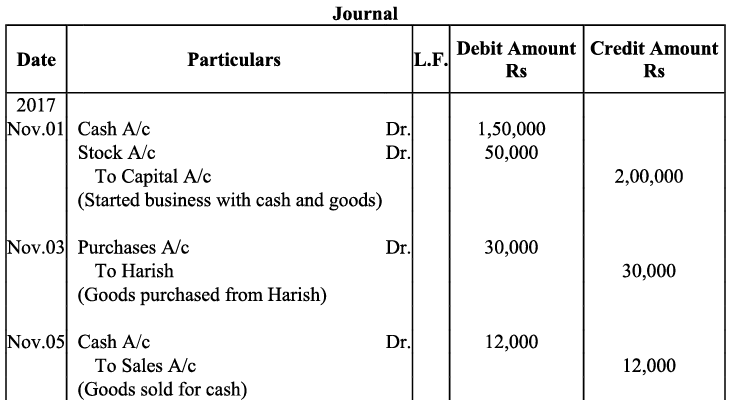

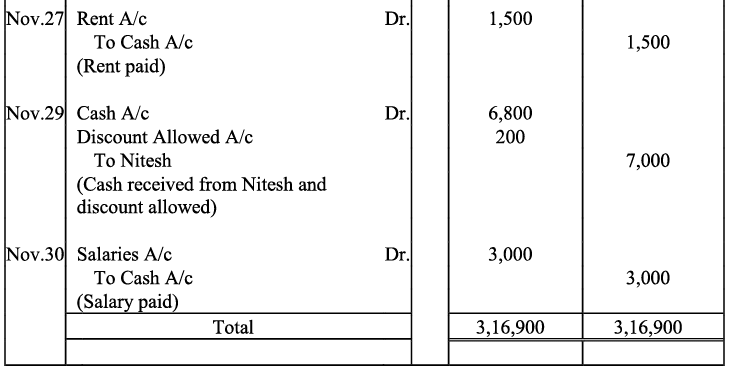
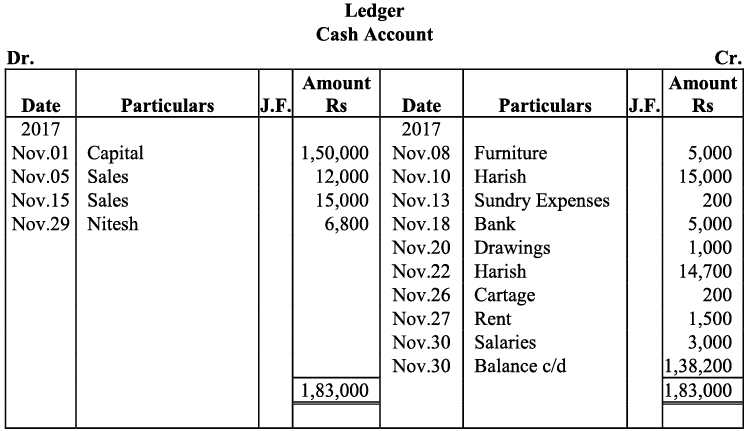
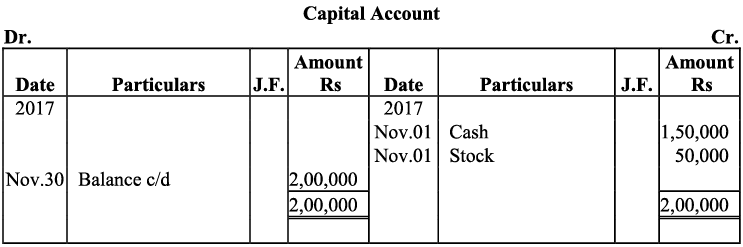
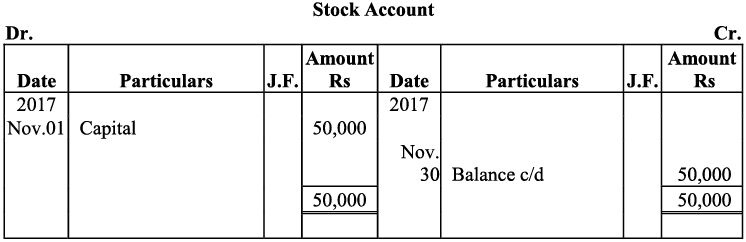
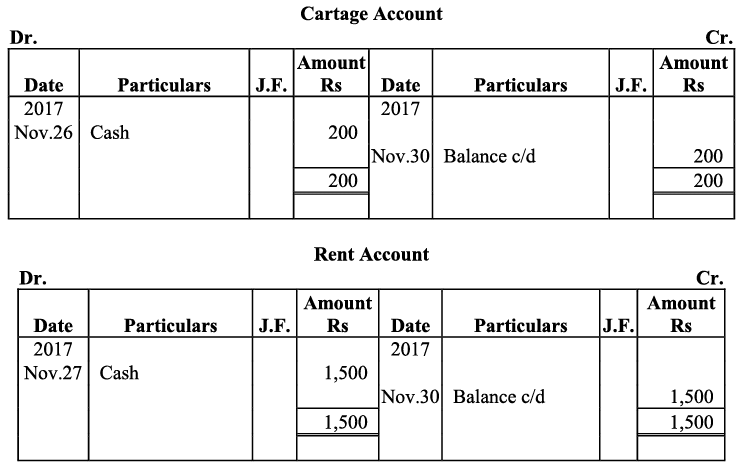
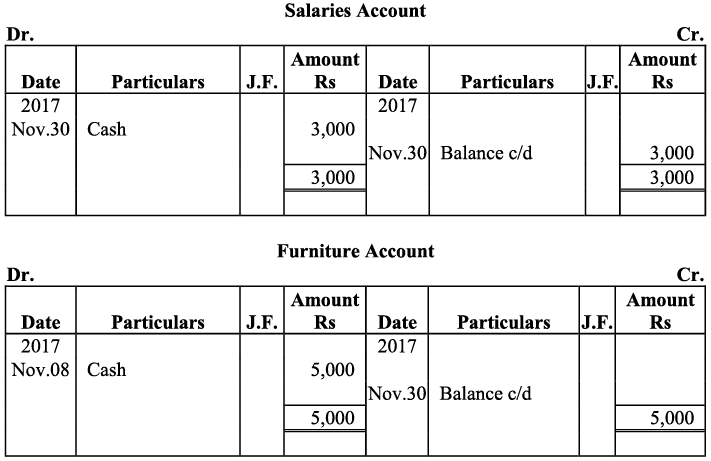
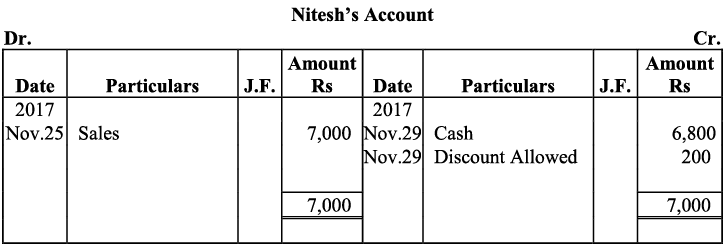
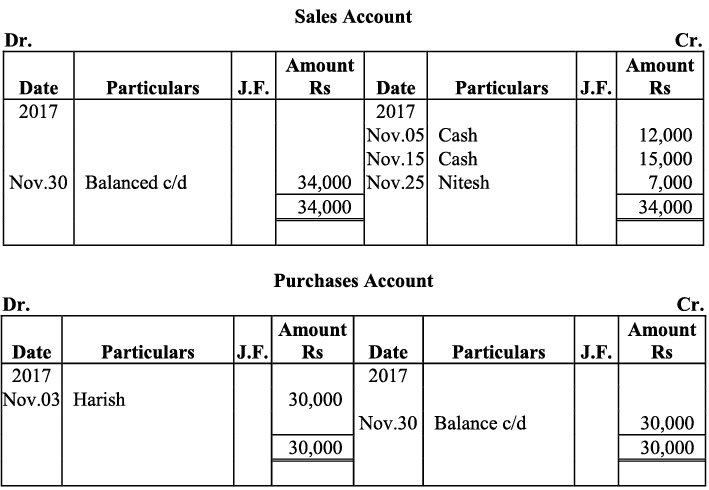
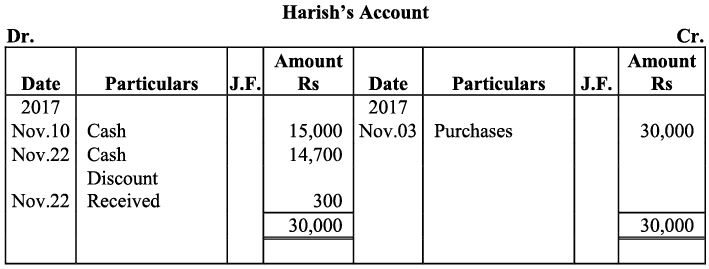
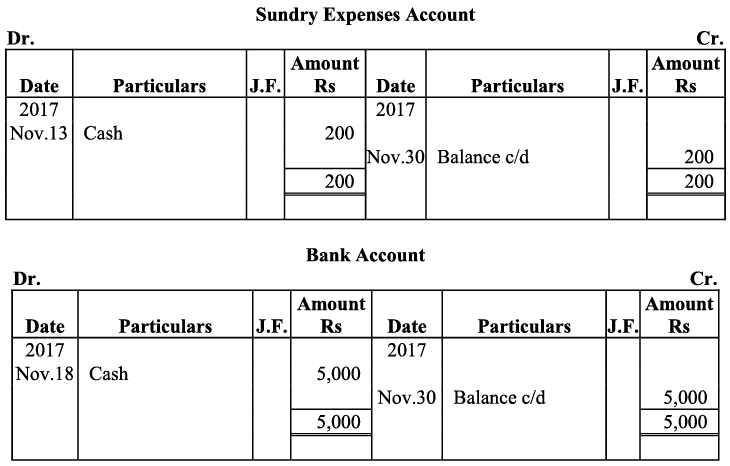
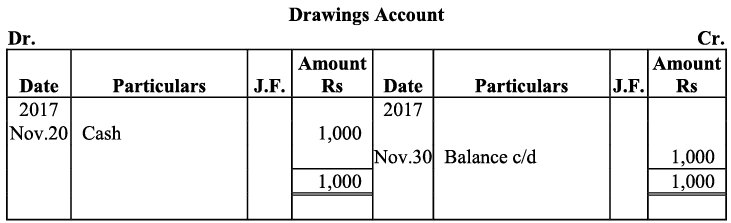
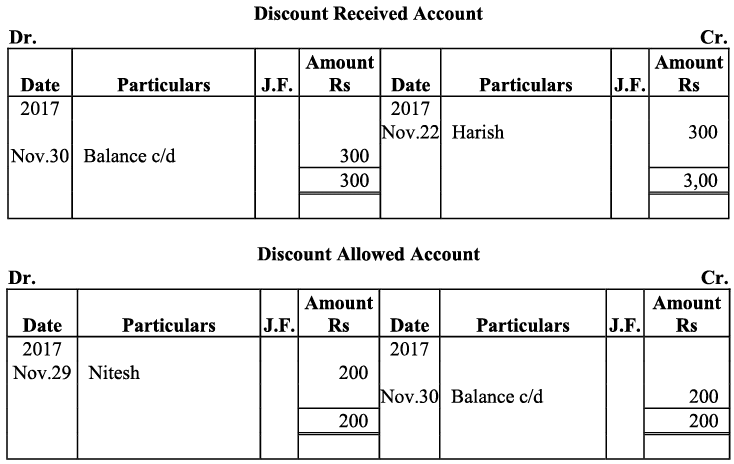
