NCERT Summary: Judiciary | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
Laws apply equally to all people. A certain set of fixed procedures needs to be followed when a law is violated. To enforce this rule of law, we have a judicial system that consists of a system of courts that a citizen can approach when a law is violated. As an organ of government, the judiciary plays a crucial role in the functioning of India’s democracy. It can play this role only because it is independent.

What is the Role of Judiciary?
- Dispute Resolution: The judicial system resolves disputes/fights between citizens, between citizens and the government, between two state governments, and between the center and state governments.
- Judicial Review: The judiciary is the final interpreter of the Constitution. Therefore, it has the power to cut down particular laws passed by Parliament if it believes that they violate the basic structure of the Constitution. This is called judicial review.
- Upholding the Law and Enforcing Fundamental Rights: Every citizen of India can approach the Supreme Court or the High Court if his/her fundamental rights have been violated.
What is an Independent Judiciary?
The Independence of the Judiciary means:- Other branches of government – the legislature and the executive – cannot interfere in the judiciary's work. The courts are not under the government and do not act on their behalf.
- Independence of the judiciary allows the courts to play a central role in ensuring that there is no misuse of power by the legislature and the executive.
- Independence of the judiciary also plays a crucial role in protecting the Fundamental Rights of citizens.
What is the Structure of Courts in India?
There are three different levels of courts in our country.
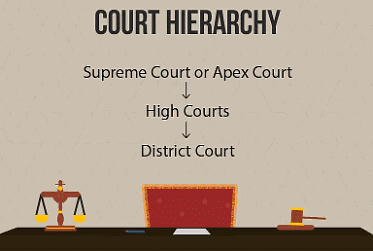
- District Court: The courts that most people interact with are called subordinate or district courts or Tehsil level court.
- High Court: Each state has a High Court which is the highest court of that state.
- Supreme Court: It is at the top level. The decisions made by the Supreme Court are binding on all other courts in India. Supreme Court of India is located in New Delhi.
In India, we have an integrated judicial system, meaning that the decisions made by higher courts are binding on the lower courts. A person can appeal to a higher court if they believe that the judgment passed by the lower court that is District Court is unjust.
What are the Different Branches of the Legal System?
The Indian legal system deals with civil and criminal cases.
- Civil laws deal with any harm or injury to the rights of individuals.
- Criminal law deals with the conduct or acts the law defines as offenses.
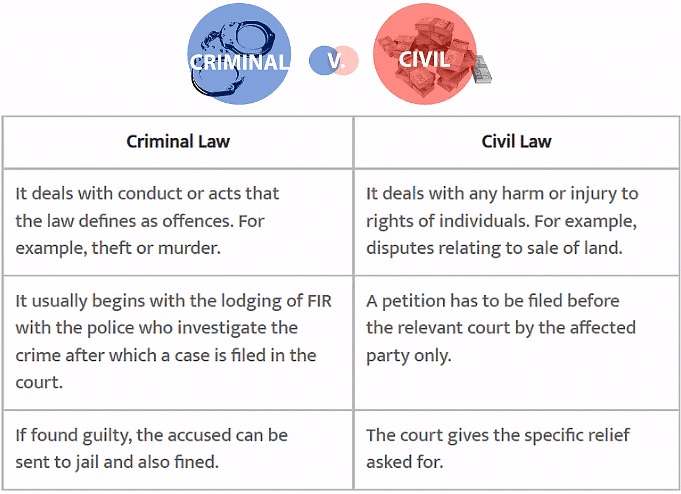
In criminal cases, it usually begins with the lodging of our First Information Report (FIR) with the police who investigate the crime after which a case is filled in the court.
Public Interest Litigation (PIL)

Public interest Litigation” or PIL is litigation filed in a court of law for the protection of “Public Interest”, such as pollution, terrorism, road safety, construction hazards etc.
PIL can be filed for the following reasons:
- Violation of basic human rights of the poor
- Content or conduct of government policy
- Force municipal authorities to perform a public duty
- Violation of religious rights or other basic fundamental rights
- Any individual or organization can file a PIL in the High Court or the Supreme
- The court on behalf of those whose rights are being violated. It is not necessary that the person filing a case should have a direct interest in the case.
Importance of Judiciary
The judiciary has played a crucial role in democratic India:
- The judiciary is the guardian of the constitution
- It also keeps a check on the powers of the executive and the legislature
- It helps in protecting the Fundamental Rights of citizens.
- The judiciary plays an important role in the interpretation of laws.

Does Everyone Have Access to the Courts?
- In principle, all citizens of India can access the courts in this country. This implies that every citizen has a right to justice through the courts.
- Legal procedures involve a lot of money and paperwork which takes up a lot of time. Poor people often avoid going to court to get justice.
- The Supreme Court devised a mechanism of Public Interest Litigation or (PIL) to increase access to justice in the 1980s. It allowed any individual or organization to file a PIL in the High Court or the Supreme Court on behalf of those whose rights were being violated.
- The legal process was simplified and even a letter or telegram addressed to the Supreme Court, or the High Court could be treated as a PIL.
- The court exercises a crucial role in interpreting the Fundamental Rights of Citizens.
- The judiciary serves as a check on the powers of the executive and the legislature and protects the Fundamental Rights of the citizens.
|
145 videos|630 docs|203 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: Judiciary - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the primary role of the judiciary in India? |  |
| 2. What does it mean to have an independent judiciary? |  |
| 3. What is the structure of the court system in India? |  |
| 4. What are the different branches of the legal system in India? |  |
| 5. How does Public Interest Litigation (PIL) function in the Indian judiciary? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















