UPSC Mains 2024 GS Paper 2 with Answers | UPSC Previous Year Question Papers and Video Analysis PDF Download
Q1: Examine the need for electoral reforms as suggested by various committees with particular reference to “one nation – one election” principle. (Answer in 150 words)
Ans:
Introduction
“One Nation – One Election (ONOE)” promotes the idea of conducting simultaneous elections across the country to enhance governance and minimize the disruptions caused by frequent elections.
ONOE was supported by:
The Election Commission, in its First Annual Report (1983), endorsed simultaneous elections for several reasons, including:
- Lowering the official expenses for the government, political parties, and candidates.
- Reducing the strain on administrative resources and security forces by cutting down on repeated election duties.
- Addressing governance challenges that arise from short-term political objectives.
- The Law Commission, in its 170th report, backed the initiative, suggesting one election every five years.
- The Parliamentary Standing Committee in 2015 supported ONOE, emphasizing "long-term good governance."
Concerns Raised Against ONOE:
- Simultaneously conducting elections for the Lok Sabha and all State assemblies may lead to national issues overshadowing local and state-specific matters.
- National political parties might gain a substantial advantage over regional parties, undermining the principle of federalism.
- Implementing ONOE would necessitate significant amendments to the Constitution, the Representation of the People Act (RPA) 1951, and the Rules of Procedure in both Lok Sabha and State legislative assemblies.
Conclusion
Although “ONOE” presents various advantages, its execution would require constitutional reforms and procedural adjustments. A phased approach, as recommended by the Kovind Panel Report (2023), could provide a feasible solution, but its effectiveness relies on reaching a consensus and careful implementation.
Q2: Explain and distinguish between Lok Adalats and Arbitration Tribunals. Whether they entertain civil as well as criminal cases? (Answer in 150 words)
Ans:
Introduction
Lok Adalats are statutory bodies established under the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987, and serve as part of the Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) system. Similarly, Arbitral Tribunals, created under the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996, consist of arbitrators who handle disputes outside conventional courts.
Difference Between Lok Adalats and Arbitration Tribunals
Nature of Dispute Resolution:
- Lok Adalats: Focus on reaching amicable settlements through mutual agreement.
- Arbitration Tribunals:Resolve disputes through legal adjudication, resulting in a binding decision.
Binding Nature:
- Lok Adalats:Decisions are final, binding, and hold the status of a civil court decree, with no option for appeal.
- Arbitration Tribunals:Decisions, or arbitral awards, are binding and enforceable, though they can be challenged on specific limited grounds.
Referral of Cases:
- Lok Adalats:Cases can be referred by courts or applied for by parties.
- Arbitration Tribunals: Parties typically agree to arbitration through a contractual agreement, and arbitrators may be appointed by institutions if parties fail to select one.
Types of Disputes
- Lok Adalats:Address both civil and compoundable criminal cases, excluding non-compoundable offenses.
- Arbitration Tribunals:Focus on civil matters, including domestic and international commercial disputes, without handling criminal cases.
Conclusion
Lok Adalats primarily facilitate amicable settlements in civil and compoundable criminal cases, while Arbitration Tribunals handle civil matters like commercial disputes. Both contribute to timely justice and reduce the judicial backlog. Strengthening institutional support and resources can further enhance their effectiveness.
Q3: "The growth of the cabinet system has practically resulted in the marginalisation of the parliamentary supremacy." Elucidate. (Answer in 150 words)
Ans:
Introduction
The cabinet system in India has evolved to emphasize collective responsibility, with the Prime Minister as "first among equals." While this evolution is not explicitly detailed in the Constitution, it has, at times, contributed to a shift away from strict parliamentary supremacy.
Concentration of Power in the Executive:
- The cabinet centralizes power in the Prime Minister and key ministers. For instance, Justice Nagarathna’s 2023 dissent noted the unconstitutionality of demonetization being enacted without parliamentary approval, emphasizing executive overreach.
Reduced Parliamentary Scrutiny:
- The cabinet often controls the legislative agenda, limiting parliamentary oversight. A key example was the 2020 Farm Laws, which faced criticism for being passed without sufficient debate.
Ordinances:
- The cabinet can bypass legislative scrutiny by issuing ordinances. The 2023 ordinance on Delhi’s administrative control, initially enacted without parliamentary debate, illustrates this capacity for executive action outside legislative purview.
Parliamentary Committee Limitations:
- Recommendations from parliamentary committees are non-binding, which means the cabinet can disregard them. Only 25% of bills in the 16th Lok Sabha were referred to committees, a stark decline from 71% in the 15th Lok Sabha, reflecting a reduction in legislative examination.
Conclusion
Although the cabinet system has shifted power dynamics, parliamentary supremacy remains constitutionally protected, with Parliament retaining core powers like no-confidence motions (Article 75). The repeal of the farm laws in 2021 demonstrates Parliament's ability to effectively check executive power, underscoring the importance of balancing efficient governance with essential oversight.
Q4: The duty of the Comptroller and Auditor General is not merely to ensure the legality of expenditure but also its proprietary? (Answer in 150 words)
Ans:
Introduction
The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India, a constitutional authority under Article 148, is responsible for auditing the accounts of both the Union and State governments to ensure that public funds are utilized legally and effectively.