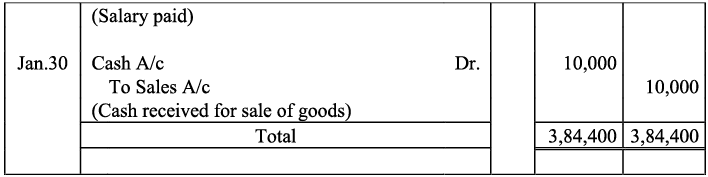
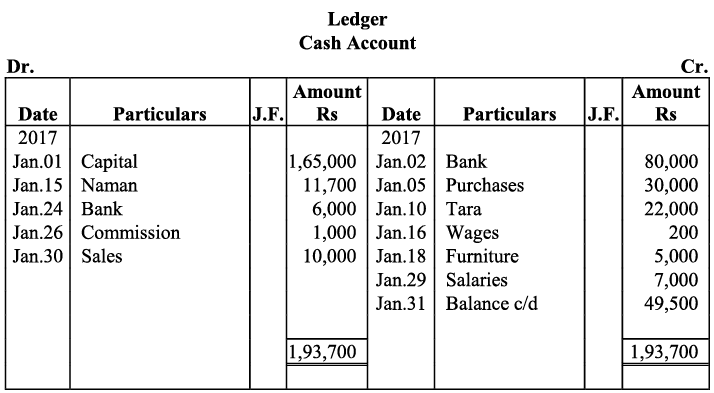
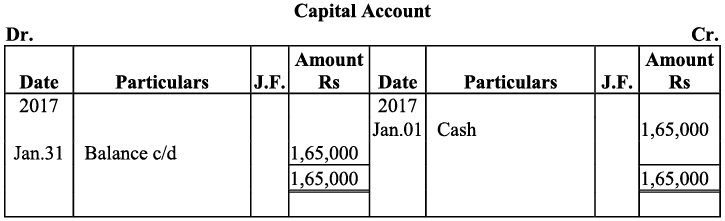
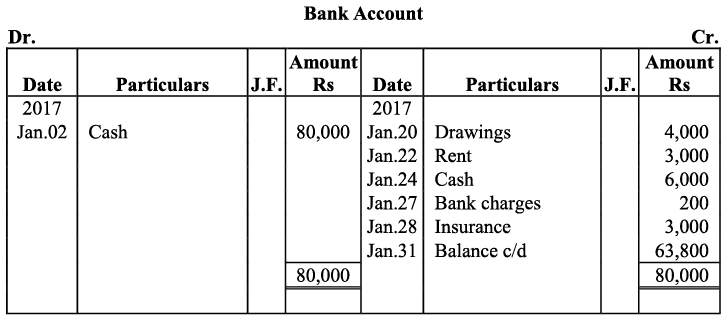
Q17: Journalise the following transactions is the journal of M/s Goel Brothers and post them to the ledger.

Ans: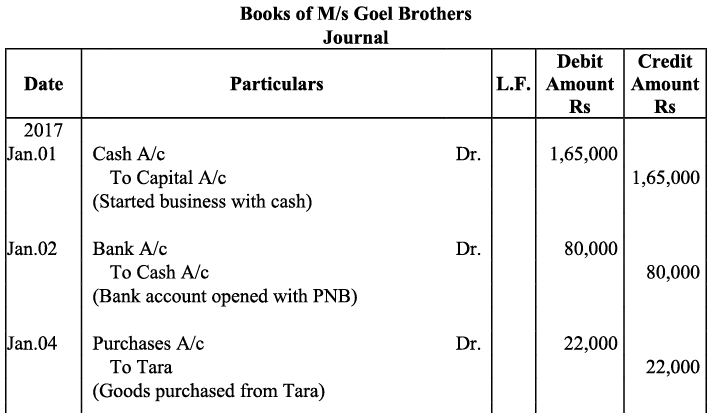
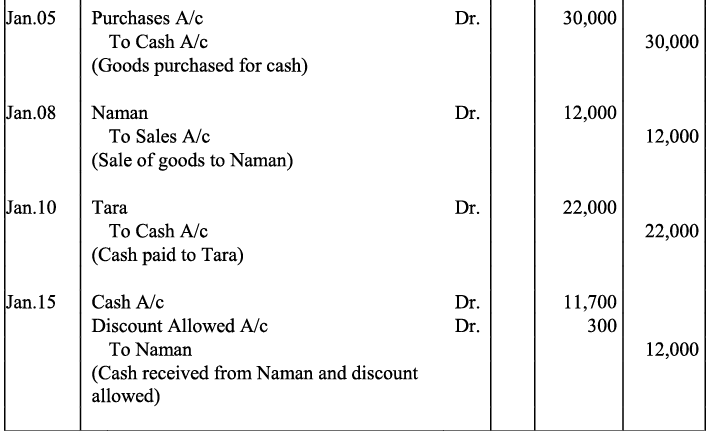
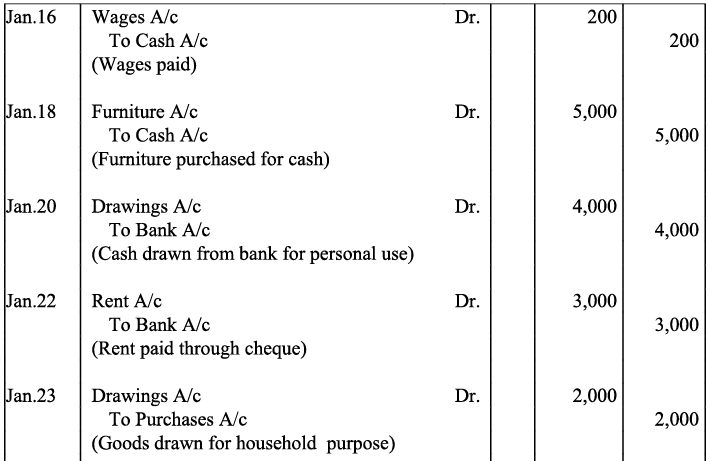
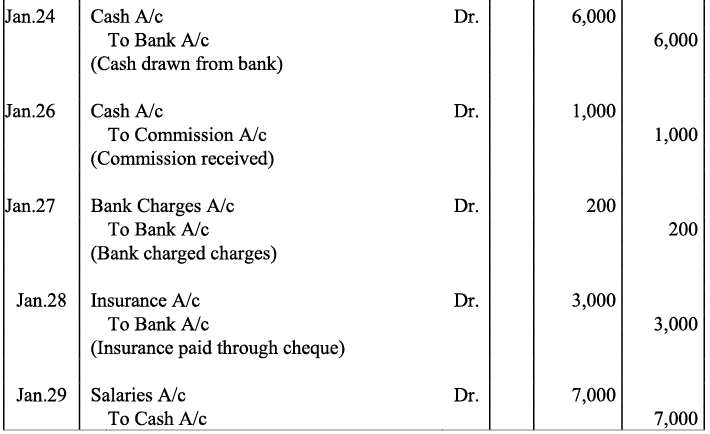
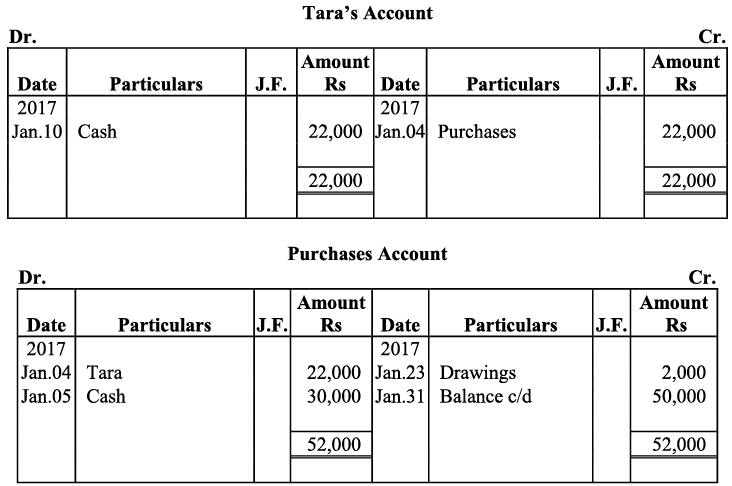
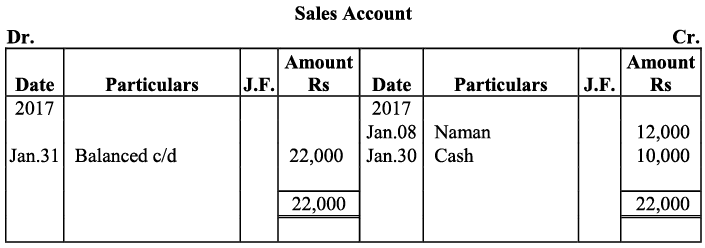
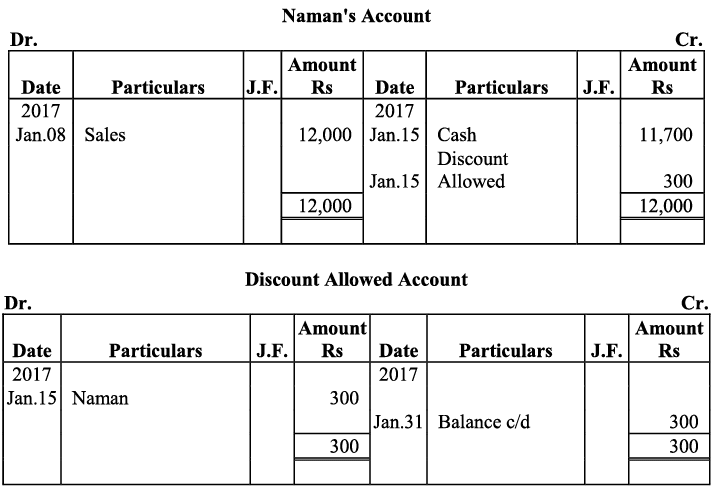
