Summary of Union Budget 2024-25 | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
A budget is a forecast of the government’s revenue and expenses for a future period, typically the upcoming financial year. The Union Budget gives a detailed account of the government's finances over the previous fiscal year, summarises new tax proposals for the upcoming fiscal year, and estimates revenue and expenditure for the next fiscal year.
The Union Budget accounts for the government's finances during the fiscal year from April 1 to March 31. The first Budget in pre-independent India was presented in 1860 by James Wilson of the British Indian Government. After independence, India's first Budget was presented in 1947 by Finance Minister RK Shanmukham Chetty. 
Union Budget 2024 Overview
The Union Budget is the yearly financial report of the Union Government of India, presented by the Finance Minister on February 1st in the Lok Sabha.
- Budget Preparation: The Department of Economic Affairs under the Ministry of Finance is in charge of creating the Budget document.
- Budget Classification: The Union Budget is divided into two main parts:
- Revenue Budget: This part outlines the government's expected income for the year, which includes taxes.
- Capital Budget: This focuses on the government's assets and debts, highlighting major expenditures such as infrastructure development.
Parts of the Budget:
- Part A: This section provides a macroeconomic overview, announcing government schemes and priorities.
- Part B: This includes the Finance Bill, which contains proposals related to taxation, such as changes in income tax.
- Finance Bill: This bill is classified as a Money Bill according to Article 110 of the Constitution.
- Authority on Money Bill: The Speaker of the Lok Sabha has the final say on whether a bill is a Money Bill.
Union Budget Constitutional Provisions
- Constitutional Provision: According to Article 112 of the Indian Constitution, the Union Budget is a report that outlines the government's expected income and spending.
- It is also referred to as the Annual Financial Statement of the Government; however, the word "budget" is not specifically used in the Constitution.
- Key Budget Documents:In addition to the Budget Speech, there are several important documents, including:
- Annual Financial Statement (as per Article 112)
- Demands for Grants (as per Article 113)
- Finance Bill (as per Article 110)
- Fiscal Policy Statements required by the FRBM Act, 2003, which include:
- The Macro-Economic Framework Statement
- The Medium-Term Fiscal Policy cum Fiscal Policy Strategy Statement
- Additional Documents:Other explanatory documents that are presented include:
- Expenditure & Receipt of Budget
- Expenditure Profile
- Budget at a Glance
- Memorandum Explaining the Provisions in the Finance Bill
- Output Outcome Monitoring Framework
- Key Features of Upcoming Financial Year Budget
- Implementation of Budget Announcements for the previous financial year
Union Budget 2024 Highlights