CAG’s Role in Ensuring the Legality of Expenditure
- The CAG verifies that financial transactions adhere to applicable laws, rules, and regulations, ensuring no misappropriation of funds.
- It ensures that public funds are spent only for their intended purposes, thereby maintaining transparency and accountability.
- By certifying the accounts of the Union and State governments, the CAG confirms that the financial statements fairly and accurately represent the financial position, which is essential for upholding the legality and integrity of government finances.
CAG’s Role in Ensuring Propriety
The CAG conducts propriety audits to evaluate the prudence, justification, and integrity of government expenditures.
- Justification for Expenditure: Assesses whether expenditures serve the public interest or if they are excessive.
- Efficiency: Evaluates whether resources are used efficiently or if there has been any wasteful spending.
- Public Interest: Ensures that expenditures align with broader societal goals and uphold fairness and equity.
- Notable CAG audits, such as those on the Commonwealth Games and coal block allocations, revealed substantial irregularities and financial losses, sparking public debate, legal actions, and demands for accountability.
Conclusion
The CAG plays a critical role in enhancing transparency, accountability, and efficiency in public financial management, thereby strengthening government integrity and fostering public confidence in the handling of national resources.
Q5: Analyse the role of local bodies in providing good governance at local level and bring out the pros and cons merging the rural local bodies with the urban local bodies. (Answer in 150 words)
Ans:
Introduction
The Constitution of India, through the 73rd and 74th Amendments (1992), established local self-governance structures, creating Panchayats for rural areas and Municipalities for urban regions. This framework includes Village, Intermediate, and District Panchayats, along with Municipal Corporations and Municipalities.
Role of Local Bodies in Good Governance
- Local bodies, as emphasized by committees like the Balwant Rai Mehta Committee (1957) and the Ashok Mehta Committee (1977), play a crucial role in planning and implementing development projects tailored to local needs, thereby promoting decentralized governance.
- They benefit from financial allocations based on the 15th Finance Commission’s recommendations, particularly for water supply and sanitation, functioning as essential public utilities at the local level.
- Local bodies ensure representation for marginalized groups through reserved seats and encourage participatory democracy via Gram Sabhas and Ward Committees.
Merging Rural Local Bodies with Urban Local Bodies (ULBs)
Pros:
- Promotes cohesive growth in peri-urban areas.
- Enhances management of the rural-urban distinction as urbanization blurs these lines.
- Larger, unified entities could undertake more substantial development projects.
Cons:
- Rural issues may be sidelined in favor of urban priorities, with concerns about rural representation if urban populations dominate.
- The unique social characteristics of rural areas may complicate governance within a merged system.
- Rural communities fear merging with ULBs may lead to higher taxes and loss of benefits like MGNREGA, as evidenced by protests in Tamil Nadu.
Conclusion
While merging rural and urban local bodies could improve efficiency and cohesion, it also poses risks to local identities and interests. Engaging all stakeholders in the decision-making process is essential to ensure balanced and inclusive governance.
Q6: Public charitable trusts have the potential to make India's development more inclusive as they relate to certain vital public issues. Comment. (Answer in 150 words)
Ans:
Introduction
Public charitable trusts (PCTs) are non-profit organizations established under the Indian Trusts Act of 1982, aiming to serve the public good. They address various socio-economic issues, including healthcare, education, poverty alleviation, disaster relief, and environmental conservation.
PCTs’ Role in Making India’s Development More Inclusive
Filling Gaps in Governance:PCTs complement government initiatives by addressing pressing social issues. For instance, Tata Trusts and the Azim Premji Foundation have made significant contributions to education and healthcare.
Empowering Marginalized Communities:PCTs work with vulnerable communities to improve livelihoods and access to resources. The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, for example, focuses on maternal health and gender equality.
Environmental Conservation:Organizations like the Bombay Natural History Society focus on preserving biodiversity and protecting wildlife.
Advocacy and Awareness: PCTs, such as the All India Nethaji Social Welfare Movement, advocate for policy changes around gender equality and human rights, raising public awareness on critical social issues.
Disaster Relief:During emergencies, PCTs provide immediate assistance. For instance, the All India Doctor Abdul Kalam Welfare Trust facilitates swift and effective disaster relief.
Conclusion
While PCTs play a vital role in promoting inclusive growth, their impact can be constrained by limited funding, bureaucratic challenges, and donor dependence. Strengthening regulations, enhancing transparency, and fostering greater collaboration with the government can amplify their effectiveness in empowering marginalized communities and fostering inclusive development.
Q7: Poverty and malnutrition create a vicious cycle, adversely affecting human capital formation. What steps can be taken to break the cycle? (Answer in 150 words)
Ans:
Introduction
Human capital refers to the skills and knowledge possessed by individuals that enhance productivity and contribute to economic growth. Poverty and malnutrition, however, impede human capital formation by leading to poor educational outcomes, health issues, and limited opportunities. This perpetuates a cycle of intergenerational poverty, reducing overall economic potential.
Steps to Break the Vicious Cycle
Capacity Development Approach:
- Developing vocational skills and knowledge for better livelihoods helps individuals and communities enhance their economic prospects.