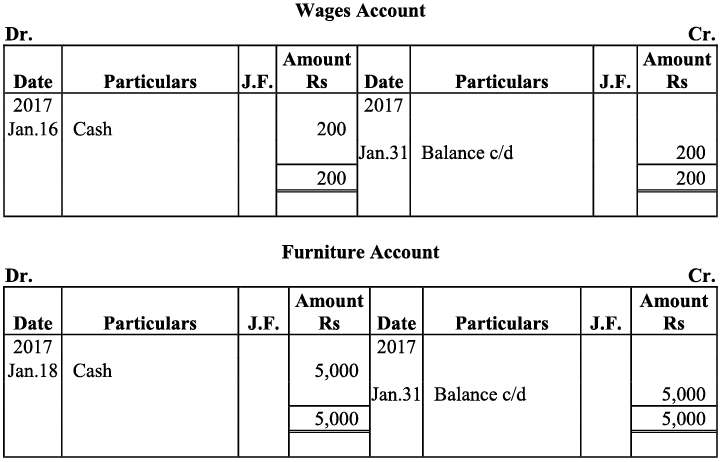
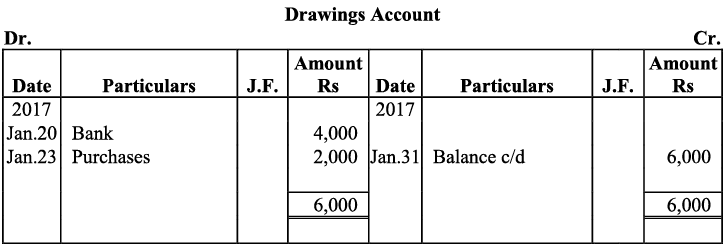
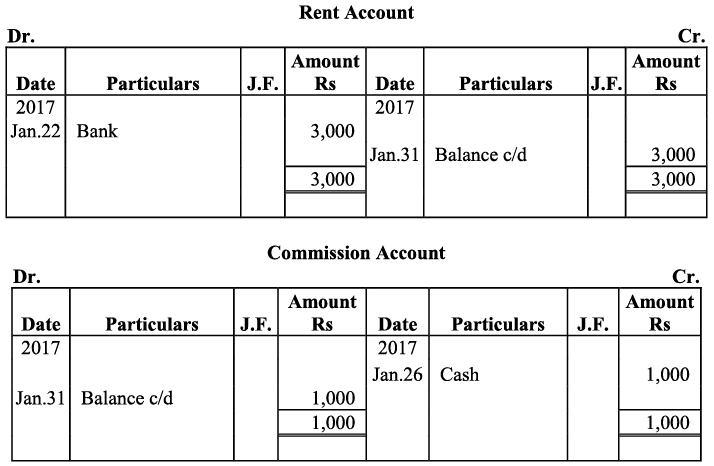
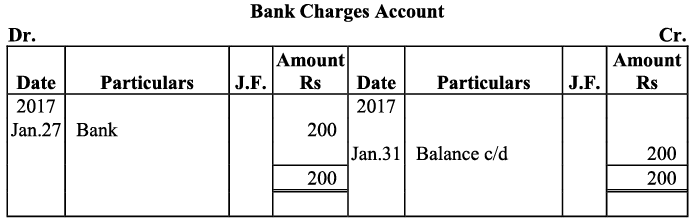
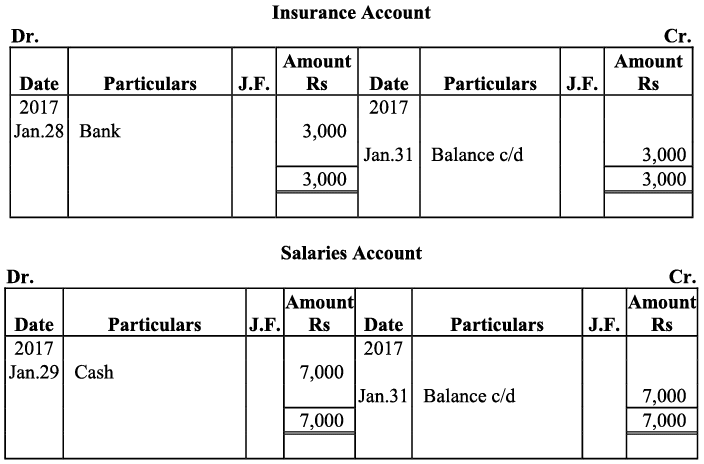
Q18: Give journal entries of M/s Mohit traders, Post them to the Ledger from the following transactions:

Ans: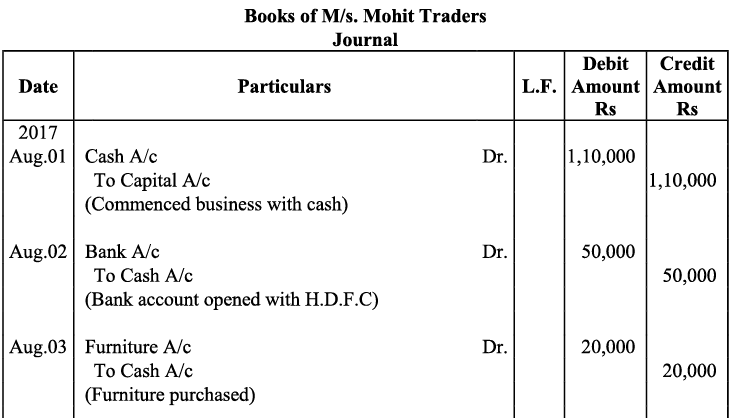

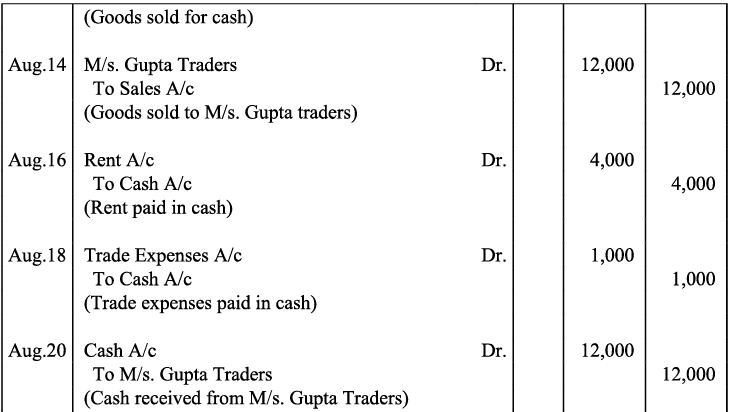
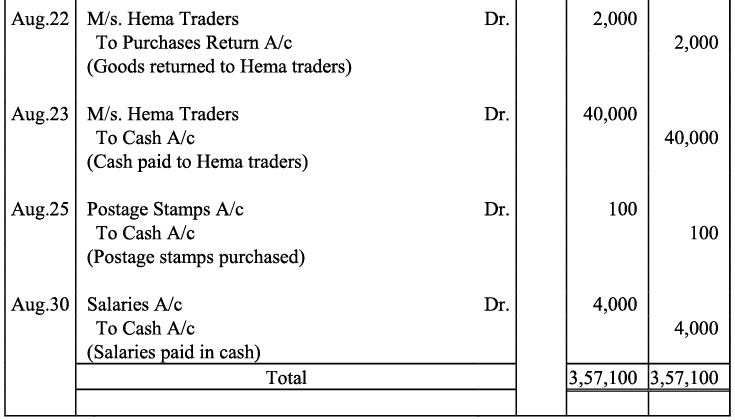
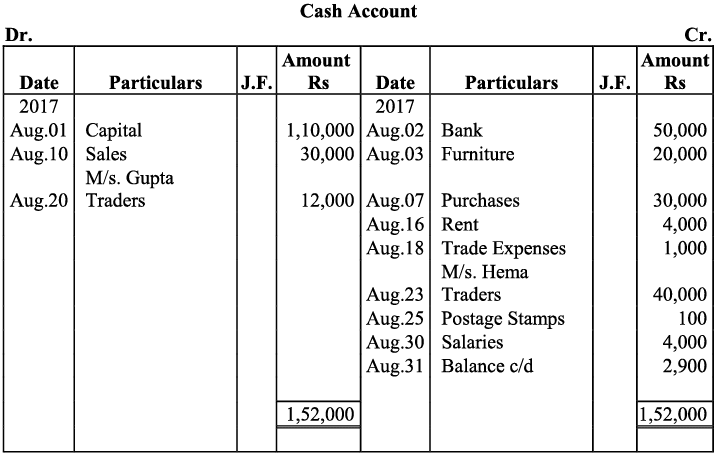
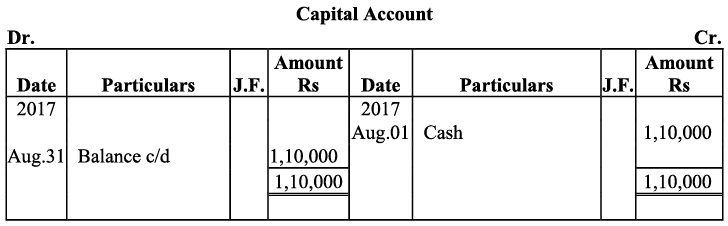