The Finance Minister presented the Union Budget for 2024-25 on July 23, 2024. Earlier, interim budget 2024 was presented in February 2024.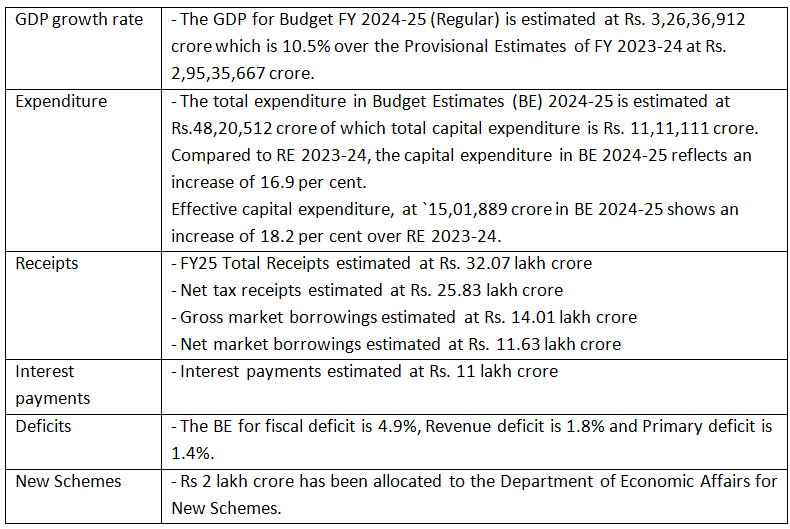
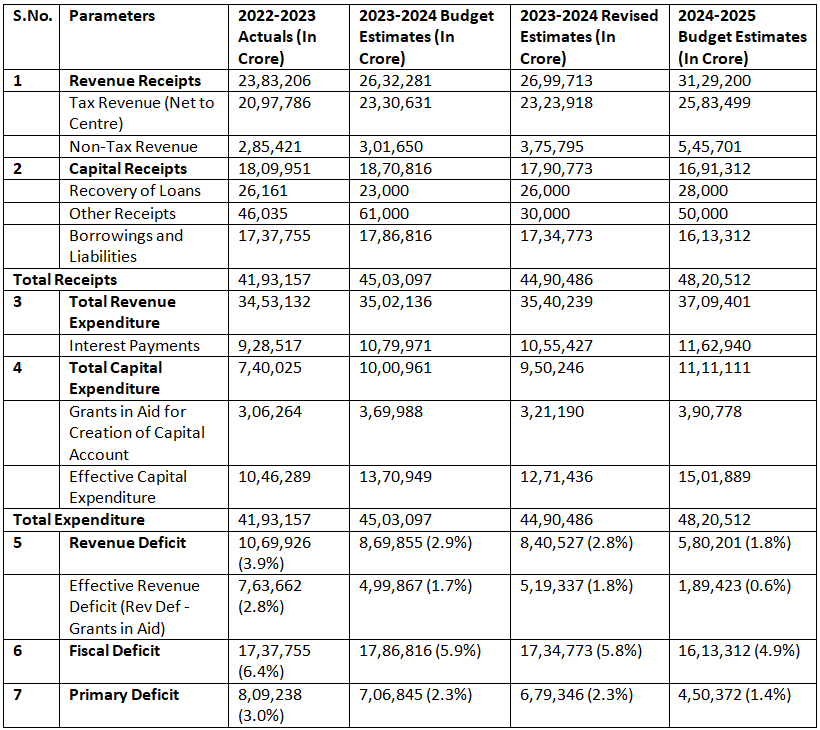
Union Budget 2024 at a Glance
Budget at a Glance shows receipts and expenditure as well as the deficits of the Government of India.
Part A: Priorities Areas of Budget
On Budget priorities, the Finance Minister said that in line with the strategy set in the interim Budget, this Budget envisages sustained efforts on the following nine priorities for generating ample opportunities for all.
Productivity and Resilience in Agriculture
- Transforming Agriculture Research: Comprehensive review of the agriculture research setup to bring focus on raising productivity and developing climate resilient varieties.
- National Cooperation Policy: For systematic, orderly and all-round development of the cooperative sector.
- Vegetable production & supply chain: Promotion of FPOs, cooperatives & start-ups for vegetable supply chains for collection, storage, and marketing.
- Release of new varieties: 109 new high-yielding and climateresilient varieties of 32 field and horticulture crops will be released for cultivation by farmers.
- Natural Farming:
- 1 crore farmers across the country will be initiated into natural farming, supported by certification and branding in next 2 years.
- 10,000 need-based bio-input resource centres to be established.
- Atmanirbharta: For oil seeds such as mustard, groundnut, sesame, soyabean and sunflower.
Employment & Skilling
- Employment and Skilling Initiatives: The Prime Minister has introduced a package of five schemes aimed at creating job opportunities and enhancing skills for 4.1 crore youth over a span of five years.
- Scheme A - First Timers: This scheme offers a monthly salary of up to ₹15,000 in three installments for first-time employees registered with the EPFO.
- Scheme B - Job Creation in Manufacturing: An incentive will be given based on the EPFO contributions of both employees and employers for the first four years of employment.
- Scheme C - Support to Employers: The government will reimburse up to ₹3,000 per month for two years towards the EPFO contributions of employers for each new employee hired.
- New Centrally Sponsored Skilling Scheme:
- Targeting to skill 20 lakh youth over five years.
- Upgrading 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes to improve training through a hub-and-spoke model.
- Course content and design will be aligned with the skill requirements of various industries.
- New Internship Scheme: This initiative aims to provide internships for 1 crore youth in 500 top companies over five years.
- Loan Scheme:
- Offering loans up to ₹7.5 lakh backed by a government-promoted fund, expected to assist 25,000 students annually.
- Financial support for loans up to ₹10 lakh for higher education in domestic institutions.
- Direct e-vouchers will be given to 1 lakh students each year with an annual interest subsidy of 3%.
Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
Purvodaya: A plan focusing on the development of rich states in the Eastern region, including Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh, to create economic opportunities for a prosperous India.
- Amritsar Kolkata Industrial Corridor: Plans to develop an industrial center in Gaya.
- Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan: Aiming to enhance the living standards of tribal communities across 63,000 villages, benefiting 5 crore tribal individuals.
- Investment for Women and Girls: Over ₹3 lakh crore allocated for various schemes that support women and girls.
- North East Development: More than 100 branches of India Post Payment Bank will be established in the North East region.
- Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act:
- Financial backing of ₹15,000 crores will be provided for the fiscal year 2024-2025.
- Completion of the Polavaram Irrigation Project to ensure food security for the country.
- Development of essential infrastructure such as water, power, railways, and roads in the Kopparthy node on the Vishakhapatnam-Chennai Industrial Corridor and the Orvakal node on the Hyderabad-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor.
Manufacturing & Services
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs in the Manufacturing Sector and Credit Support to MSMEs during Stress Period
- Enhanced scope for mandatory onboarding in TReDS
- New assessment model for MSME credit
- Mudra Loans: The limit enhanced to ₹ 20 lakh from the current ₹ 10 lakh under the ‘Tarun’ category.
- MSME Units for Food Irradiation, Quality & Safety Testing
- Twelve industrial parks under the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme
- Rental housing with dormitory type accommodation for industrial workers in PPP mode with VGF support.
- Critical Minerals Mission for domestic production, recycling and overseas acquisition.
- Strengthening of the tribunal and appellate tribunals to speed up insolvency resolution and additional tribunals to be established
- Internship Opportunities:
- Scheme for providing internship opportunities in 500 top companies to 1 crore youth in 5 years.
- Allowance of ₹5,000 per month along with a one-time assistance of ₹6,000 through the CSR funds.
Urban Development
- Stamp Duty: Encouraging states to lower stamp duties for properties purchased by women.
- Street Markets: Envisioning a scheme to develop 100 weekly ‘haats’ or street food hubs in select cities
- Transit Oriented Development: Transit Oriented Development plans for 14 large cities with a population above 30 lakh
- Water Management: Promote water supply, sewage treatment and solid waste management projects and services for 100 large cities through bankable projects.
- PM Awas Yojana Urban 2.0:
- Needs of 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families will be addressed with an investment of ₹10 lakh crore
- Enabling policies and regulations for efficient and transparent rental housing markets with enhanced availability will also be put in place.
Energy Security
Collaborations with the Private Sector in Nuclear Energy:
- Establishment of Bharat Small Reactors: Initiatives are underway to create small reactors within the country.
- Research and Development: Focus on the Bharat Small Modular Reactor and the development of new technologies for nuclear energy.
- Pumped Storage Policy: This policy aims to improve electricity storage and support the integration of more renewable energy sources.
- AUSC Thermal Power Plants: A partnership between NTPC and BHEL is working on an 800 MW commercial power plant.
- Energy Audit:
- Financial Assistance: Providing support to help small and micro industries switch to cleaner energy options.
- Energy Audits: Implementing investment-grade energy audits across 60 clusters, with plans to extend this to 100 clusters in the next phase.
- PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana: A program that provides free electricity of up to 300 units per month to 1 crore households.
Infrastructure
- Provision of ₹11,11,111 crore for infrastructure (3.4% of GDP).
- ₹1.5 lakh crore to states as longterm interest free loans to support resource allocation.
- Phase IV of PMGSY will be launched to provide allweather connectivity to 25,000 rural habitations.
- Irrigation and Flood Mitigation:
- Financial support for projects with estimated cost of ₹11,500 crore such as the Kosi-Mechi intra-state link and 20 other ongoing and new schemes
- Assistance for flood management and related projects in Assam, Sikkim & Uttarakhand
- Assistance for reconstruction and rehabilitation in Himachal Pradesh
- Tourism
- Development of Vishnupad Temple Corridor and Mahabodhi Temple Corridor modelled on Kashi Vishwanath Temple Corridor
- Comprehensive development initiative for Rajgir will be undertaken which holds religious significance for Hindus, Buddhists and Jains.
- The development of Nalanda as a tourist centre besides reviving Nalanda University to its glorious stature.
