Mnemonics: Kinematics | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Motion in a Straight Line |

|
| 2. Scalars and Vectors |

|
| 3. Addition of Vectors |

|
| 4. Angle of Maximum Range |

|
KINEMATICS the study of motion, can often seem daunting due to its numerous equations and concepts. To simplify and make learning more engaging, mnemonics provide an effective way to remember key principles, formulas, and processes. 
This Edurev document compiles easy-to-remember phrases that break down the complexities of kinematics into manageable and fun learning tools, ensuring you grasp the essence of the subject effortlessly.
1. Motion in a Straight Line
Mnemonic: "Delhi to Vadodara via Tundla Agra".
Explanation:
- Delhi: Displacement
- To: Time
- Vadodara: Velocity
Displacement / time = Velocity
- Via: Velocity
- Tundla: Time
- Agra: Acceleration
Velocity / time = Acceleration
Uses in almost every question to solve numericals of Kinematics.
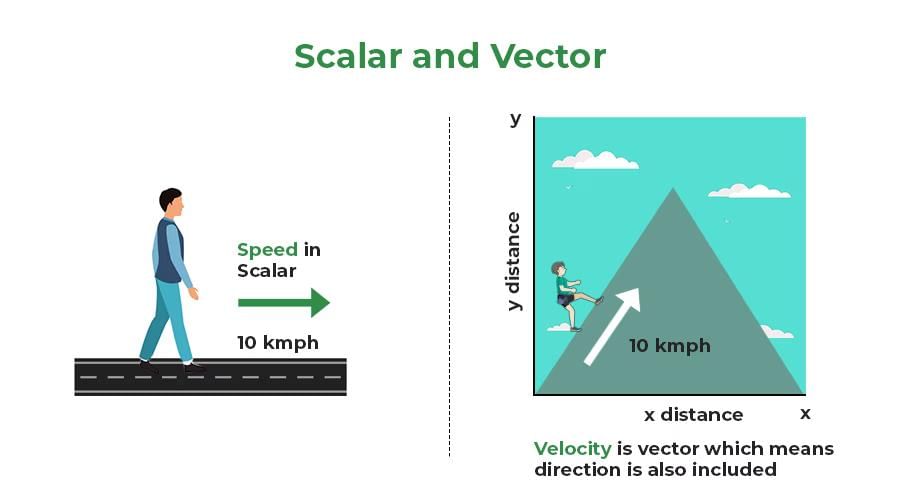
2. Scalars and Vectors
Mnemonic: "Some Values Need Direction!"
Explanation:
Scalars: Represent "Some Values"
- Scalars are quantities that only have magnitude (size) but no direction.
- Examples: Speed, Distance, Mass, Energy, Time, etc.
Vectors: Represent "Need Direction"
- Vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction.
- Examples: Velocity, Displacement, Force, Acceleration, etc.
3. Addition of Vectors
Mnemonic: "Tail-Head Adds Right!"
Explanation:
This mnemonic simplifies the process of vector addition using the head-to-tail rule:
"Tail-Head"
- When adding vectors, place the tail of the second vector at the head of the first vector.
- This method ensures that vectors are connected in a sequence.