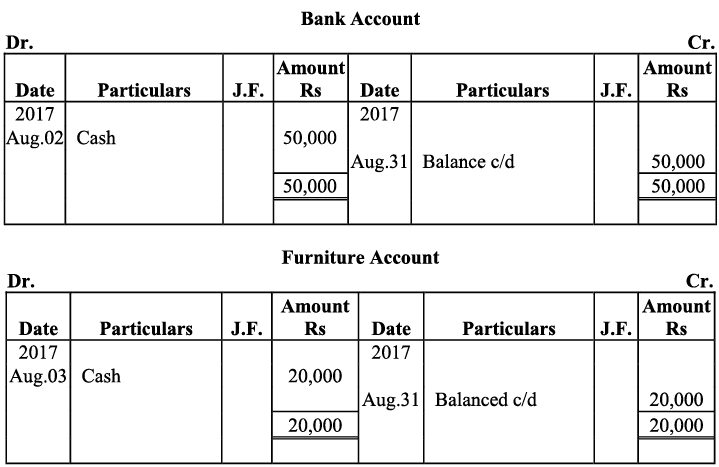
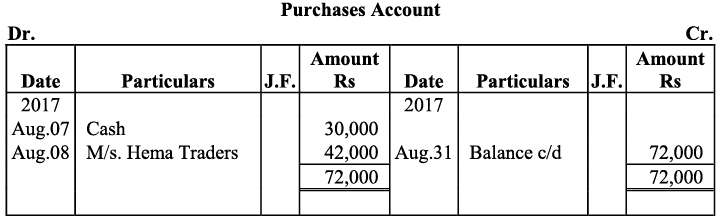
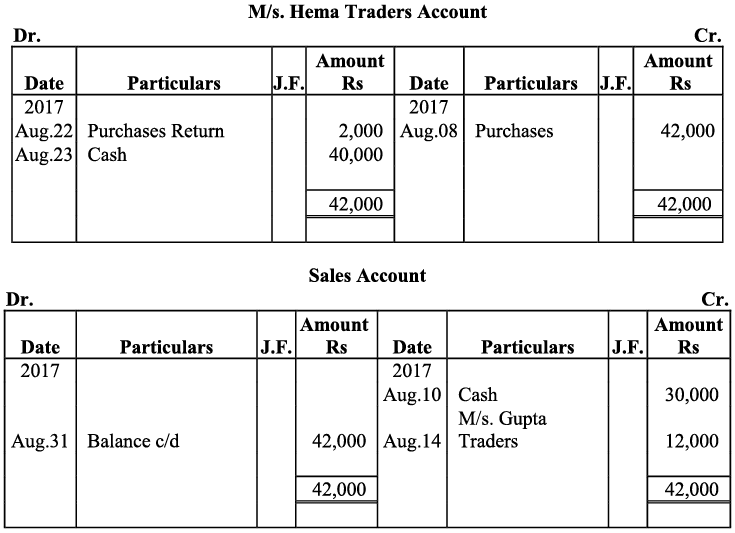
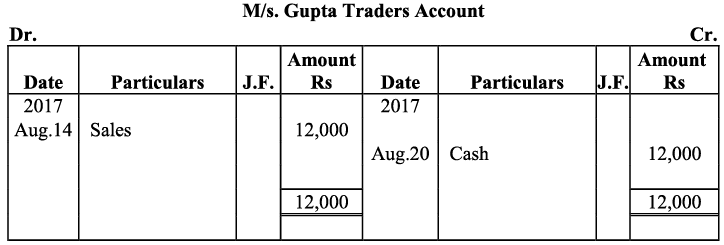
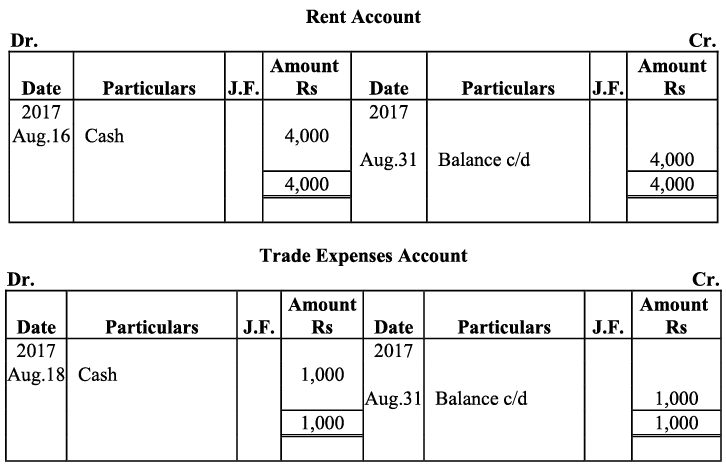
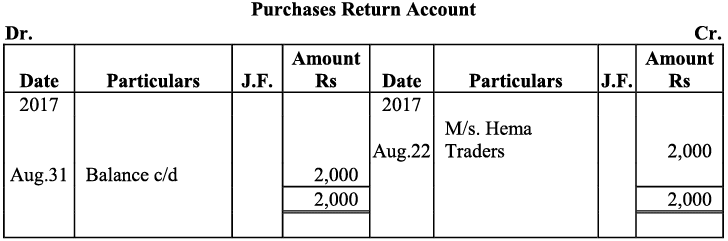
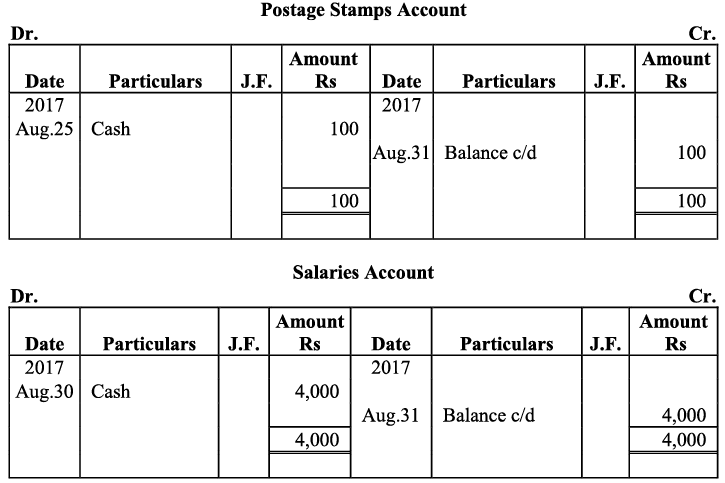
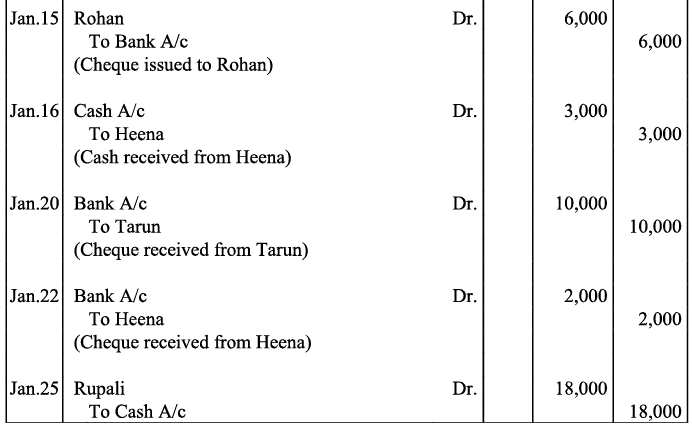
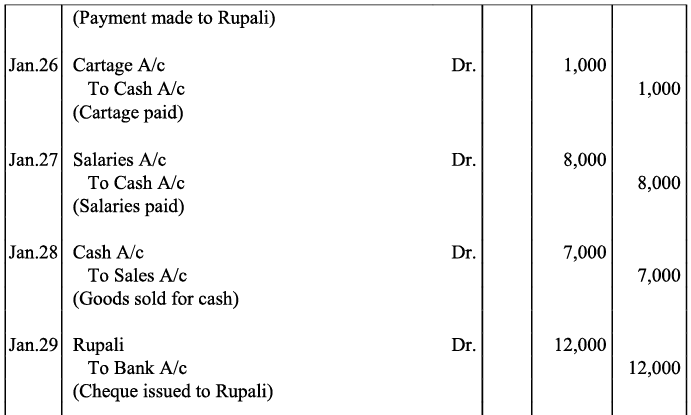
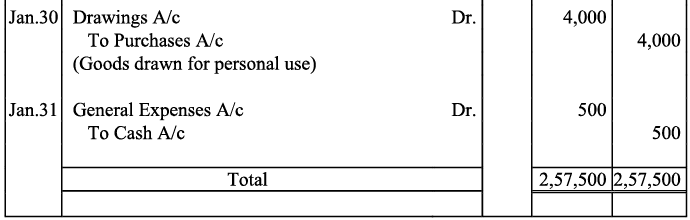
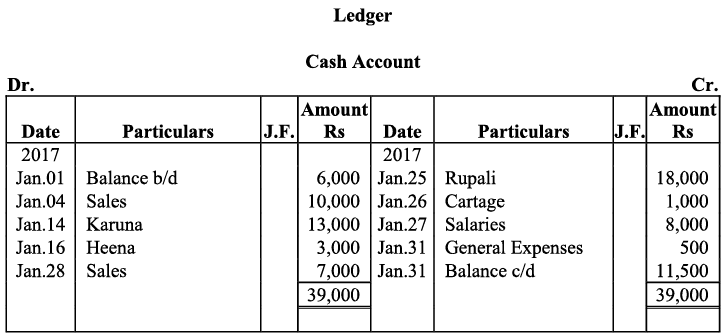
Q19: Journalise the following transaction in the Books of the M/s Bhanu Traders and Post them into the Ledger.