- Strengthening local institutions also promotes governance and accountability by involving communities in decision-making. Example: Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY).
Consumption Approach:
- Increasing the purchasing power of low-income households through direct income transfers and subsidies helps improve living standards. Examples: PM-KISAN and PM Garib Kalyan Yojana.
Generational Poverty Alleviation Approach:
- Providing opportunities to learn additional skills beyond regular professions allows individuals to supplement their incomes and build resilience against economic shocks. Example: Self-Help Groups (SHGs).
Educational and Awareness:
- Raising awareness of and improving access to nutritious food, as opposed to fast food influenced by consumerism, promotes informed dietary choices and better health.
Conclusion
Breaking the cycle of poverty and malnutrition is crucial for achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 2 and 3, which target hunger and health. Ensuring the well-being of individuals through targeted interventions fosters effective human capital formation, ultimately contributing to long-term national prosperity.
Q8: The Doctrine of Democratic Governance makes it necessary that the public perception of the integrity and commitment of civil servants becomes absolutely positive. Discuss. (Answer in 150 words)
Ans:
Introduction
The doctrine of democratic governance is a system in which government institutions operate according to democratic principles, processes, and norms, fostering trust between the people and those who govern them.
Standards Required from Civil Servants for Positive Public Perception
Accountability:Civil servants must be responsible for their actions and answerable to the public. Example: Social Audits ensure that public officials are accountable to the community.
Fairness: All citizens must be treated equally and without bias, ensuring justice in service delivery. Example: The values of "Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas" emphasize inclusive growth.
Transparency: Providing clear, accessible information about processes, decisions, and policies is essential. Example: The Right to Information (RTI) Act promotes transparency in government actions.
Responsiveness: Civil servants should promptly address citizens' needs and feedback. Example: Citizen Charters define standards of service, helping to make government more responsive.
Ethical Conduct:Adherence to ethical standards is crucial to avoid corruption and misuse of power. Example: The Code of Conduct outlines expectations for ethical behavior in public service.
Professionalism: Competence, dedication, and respect in roles are essential. Example: The successful COVID-19 vaccination drive demonstrated a high level of professionalism among healthcare and administrative workers.
Empathy: Understanding the diverse needs of the community and valuing different perspectives is key. Example: Addressing the needs of specially-abled individuals reflects empathetic governance.
Collaboration: Working with citizens and various stakeholders enhances governance. Example: Swachh Bharat Abhiyaan is a collaborative effort involving both the government and citizens.
Commitment to Public Service:Prioritizing the well-being of the community and striving to improve public welfare are fundamental principles of democratic governance.
Challenges
- Issues like corruption, bureaucratic inertia, lack of transparency, and ineffective communication can erode public trust in civil servants.
Conclusion
Building a positive public perception of civil servants' integrity and dedication requires a multifaceted approach that addresses root causes of public distrust and emphasizes principles of good governance, accountability, and transparency. Only through sustained efforts to uphold these values can governments ensure the legitimacy and effectiveness of democratic institutions.
Q9: “The West is fostering India as an alternative to reduce dependence on China’s supply chain and as a strategic ally to counter China’s political and economic dominance.” Explain this statement with examples. (Answer in 150 words)
Ans:
Introduction
As China's economic power and assertive expansionist tactics grow, Western nations are implementing a 'China+1' strategy, with India emerging as a primary alternative.
Reducing Dependence on China’s Supply Chain:
- The US-India Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies aims to enhance collaboration in areas such as the semiconductor ecosystem, AI, and defense to lessen reliance on Chinese technology.
- The European Union is engaging in free trade agreement negotiations with India to strengthen economic relationships and lower tariffs.
- Companies like Apple and Samsung are diversifying their operations in India to mitigate dependence on Chinese supply chains while tapping into India's consumer market.
India as a Strategic Ally Against China’s Dominance:
- The proposed India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) is seen as a potential counterbalance to China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in Eurasia, aiding in curbing China’s growing economic and political sway.
- The Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad) promotes stability in the Indo-Pacific through security, economic, and environmental cooperation.
- India’s 2+2 Dialogues with the US, Japan, and Australia, along with joint exercises such as Malabar and RIMPAC, enhance military interoperability and collective security.
- The US-led Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) collaborates with India to address economic challenges and counter China's trade influence.
Conclusion
In the future, India has the potential to become a significant player in global supply chains, provided it resolves internal challenges like infrastructure and regulatory issues. By leveraging this partnership, India can strengthen its economy and help create a more balanced global landscape.
Q10: Critically analyse India's evolving diplomatic, economic and strategic relations with Central Asian Republics highlighting their increasing significance in regional global geopolitics. (Answer in 150 words)
Ans:
Introduction
India has significantly expanded its diplomatic, economic, and strategic ties with the Central Asian Republics (CARs) to secure its interests in Central Asia.
Evolution of India-CARs Relations
Diplomatic Engagements:
- The Connect Central Asia Initiative (2012) was launched to strengthen India's ties with Central Asia.
- Platforms like the India-Central Asia Summit and Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) demonstrate India’s enhanced engagement with CARs.
