Cheat Sheet: Emergency Provisions | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
The Indian Constitution incorporates emergency provisions that empower the Central government to take control during crises to safeguard the nation's sovereignty, unity, and democratic principles. These provisions allow the Constitution to shift between federal and unitary forms depending on the situation, reflecting its flexibility and adaptability. This document provides a detailed chronology of the emergency provisions (Articles 352 to 360), focusing on National Emergency, President's Rule, and Financial Emergency, along with their impacts on governance and constitutional processes.

National Emergency (Article 352)

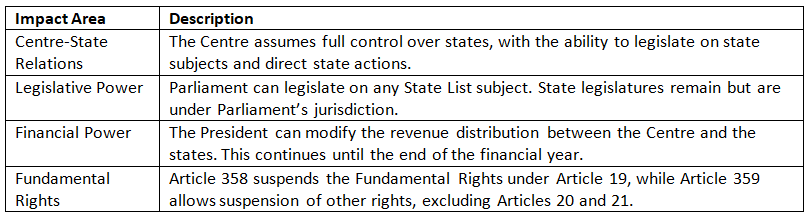
Effects of National Emergency
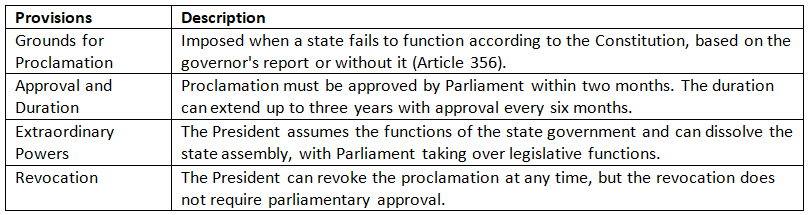
President's Rule (Article 356)
Judicial Review of President's Rule

Instances of National Emergency

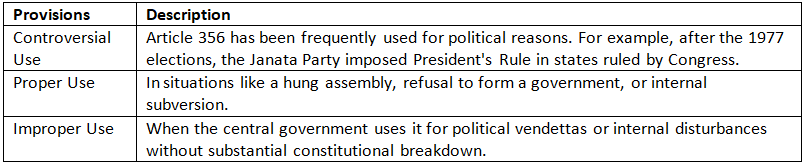
President's Rule - Controversies and Proper Use
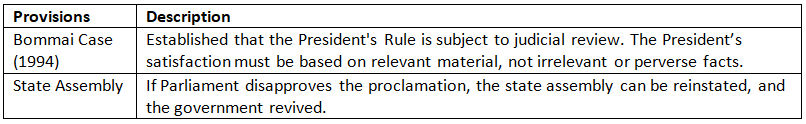
Scope of Judicial Review in Article 356
Conclusion
The emergency provisions within the Indian Constitution provide a framework that allows the Centre to assume greater powers in times of national crisis. While these provisions are designed to safeguard the country’s unity, sovereignty, and stability, they have been the subject of political debates and misuse, especially Article 356, which grants significant power to dissolve state governments. The judicial review of these provisions ensures that they cannot be arbitrarily used, maintaining the Constitution's core values. Through a careful balance of power, the Constitution allows for the federal structure to temporarily shift to a more unitary form, reflecting its flexibility and adaptability in responding to crises.
|
170 videos|999 docs|259 tests
|
