Ans: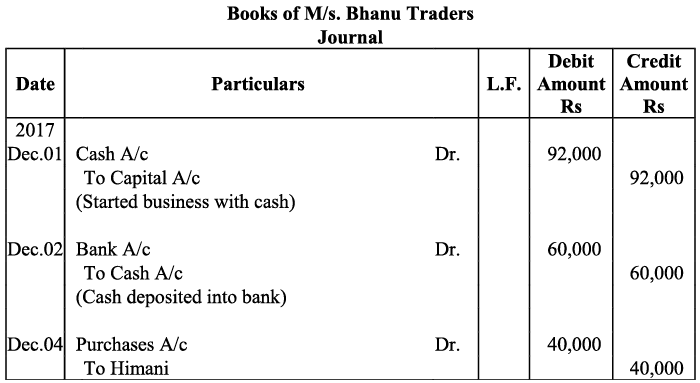
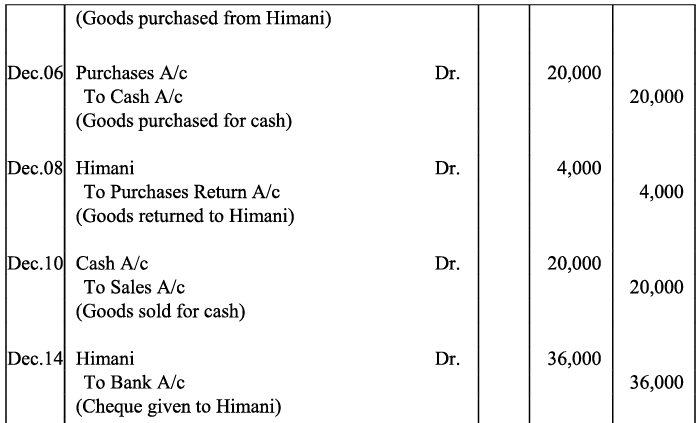
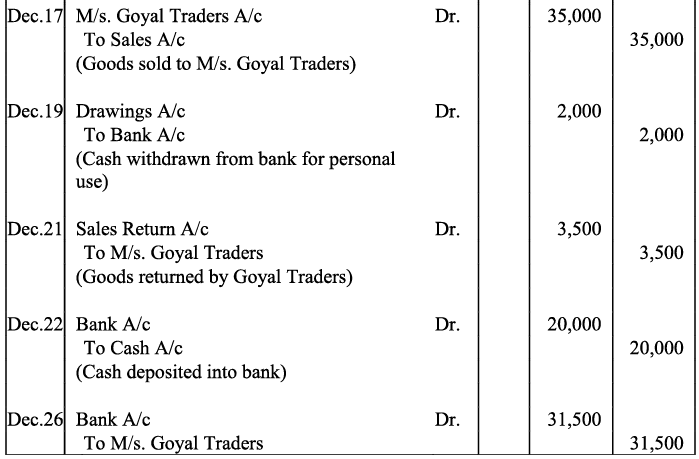
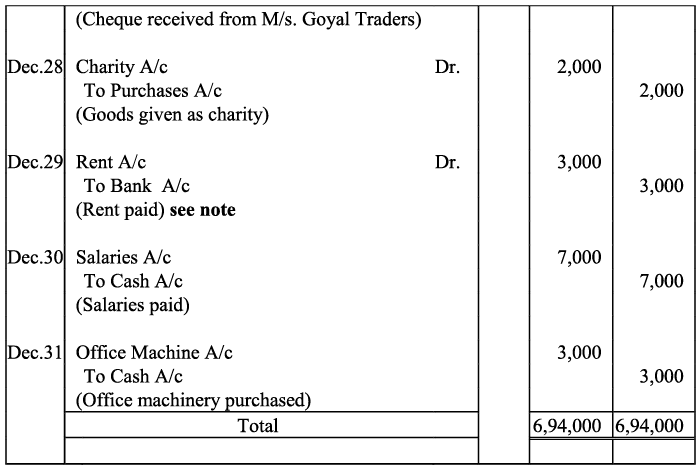
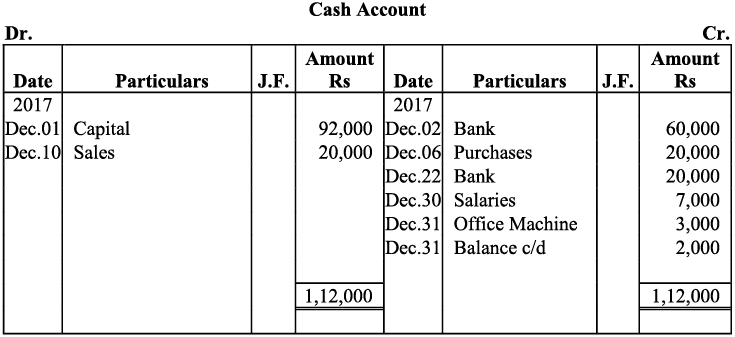
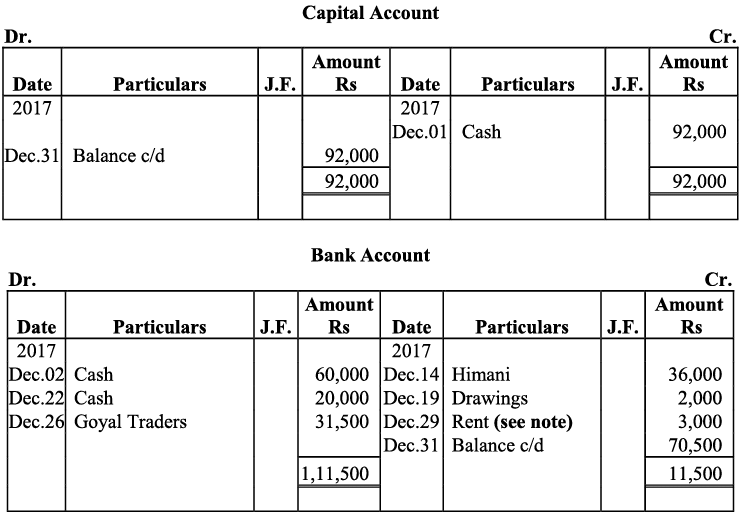 Note: For transaction on December 29, 2017, it has been assumed that the rent of Rs 3,000 is paid through cheque. If instead the rent would have been paid in cash, the cash account would have shown a credit (negative) balance and that is logically not correct.
Note: For transaction on December 29, 2017, it has been assumed that the rent of Rs 3,000 is paid through cheque. If instead the rent would have been paid in cash, the cash account would have shown a credit (negative) balance and that is logically not correct.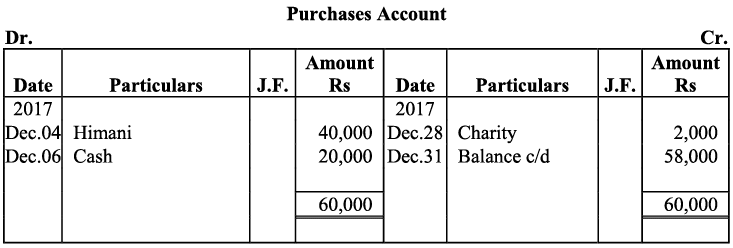
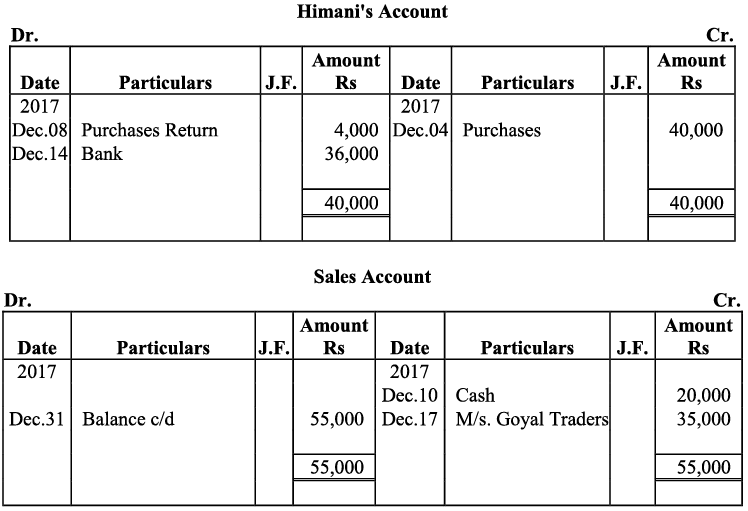
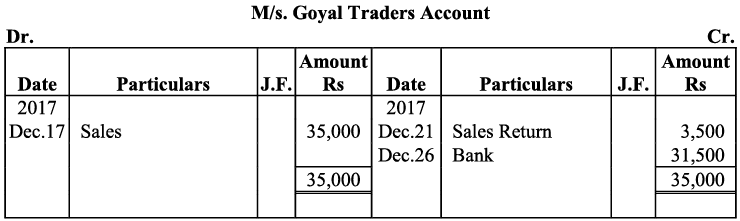
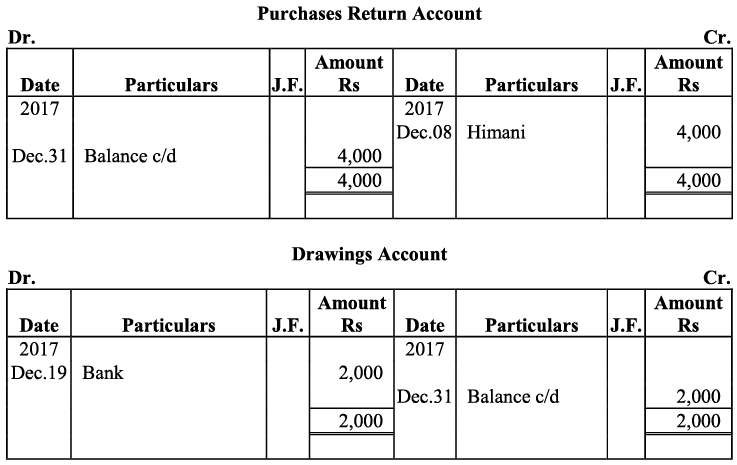
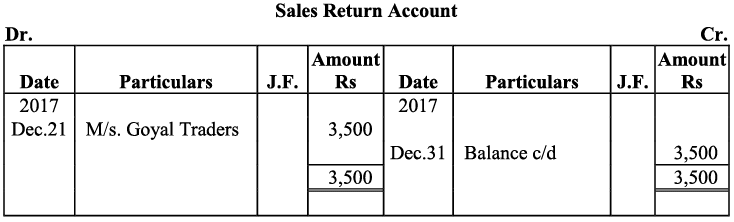
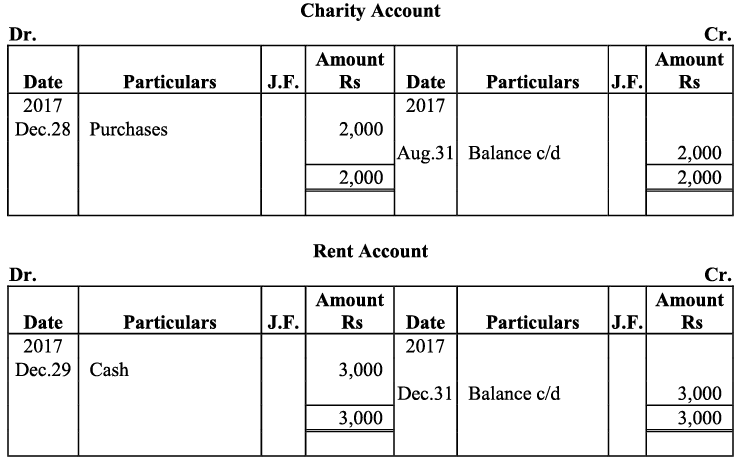
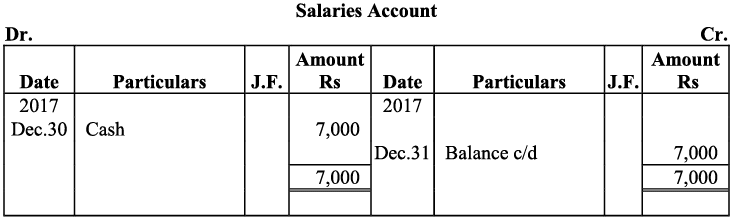
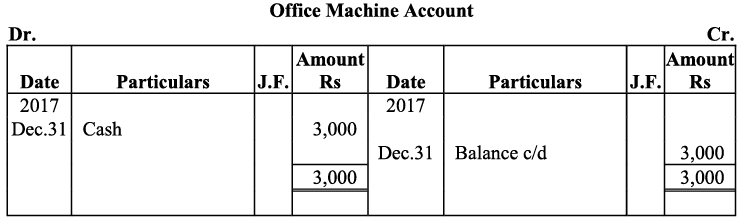
Q20: Journalise the following transaction in the Book of M/s Beauti traders. Also post them in the ledger.