Economic Relations:
- Projects like the TAPI pipeline and Ashgabat Agreement improve India’s access to energy resources in Central Asia.
- Chabahar Port facilitates trade routes through Iran to the South Caucasus, Central Asia, and beyond, expanding India’s economic reach in Eurasia.
Strategic Relations:
- CARs share borders with Afghanistan, a region affected by religious extremism.
- India maintains military cooperation in the region, including bases in Tajikistan and joint exercises with Uzbekistan.
Critical Analysis
Challenges in Connectivity:
- An unstable Afghanistan and tense India-Pakistan relations complicate direct connectivity between India and CARs.
Economic Disparities:
- India’s trade with Central Asia is around USD 2 billion, significantly lower than China’s trade with Central Asia, which stands at approximately USD 100 billion.
Geopolitical Influences:
- India’s Central Asian strategy is influenced by its policies toward Afghanistan, China, and Pakistan, as well as the interests of major powers like Russia and the United States.
Conclusion
India should continue proactive diplomatic engagements with Central Asian nations, emphasizing political, economic, and security cooperation through the India–Central Asia Dialogue. As a full SCO member, India has the opportunity to strengthen its role in regional security and economic dialogues, further solidifying its position in Central Asia.
Q11: What are the aims and objects of recently passed and enforced, The Public Examination (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024? Whether University/State Education Board examinations, too, are covered under the Act? (Answer in 250 words)
Ans:
Introduction
In response to the growing incidents of question paper leaks and other malpractices in public examinations, the Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024, was enacted by Parliament to enhance integrity, transparency, and credibility in India’s examination system.
Aims and Objectives of the Act
- The Act aims to curb unfair practices in public examinations, particularly organized cheating and malpractices.
- It defines specific offenses, such as leaking question papers, unauthorized possession of OMR sheets, tampering with documents, and creating fake websites.
- Strict guidelines and penalties have been established to deter these activities, thus restoring public trust in the examination system.
- Offenses under the Act are cognizable and non-bailable, with penalties ranging from three to five years in prison and fines up to Rs. 10 lakh. Investigations are conducted by officers at the rank of Deputy Superintendent or Assistant Commissioner.
- A High-Level National Technical Committee will develop protocols for securing digital platforms and enhancing IT security in examinations.
Coverage of Examinations
- Broad Definition of Public Examinations: The Act covers public exams conducted by specified authorities, such as UPSC and SSC.
- Definition of Institutions: It defines an "institution" as any agency or organization involved in public exams, excluding authorities and their service providers.
- Inclusion of Universities and State Boards: Although university and state board exams are not specifically mentioned, the central government can extend the Act’s coverage to additional authorities as needed.
- Model for State Adoption: The Act serves as a model for states, helping to prevent malpractices in state-level examinations.
Conclusion
The Public Examinations Act, 2024, strengthens the integrity of India’s public examinations by fostering transparency, accountability, and fairness. This Act is a significant step toward combating corruption and ensuring a trustworthy examination process for all candidates.
Q12: Right to Privacy is intrinsic to life and liberty and is inherently protected under Article 21 of the constitution. Explain. In this reference discuss the law relating to DNA testing of Child in the womb to establish its paternity. (Answer in 250 words)
Ans:
Introduction
The Right to Privacy is fundamental to the concepts of life and personal liberty enshrined in Article 21 of the Indian Constitution.
The Right to Privacy is Intrinsic to Life and Liberty
- The Right to Privacy, under Article 21, empowers individuals to make personal choices without state interference, thereby fostering freedom and autonomy.
- It includes the right to make decisions about one’s body, health, and reproductive matters, free from coercion, and to manage personal data to prevent unauthorized collection or use.
- The right also safeguards the confidentiality of personal communications, such as phone calls, emails, and letters, protecting individuals from unwarranted surveillance.
- This multifaceted right underscores the importance of personal dignity and autonomy.
Laws for DNA Testing for Paternity
Right to Privacy:
- The Puttaswamy judgment (2017) established that any intrusion into privacy, including DNA testing, must satisfy the criteria of legality, necessity, and proportionality, respecting the privacy of the woman and unborn child.
Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam (Section 116):
- It presumes that a child born within wedlock is legitimate. DNA testing may be ordered if prima facie evidence challenges paternity, as seen in the Nandlal Wasudeo Case (2014), where DNA evidence can override this presumption.
Pre-Conception and Pre-Natal Diagnostic Techniques (PCPNDT) Act, 1994:
- Regulates prenatal diagnostic tests, including DNA testing, to prevent misuse and gender-based discrimination, except for legitimate medical purposes.
DNA Technology Regulation Bill, 2019:
- Requires consent for DNA testing and allows court intervention in legal disputes, protecting privacy and penalizing DNA data misuse.
Judicial Observations:
- In the Aparna Ajinkya Firodia Case (2023), the court held that DNA testing in matrimonial disputes should only be ordered if sufficient prima facie evidence exists, given its potential impact on children.
Conclusion
While DNA testing for paternity may be permitted, it must respect privacy rights, legal safeguards, and medical ethics. Courts must carefully balance these competing rights, ensuring both privacy and justice based on the circumstances of each case.