"Adds Right"
- The resultant vector is drawn from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector.
- This resultant represents the combined effect of the vectors being added.
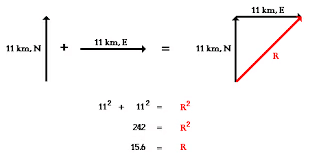
Without knowing how to add vectors, one cannot proceed to solve the numericals which necessarily comes in exams.
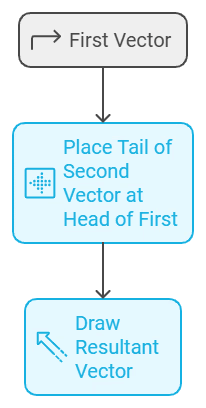
For Example -
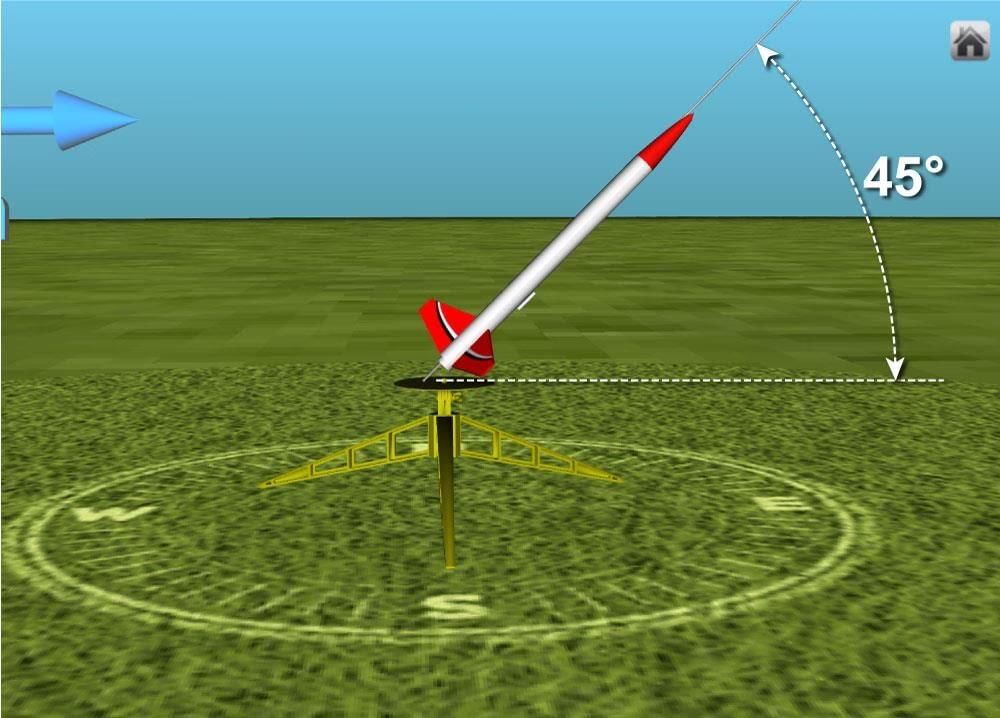
4. Angle of Maximum Range
Mnemonic: "Fly at Forty-Five"
Explanation:
This mnemonic is related to projectile motion and reminds you of the optimal angle for achieving maximum range:
"Fly"
- Refers to the projectile's motion, indicating the object is launched.
"Forty-Five"
- The maximum range of a projectile is achieved when it is launched at an angle of 45° to the horizontal.
- This is because, at 45°, the horizontal and vertical components of the velocity are equal, optimizing both height and horizontal distance.
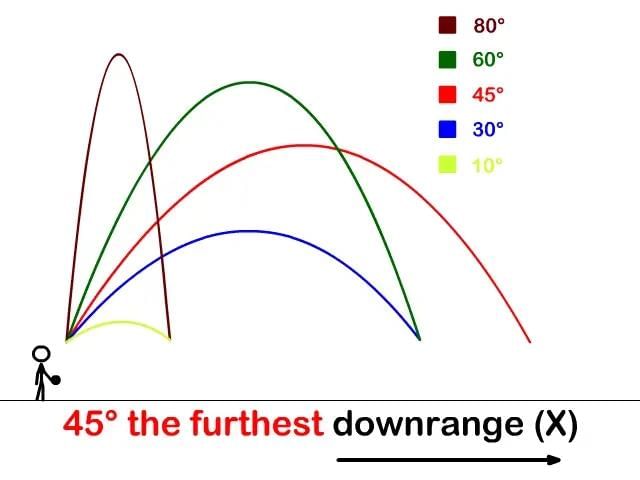
Information about Projectile must to have as Projectile Motion is an important part of Kinematics to understand the motion.
For example-
Visualize a rocket flying perfectly at a 45-degree angle for the farthest reach.
|
119 videos|494 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Kinematics - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the difference between scalars and vectors in motion? |  |
| 2. How do you add vectors geometrically? |  |
| 3. What factors affect the angle of maximum range in projectile motion? |  |
| 4. How does motion in a straight line differ from motion in a curved path? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the equations of motion in kinematics? |  |