Ans: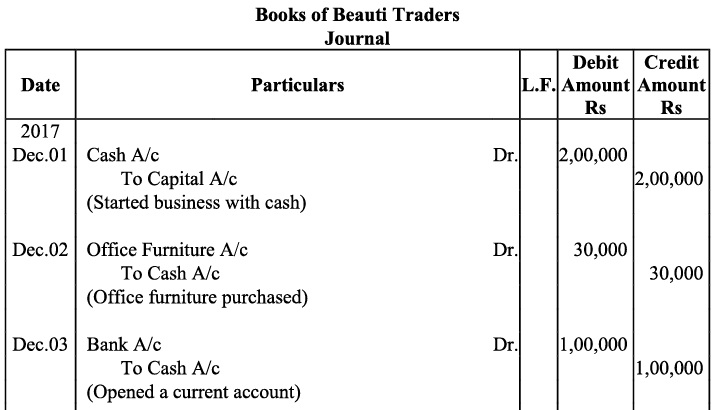

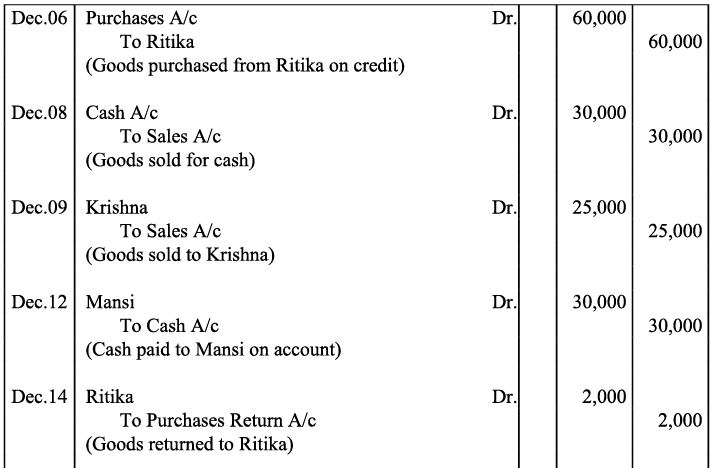
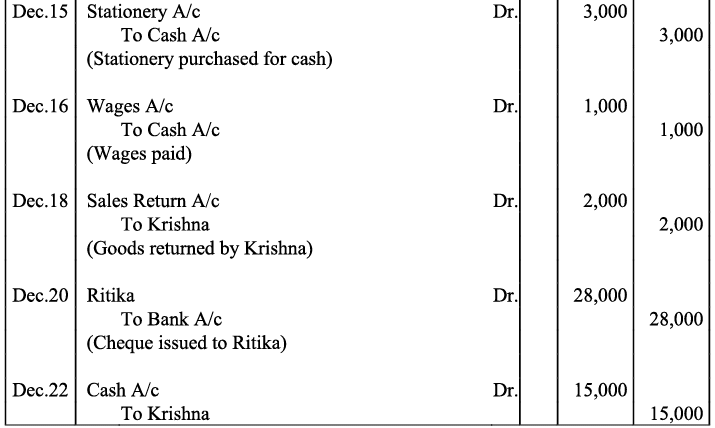
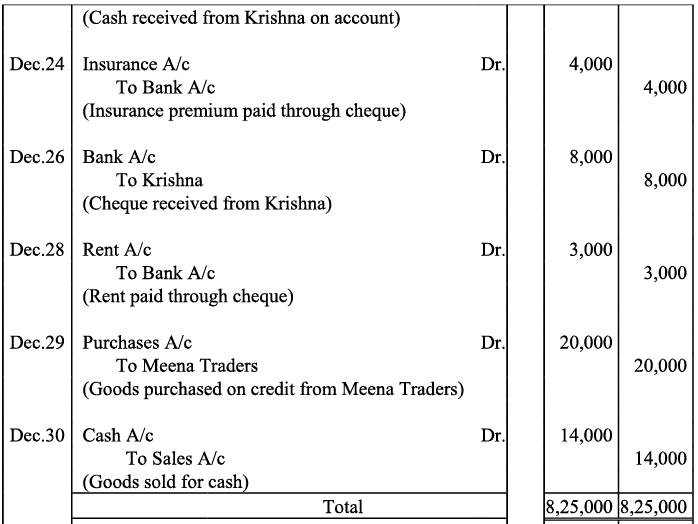
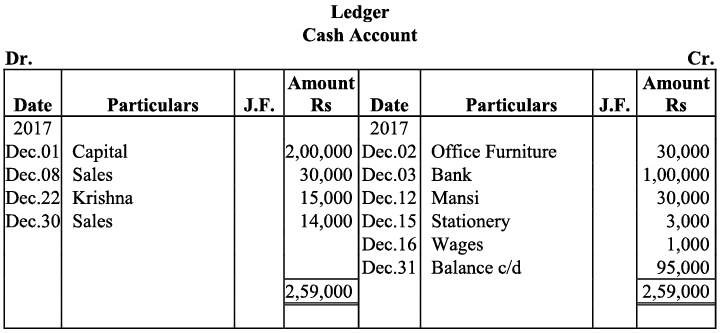
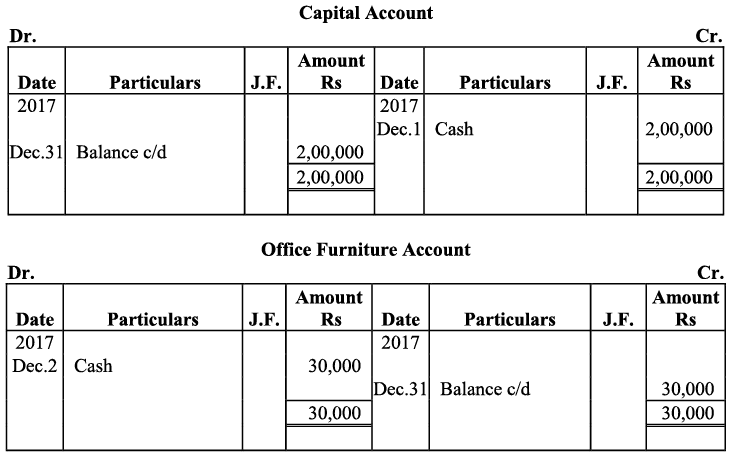
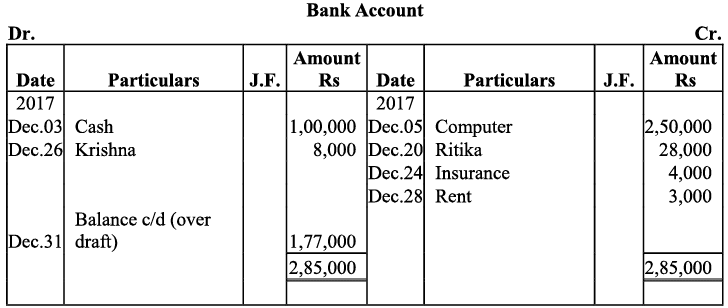
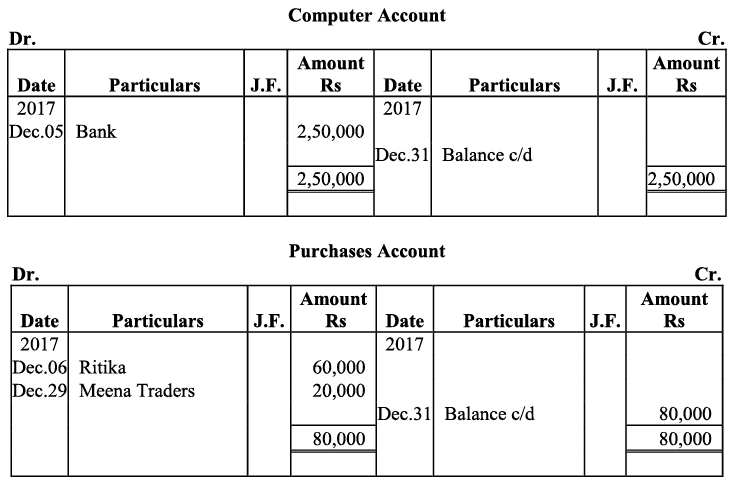
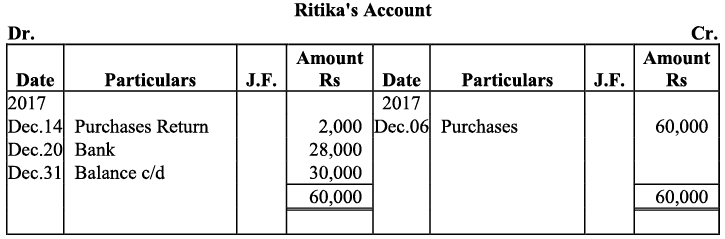
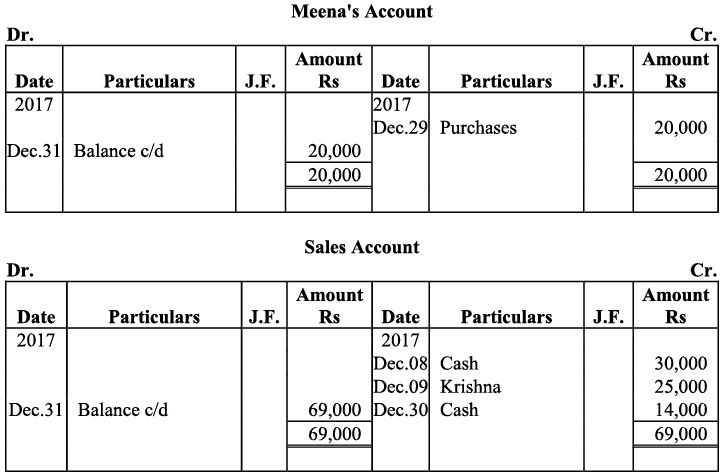
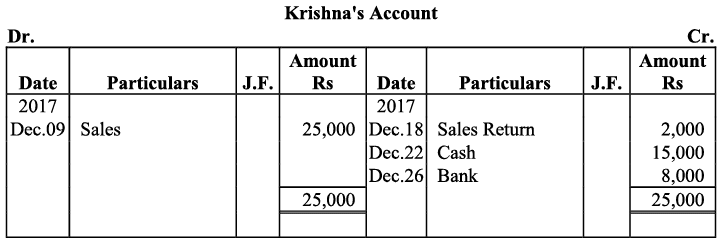
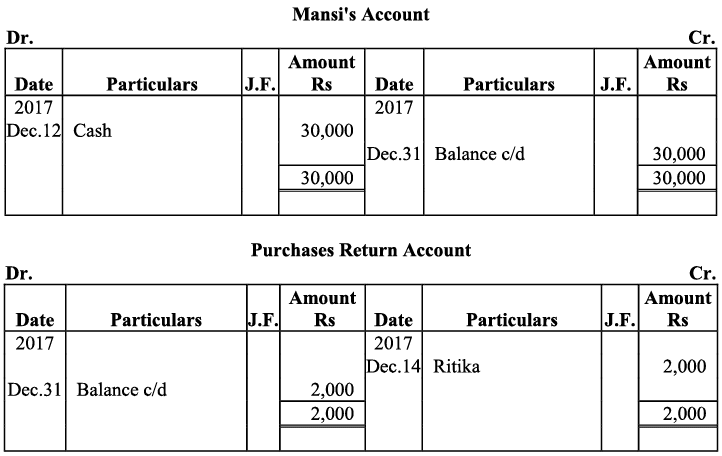
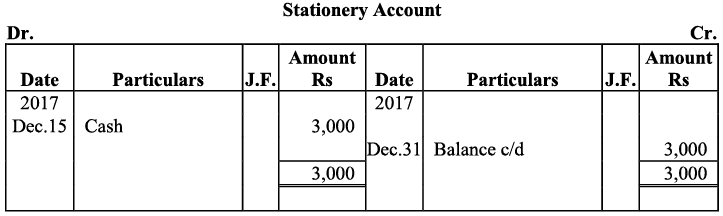
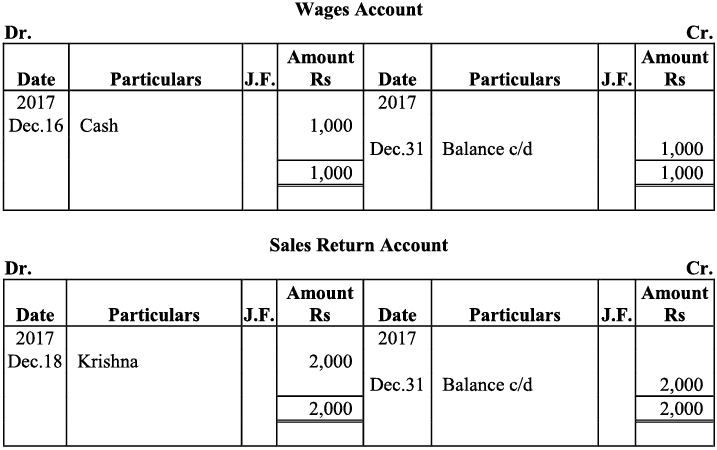
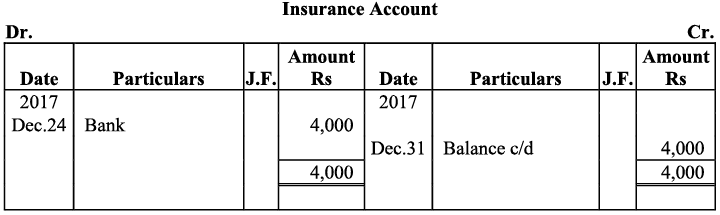
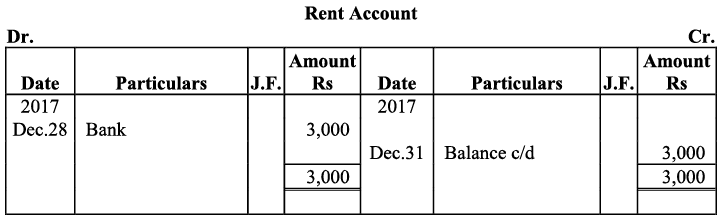
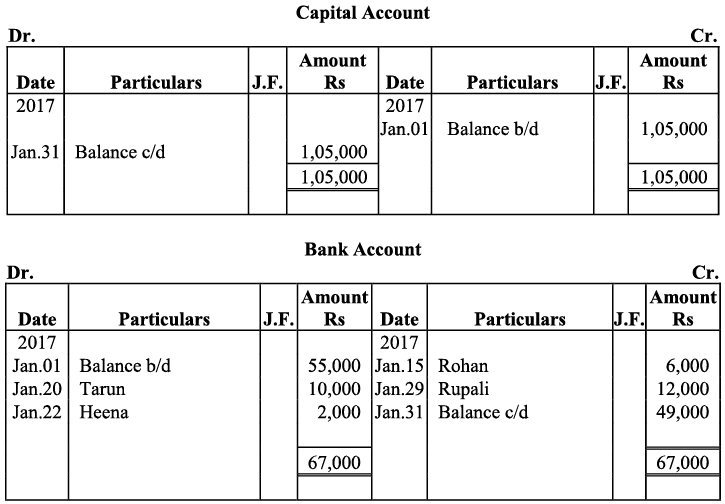
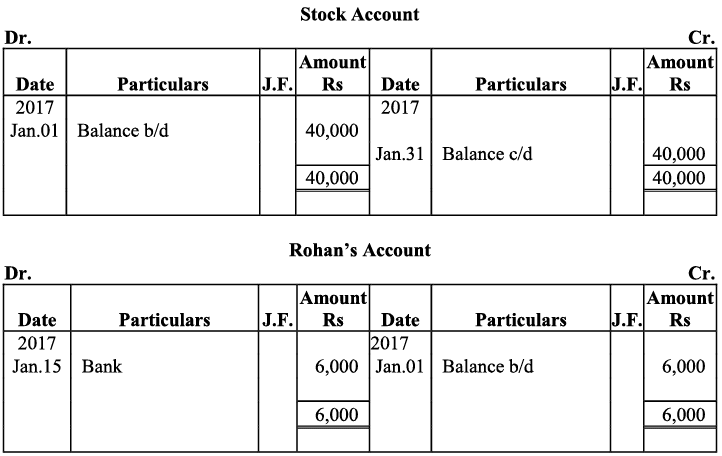
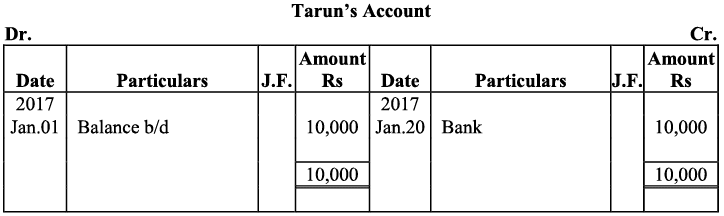
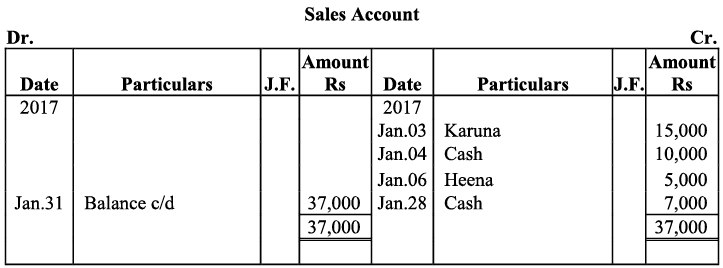
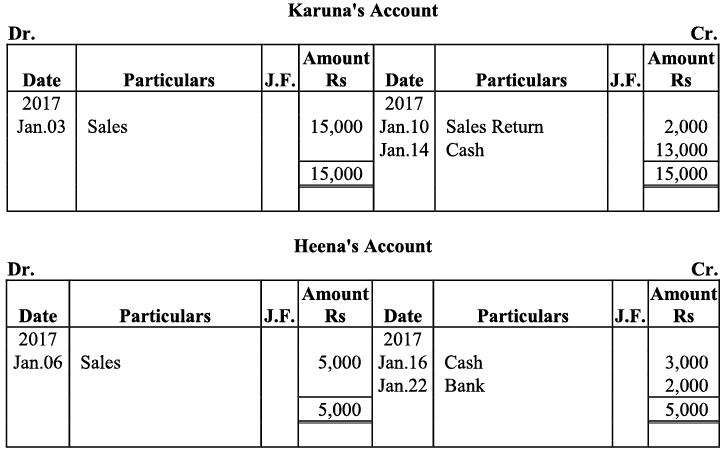
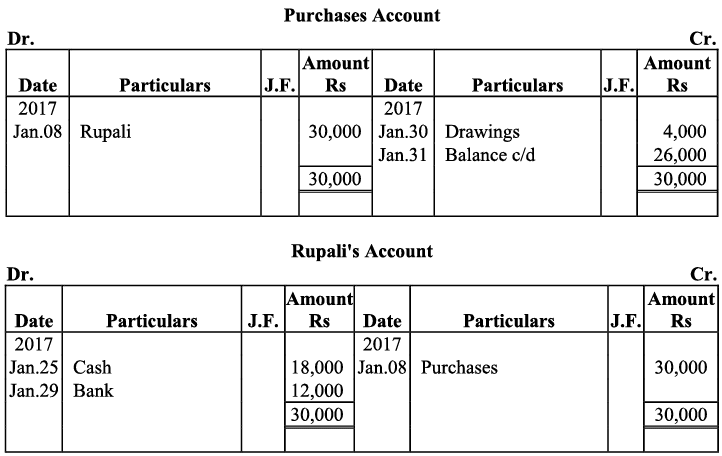