Q13: What changes has the Union Government recently introduced in the domain of Centre-State Relations? Suggest measures to be adopted to build the trust between the Centre and the States for strengthening federalism. (Answer in 250 words)
Ans:
Introduction
Centre-state relations in India define the division of powers and responsibilities between the central and state governments, which form the backbone of Indian democracy. This framework is outlined in Part XI of the Constitution.
Recent Changes in Centre-State Relations
At the Administrative Level:
- In 2014, the Union government replaced the Planning Commission with NITI Aayog to promote cooperative federalism.
At the Legislative Level:
- The abrogation of Article 370 in 2019 enabled the full integration of Jammu and Kashmir into the Union of India.
- In 2024, the Cabinet approved the “one nation, one election” proposal, advocating for synchronized elections across the country.
At the Financial Level:
- The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) marked a significant reform in fiscal federalism. However, it reduced fiscal autonomy for states, as GST rates are set by the GST Council.
Concerns in Centre-State Relations
Administrative Concerns:
- Misuse of Article 356, deployment of central forces without state consent, and the role of Governors have raised concerns about administrative overreach.
- Increased allocations for Centrally Sponsored Schemes restrict states’ ability to prioritize their unique needs.
Legislative Concerns:
- Encroachment by the Center on state-list subjects and delays in assenting to state bills are ongoing issues.
- Example: The invocation of the Disaster Management Act, 2005, during the COVID-19 pandemic imposed central guidelines on states, although public health is primarily a state subject.
Financial Concerns:
- Centralization of resource mobilization, allocation, and economic decision-making has limited states’ fiscal autonomy.
Building Trust between Centre and States
- Strengthening Dialogue: Enhanced communication between the Centre and states is essential, with a focus on empowering the Inter-State Council, as recommended by the Sarkaria Commission (1983).
Second ARC Report (1969) Recommendations:
- Establish an Inter-State Council.
- Delegate maximum powers to the states.
- Augment states’ financial resources through increased fiscal transfers from the Centre.
- Appoint non-partisan individuals with extensive public experience as Governors.
- Limit the use of Articles 355 and 356 to safeguard state autonomy.
Conclusion
Strengthening federalism requires improved dialogue through the Inter-State Council, timely legislation, and enhanced fiscal autonomy for states, fostering a more balanced and cooperative relationship between the Centre and states.
Q14: Explain the reasons for the growth of public interest litigation in India. As a result of it, has the Indian Supreme Court emerged as the world's most powerful judiciary? (Answer in 250 words).
Ans:
Introduction
Public Interest Litigation (PIL) is a legal mechanism that allows concerned individuals or groups to bring a matter to court to protect public interests or the rights of marginalized groups. Justice Krishna Iyer pioneered the concept of PIL in India in Mumbai Kamagar Sabha vs. Abdul Thai (1976). It is not defined in statutory law but emerged through judicial review.
Reasons for the Growth of PILs
- Constitutional Framework: PILs are grounded in the Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of the Constitution, promoting social justice.
- Relaxation of Locus Standi: Courts relaxed the principle of locus standi for PILs, allowing concerned citizens or organizations to file petitions on behalf of marginalized groups.
- Judicial Activism: The judiciary has actively expanded the scope of PILs, particularly when executive bodies fail to ensure justice, as seen in Bandhua Mukti Morcha v. Union of India (1984), which liberalized access to courts for social causes.
- Government Inaction: Many PILs emerge due to the failure of government agencies to address public grievances effectively, often stemming from bureaucratic delays or corruption.
Growth of PILs Making the Supreme Court the World’s Most Powerful Judiciary
Power to Strike Down Laws: The Supreme Court’s power to strike down unconstitutional laws, as seen when it invalidated the NJAC Act and the 99th Constitutional Amendment in 2021, underscores its role in shaping legislation.
Addressing Government Inaction via Judicial Review: In M.C. Mehta v. Union of India (1988), the court issued orders to control pollution and clean the Ganga. In the 2024 NEET paper leak case, the court expanded the scope of a Centre-appointed panel to review the functioning of the National Testing Agency (NTA) and recommend reforms.
Wider Interpretation of Rights: The Supreme Court has expanded the interpretation of rights under Article 21, affirming the right to privacy in the Puttaswamy case (2017) and the dignity of sex workers in the Budhadev Karmaskar case (2022).
Suo Motu Powers: The court’s ability to take up matters on its own accord, such as its response to the mishandling of the Kolkata Murder-Rape case in 2024, shows its commitment to addressing serious societal issues.
Judicial Activism and Overreach: The Supreme Court has taken significant steps to uphold rights and curb social issues, as seen in the Navtej Singh Johar case that decriminalized homosexuality, and in Shayara Bano (2017), where it invalidated triple talaq. In 2017, it ordered a ban on liquor sales within 500 meters of highways to reduce road accidents, reflecting its proactive stance.
Conclusion
While PILs have expanded the judiciary's role in promoting justice and have made the Supreme Court one of the world’s most powerful judiciaries, judicial overreach has been criticized for encroaching on legislative and executive domains. In countries with similar systems, such as the US and Australia, the principle of separation of powers is more rigorously observed. Respecting this separation is essential for upholding the democratic spirit and maintaining balanced governance.