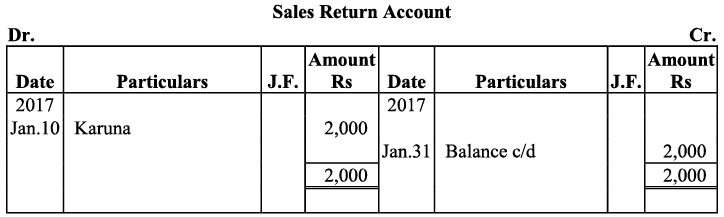
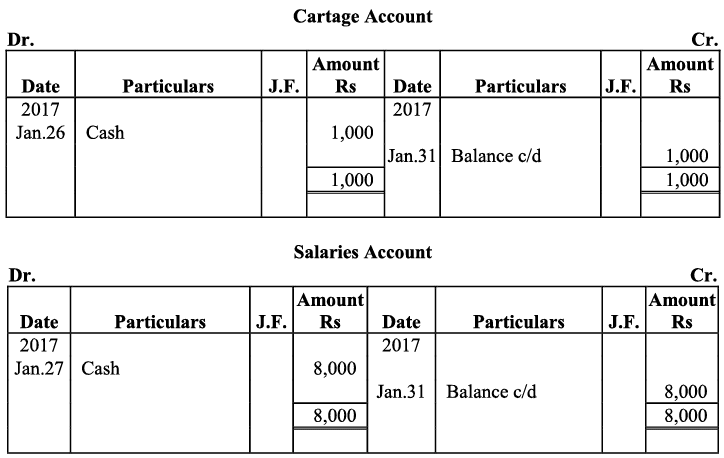
Q21: Journalise the following transaction in the books of Sanjana and post them into the ledger:

Ans: 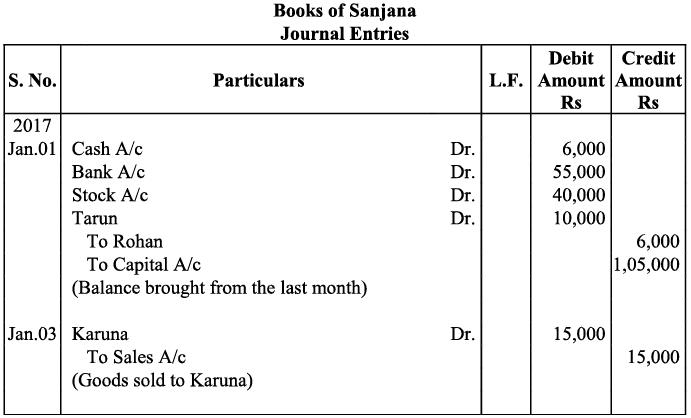
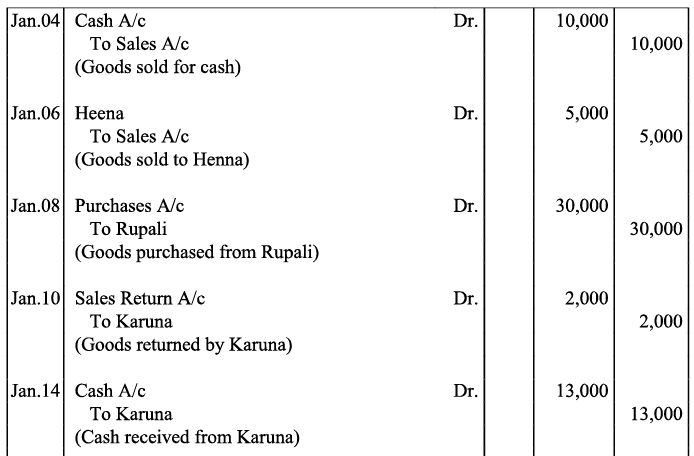
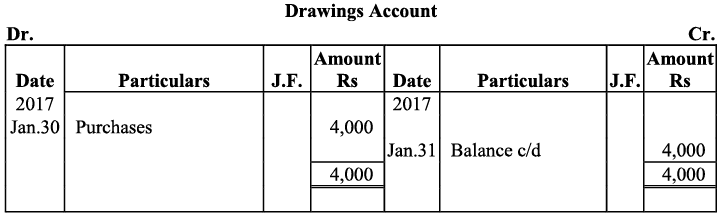
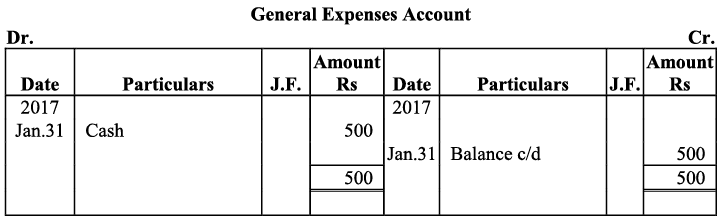
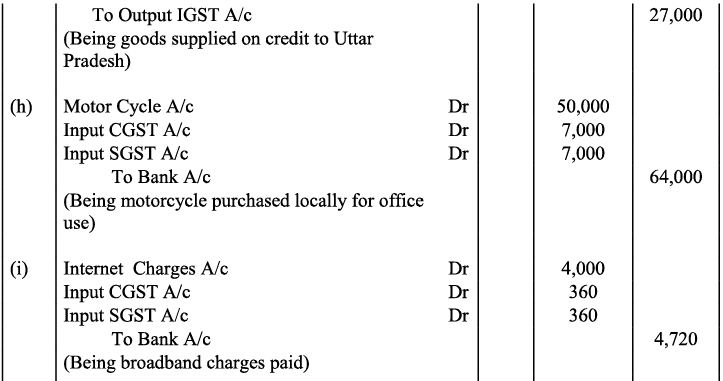
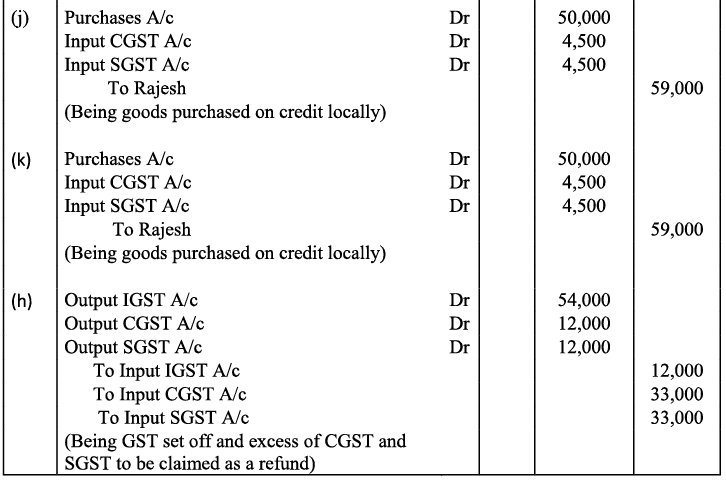
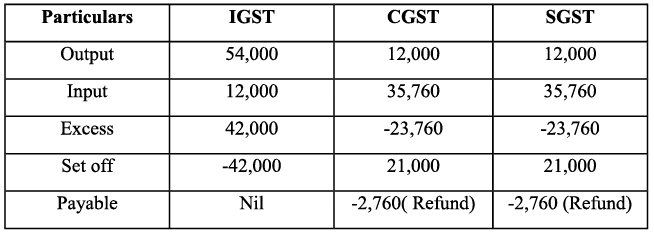
Q22: Record journal entries for the following transactions in the books of Anudeep of Delhi:
(a) Bought goods ₹ 2,00,000 from Kanta of Delhi (CGST @ 9%, SGST @ 9%)
(b) Bought goods ₹ 1,00,000 for cash from Rajasthan (IGST @ 12%)
(c) Sold goods ₹ 1,50,000 to Sudhir of Punjab (IGST @ 18%)
(d) Paid for Railway Transport ₹ 10,000 (CGST @ 5%, SGST @ 5%)
(e) Sold goods ₹ 1,20,000 to Sidhu of Delhi (CGST @ 9%, SGST @ 9%)
(f) Bought Air-Condition for office use ₹ 60,000 (CGST @ 9%, SGST @ 9%)