Q15: Discuss India as a secular state and compare with the secular principles of the US constitution. (Answer in 250 words)
Ans:
Introduction
The concept of secularism differs notably between India and the United States, both in theory and practice.
In India, secularism reflects a positive approach, giving equal respect to all religions, regardless of their size or influence. In contrast, the Western model, seen in the US, emphasizes a strict separation between religion and the state.
Comparative Analysis of Secularism in India and the United States
Constitutional Basis:
- India: Secularism is enshrined in the Preamble (42nd Constitutional Amendment Act of 1976) and Articles 15 and 25-28.
- United States: The First Amendment, particularly the "Establishment Clause," establishes the secular basis.
Definition of Secularism:
- India: Involves equal respect for all religions.
- United States: Emphasizes a separation between church and state.
State Involvement in Religion:
- India: The state actively engages in religious affairs, such as managing temples and subsidizing pilgrimages.
- United States: State involvement is minimal, with a prohibition on endorsing or interfering in religious matters.
Religious Education:
- India: Religious education is not permitted in fully state-funded schools.
- United States: Prohibited in public schools but allowed in private institutions.
Personal Laws:
- India: Different religious communities follow separate personal laws, such as the Hindu Marriage Act and Muslim Personal Law.
- United States: A uniform family law applies to all citizens, without religious distinctions.
State Funding for Religious Activities:
- India: Permitted for secular aspects related to religion, such as funding for education (Maulana Azad Education Foundation) and healthcare (Christian Medical College).
- United States: Generally prohibited, with limited exceptions (e.g., faith-based initiatives).
Recent Legal Challenges:
- India: Issues include debates over the CAA 2019 and the Hijab ban in Karnataka's educational institutions (2022).
- United States: Challenges involve school prayer and religious symbols in public spaces.
Conclusion
Both India and the United States face challenges in balancing religious influence in politics with the protection of individual rights. The effectiveness of secularism in fostering harmony and supporting democracy depends on a steadfast commitment to constitutional principles in both countries.
Q16: The Citizen Charter has been a landmark initiative in ensuring citizen centric administration. But it is yet to reach its full potential. Identify the factors hindering the realisation of its promise and suggest measures to overcome them? (Answer in 250 words)
Ans:
Introduction
The Citizen's Charter is an important initiative aimed at improving transparency, accountability, and efficiency in delivering public services. The Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) is responsible for coordinating, formulating, and operationalizing Citizen's Charters.
Factors/Challenges Hindering the Realization of Citizen Charters
- Lack of Awareness: Many citizens are unaware of the Citizen’s Charter or the rights it provides, resulting in a lack of accountability for public authorities.
- Limited Enforcement: Although the Citizen's Charter outlines service standards, there are few mechanisms to enforce compliance or penalize government officials for failing to meet these standards.
- Infrequent Updates: Some departments do not update their charters regularly, leading to inconsistencies and unequal service delivery.
- Perception as Burden: Many officials view the Citizen's Charter as an additional workload and show reluctance in meeting its standards.
- Insufficient Training: Public officials often lack adequate training in citizen-centered service delivery and understanding of the Citizen's Charter, which limits effective implementation.
Measures to Overcome the Challenges
- Accountability Measures: The Second Administrative Reforms Commission (ARC) recommended implementing punitive measures for non-compliance, such as financial penalties or disciplinary actions for officials, to enhance accountability.
- Focused Commitments: Charters should prioritize a few achievable commitments rather than an extensive list of promises that may go unfulfilled.
- Tailored Charters: Uniform charters across organizations can reduce effectiveness; hence, it’s essential to develop charters tailored to local contexts and specific organizational needs.
- Accountability for Unmet Commitments: Officers should be held accountable if the commitments in the Citizen's Charter are not met, reinforcing their responsibility to uphold public trust.
- Regular Reviews: Citizen’s Charters should be reviewed and updated frequently to ensure they stay relevant and meet the changing needs and expectations of the public.
- Organizational Restructuring: Before creating a charter, organizations should reorganize structures and processes to facilitate effective implementation.
Conclusion
The Citizen's Charter has the potential to transform governance by enhancing transparency, efficiency, and a citizen-focused approach. Achieving this potential requires addressing implementation challenges through increased public awareness, enhanced accountability, effective training, and fostering a culture that prioritizes citizens’ needs.
Q17: In a crucial domain like the public healthcare system the Indian State should play a vital role to contain the adverse impact of marketisation of the system. Suggest some measures through which the State can enhance the reach of public healthcare at the grassroots level. (Answer in 250 words)
Ans:
Introduction
India’s healthcare sector reached USD 372 billion in 2023, with the private sector dominating secondary and tertiary care, primarily in metro, tier-I, and tier-II cities. The increasing marketization of healthcare raises concerns, as it can lead to viewing health as a commodity, focusing on profit over patient welfare, potentially compromising care quality and worsening healthcare access inequalities.
Role of the State in Containing the Adverse Impact of Marketization of the Healthcare System
Right to Health:
- Article 21 of the Constitution includes the right to health, obligating the state to safeguard this right amid marketization pressures that could lead to inequality and reduced service quality.