(g) Sold goods ₹ 1,50,000 for cash to Sunil to Uttar Pradesh (IGST 18%)
(h) Bought Motor Cycle for business use ₹ 50,000 (CGST 14%, SGST @ 14%)
(i) Paid for Broadband services ₹ 4,000 (CGST @ 9%, SGST @ 0%)
(j) Bought goods ₹ 50,000 from Rajesh, Delhi (CGST @ 9%, SGST @ 9%)
Ans:
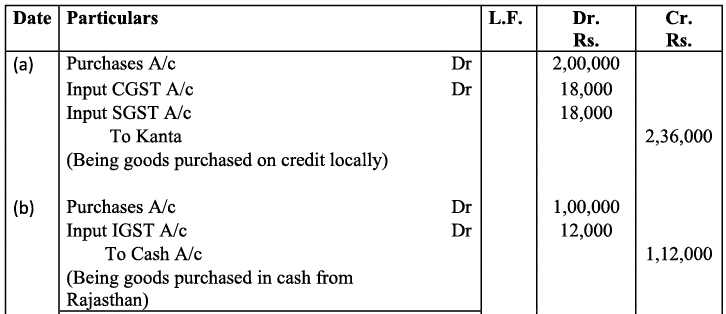
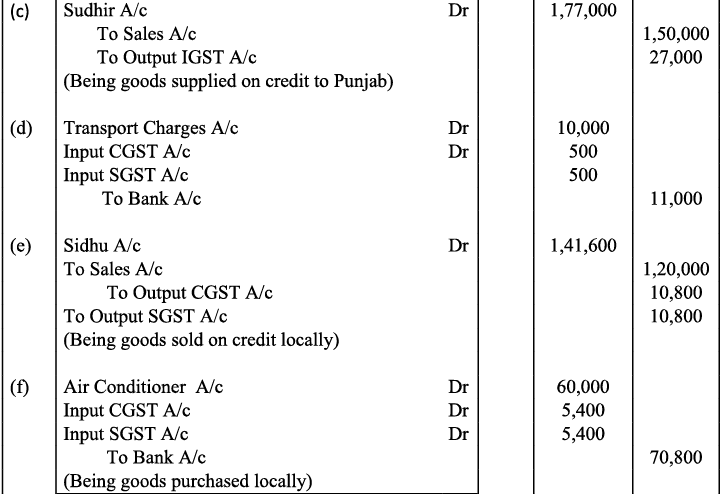

 Working Note :
Working Note :
FAQs on NCERT Solution: Recording of Transactions-I - Commerce
| 1. What are the basic principles of recording transactions in accounting? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of source documents in recording transactions? |  |
| 3. How do you differentiate between capital and revenue expenditures? |  |
| 4. What role does the journal play in the accounting process? |  |
| 5. How can errors in recording transactions be corrected in accounting? |  |






