State as a Benefactor:
- The state ensures healthcare access for all, especially vulnerable populations, through public hospitals and subsidized care schemes like the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS).
- It establishes quality standards and measures for patient satisfaction to uphold dignity and protect patient rights.
State as a Regulator:
- Through the Indian Medical Council (Professional Conduct, Etiquette and Ethics) Regulations, 2002, the state sets norms to curb profit-driven degradation of services and safeguard citizen health.
State as a Facilitator:
- The state promotes public-private partnerships (PPPs) to improve service delivery in underserved areas and mobilizes funds for equitable healthcare financing.
Measures to Enhance Public Healthcare Reach at the Grassroots Level
Training Community Health Workers:
- Training community health workers, such as ASHAs and ANMs, enables them to act as liaisons between healthcare systems and communities, facilitating health education and early detection of diseases.
Expanding Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres:
- Expanding these centers helps ensure comprehensive primary healthcare services, including preventive, promotive, and curative care, are available at the local level.
Utilizing 15th Finance Commission Grants:
- These grants should be used to strengthen local health systems and implement community-specific health programs.
Targeted Initiatives for Vulnerable Areas:
- Initiatives like Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyay Maha Abhiyaan should be implemented to improve immunization in low-coverage areas, particularly in tribal and remote regions.
Expanding Medical Education and Telehealth:
- Establishing new medical colleges in aspirational districts, using data from Rural Health Statistics for informed decisions, and integrating telehealth services can improve healthcare accessibility and effectiveness.
Conclusion
The state can leverage marketization to foster competition, making high-quality healthcare more affordable and accessible. By prioritizing patient welfare and enhancing access for vulnerable populations, the state can ensure healthcare systems serve public needs effectively.
Q18: e-governance is not just about the routine application of digital technology in service delivery process. It is as much about multifarious interactions for ensuring transparency and accountability. In this context evaluate the role of the ‘Interactive Service Model’ of e-governance. (Answer in 250 words)
Ans:
Introduction
E-governance involves the use of digital technology by governments to deliver services to citizens. Examples include DigiLocker, Jeevan Pramaan, and Mobile Seva. The interactive service model (ISM) in e-governance transforms traditional one-way service delivery into a dynamic dialogue, enabling citizens to voice concerns and participate in decision-making.
Role of Interactive Service Model (ISM) in Ensuring Transparency and Accountability
Two-way Communication: Initiatives like MyGov in India allow direct interaction between citizens and the government, fostering engagement and gathering public feedback.
Access to Information: Portals like the Right to Information mechanism and the National Portal of India provide citizens with easy access to comprehensive updates and information.
Grievance Redressal: Systems like the Centralised Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS) enable citizens to report issues and receive timely responses, improving accountability.
Citizen Engagement: Programs such as “Bhagidari” encourage active citizen participation in governance, reinforcing a partnership between the government and the public.
Feedback Mechanisms: Projects like Karnataka’s Bhoomi platform facilitate real-time citizen feedback on digitized land records, enhancing responsiveness in service delivery.
Ensuring Transparency: Initiatives like social audits, with Meghalaya being the first state to pass social audit legislation, promote openness in government processes and build public trust.
Challenges in Implementing the Interactive Service Model
Digital Divide: Unequal access to technology is a challenge, with internet penetration at 67% in urban areas compared to only 31% in rural regions.
Bureaucratic Resistance: Resistance to adopting new systems can hinder the effective implementation of ISM.
Data Privacy Concerns: Concerns over data security and privacy may limit citizen participation and trust in digital platforms.
Conclusion
To address these challenges, the government should focus on bridging the digital divide through rural connectivity and promoting digital literacy. Ensuring robust data privacy measures and encouraging bureaucratic reforms are also essential. These steps will enhance transparency and empower citizens by making government services more accessible and responsive through digital platforms and social media.
Q19: Terrorism has become a significant threat to global peace and security. Evaluate the effectiveness of the United Nations Security Council’s Counter-Terrorism Committee (CTC) and its associated bodies in addressing and mitigating this threat at the international level. (Answer in 250 words).
Ans:
Introduction
The Global Terrorism Index 2024 reports a 22% rise in terrorism-related deaths globally, marking the highest level since 2017. In response, the UN Security Council’s Counter-Terrorism Committee (CTC) plays a critical role in fostering international cooperation to address this growing threat.
Threat of Terrorism to Global Peace and Security
Erosion of State Sovereignty: Weak states like Afghanistan and Somalia have seen groups like the Taliban and Al-Shabaab thrive, undermining governance.
Economic Impact: The 9/11 attacks caused an estimated USD 40 billion in losses for the U.S. economy, while the 2015 Paris attacks significantly impacted European tourism.
Humanitarian Crises: The rise of ISIS and conflicts in Syria and Iraq have triggered large-scale refugee crises, placing immense strain on host countries.
Political Tensions: Terrorism exacerbates geopolitical conflicts, such as those between India and Pakistan, as seen in the 2019 Pulwama attack.
UNSC-CTC and its Effectiveness
The CTC was established by Resolution 1373 following the 9/11 attacks to coordinate international efforts to combat terrorism.
It supports the implementation of legal frameworks, such as UNSC Resolutions 1373 and 1540, requiring member states to prevent terrorism and stop the proliferation of weapons.
The CTC promotes capacity-building initiatives, facilitates international collaboration in intelligence sharing, and adopts modern strategies to counter cyber-terrorism and social media recruitment.
Challenges of the UNCTC
Lack of Universal Definition: Varied definitions of terrorism lead to inconsistent international responses.
Enforcement Issues: Counter-terrorism efforts face significant obstacles in regions like Somalia due to governance and logistical challenges.
Political Complexities: The veto power, particularly from China, sometimes hinders consensus on designating terrorist groups.
Evolving Threats: New forms of terrorism, including cyber-terrorism and lone-wolf attacks, present emerging challenges.
Suggestions for Improvement
Create Binding Counter-Terrorism Frameworks: Developing universally binding frameworks can improve consistency in counter-terrorism efforts.
Enhance Real-Time Information Sharing: Improving coordination on financing and movement tracking can help combat terrorism financing.
Community Collaboration: Working with local communities can play a key role in preventing radicalization at the grassroots level.
Increase Financial and Technical Aid: Providing more resources for developing nations enhances their capacity to tackle terrorism.
Conclusion
While the CTC has made significant progress in countering terrorism, a proactive and adaptive approach is essential. Strengthening legal frameworks, enhancing intelligence-sharing mechanisms, and fostering community-based initiatives will better equip the international community to address evolving threats and promote global security.
Q20: Discuss the geopolitical and geostrategic importance of Maldives for India with a focus on global trade and energy flows. Further also discuss how this relationship affects India's maritime security and regional stability amidst international competition ? (Answer in 250 words)
Ans:
Introduction
The Maldives, a vital element of India’s “neighbourhood first” policy, holds significant geopolitical and geostrategic value due to its strategic location in the Indian Ocean along critical maritime routes. This importance extends far beyond its small physical size.
Geopolitical and Geostrategic Importance of Maldives
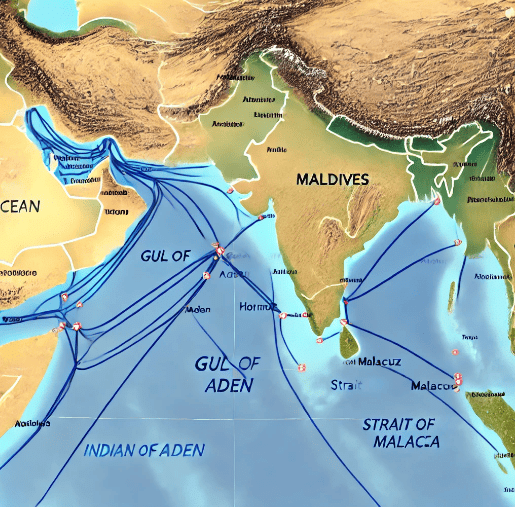
Sea Lanes of Communication (SLOCs):
- The Maldives controls two key SLOCs at its southern and northern ends, which are essential for maritime trade connecting the Gulf of Aden, the Gulf of Hormuz, and the Strait of Malacca.
- These SLOCs are critical for India, with 50% of its external trade and 80% of its energy imports passing through the Arabian Sea.
Indian Ocean as India’s Backyard:
- The Maldives’ strategic location makes it integral to India’s role as a net security provider in the Indian Ocean. India’s collaboration with the Maldives in defense, maritime surveillance, and humanitarian assistance enhances regional security.
Impact of Changing India-Maldives Relationship
In recent years, there has been a perceived decline in India-Maldives relations, with several key implications:
Strategic Dynamics:
- India’s limited engagement has allowed China to increase its influence in the Maldives through Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) investments, which threatens India’s control over critical maritime routes and its broader maritime security.
Economic Competition:
- China has become a major economic player in the Maldives through chequebook diplomacy, challenging India’s traditional role as the primary partner in the region.
Diplomatic Strain:
- The Maldives’ balancing strategy, fueled by perceptions of India’s “Big Brother syndrome,” complicates India’s diplomatic outreach and reduces its influence in the Indian Ocean.
Maritime Security:
- China’s submarine and destroyer deployments, along with new docking facilities in the Maldives and Sri Lanka, pose a direct threat to India’s maritime interests.
Terrorism:
- Growing anti-India sentiment and the Maldives’ focus on Islamic values raise concerns about terrorism, potentially destabilizing the region and impacting India’s security.
Conclusion
In the face of rising Chinese influence and anti-India sentiment, strengthening India-Maldives relations is crucial for regional stability and shared prosperity. A strong partnership will not only support economic growth and cultural ties but also reinforce security cooperation, creating a resilient future for both nations.
|
180 videos|454 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Mains 2024 GS Paper 2 with Answers - UPSC Previous Year Question Papers and Video Analysis
| 1. What is the significance of GS Paper 2 in the UPSC Mains exam? |  |
| 2. What are the main topics covered in GS Paper 2? |  |
| 3. How can candidates effectively prepare for GS Paper 2? |  |
| 4. What is the marking scheme for GS Paper 2 in the UPSC Mains exam? |  |
| 5. How important is current affairs for GS Paper 2 preparation? |  |
