- Assistance to development of Odisha’s scenic beauty, temples, monuments, craftsmanship, wildlife sanctuaries, natural landscapes and pristine beaches making it an ultimate tourism destination.
Innovation, Research & Development
- Operationalization of the Anusandhan National Research Fund for basic research and prototype development. Priorities for Viksit Bharat
- Private sector-driven research and innovation at commercial scale with a financing pool of ₹1 lakh crore
- Space Economy: A venture capital fund of ₹1,000 crore is to be set up
Next Generation Reforms
- Rural and Urban Land Actions: Initiatives related to land management in both rural and urban areas.
- Bhu-Aadhaar: Assigning a unique identification number for all land parcels.
- Urban Land Records: Digitizing land records in cities using GIS (Geographic Information System) mapping.
- Current Ownership Surveys: Conducting surveys to map land subdivisions based on current ownership.
- Linking to Farmers’ Registries: Connecting land records to farmers’ registries for better tracking.
- Digitizing Cadastral Maps: Transforming traditional land maps into digital formats.
- Establishing Land Registry: Creating a formal system for registering land ownership.
- Climate Finance Taxonomy: Improving access to funds for investments aimed at climate change adaptation and mitigation.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Streamlining processes to make it easier for foreign investments and promoting the use of the Indian Rupee for overseas investments.
- NPS Vatsalya: A program that allows parents and guardians to contribute for minors' future needs.
- Data Governance Improvement: Enhancing the management, collection, and processing of data and statistics.
- New Pension Scheme (NPS): Developing a new pension plan that addresses key issues, protects citizens, and ensures fiscal responsibility.
Part B: Tax-Related Proposals
Simplifying New Tax Regime:
- Standard deduction for salaried employees increased from ₹50,000 to ₹75,000.
- Deduction on family pension for pensioners enhanced from ₹15,000/- to ₹25,000/-
In the new tax regime, the tax rate structure is proposed to be revised, as follows:
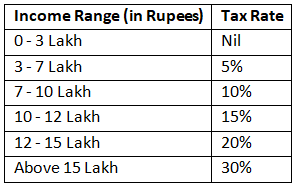
Review of the Income Tax Act, 1961
- The Finance Minister has initiated a complete review of the Income Tax Act of 1961. The aim is to make the Act more concise, clear, and easy to understand. This will help to lower disputes and legal issues, providing tax certainty for taxpayers. The review is expected to be finished within six months.
- The Finance Bill starts with efforts to simplify the tax rules for charities, adjust the TDS rate structure, modify the reassessment and search provisions, and update capital gains taxation.
Litigation & Appeals
- To tackle the backlog of first appeals, the government will assign more officers to handle and resolve these appeals, focusing especially on those that involve significant tax amounts.
- The government has introduced the Vivad Se Vishwas Scheme, 2024 to settle certain income tax disputes that are currently under appeal.
- To lessen legal disputes and ensure certainty in international taxation, the government will expand and enhance the safe harbour rules.
Expanding the Tax Base
- The Security Transactions Tax on futures and options will be raised to 0.02% and 0.10%, respectively.
Simplifying Reassessment
- Assessments can be reopened beyond three years up to five years from the end of the Assessment Year only if the escaped income is ₹ 50 lakh or more.
- In search cases, the time limit will be shortened from ten years to six years prior to the year of the search.
Simplification and Rationalization of Capital Gains
- Short-term gains on certain financial assets will now be taxed at a rate of 20%.
- Long-term gains on all financial and non-financial assets will be taxed at a rate of 12.5%.
- The exemption limit for capital gains on specific financial assets has been increased to ₹ 1.25 lakh per year.
Taxpayer Services
- All remaining services related to Customs and Income Tax, including corrections and orders following appellate decisions, will be digitalized over the next two years.
Other Important Proposals in the Finance Bill
- The Vivad Se Vishwas Scheme, 2024 will help resolve income tax disputes that are pending appeals.
- Monetary limits for filing appeals related to direct taxes, excise, and service tax in Tax Tribunals, High Courts, and the Supreme Court have been increased to ₹ 60 lakh, ₹ 2 crore, and ₹ 5 crore, respectively.
- Safe harbour rules will be expanded to minimize litigation and provide certainty in international taxation.
Employment and Investment
- The angel tax for all types of investors has been removed to support the start-up ecosystem.
- A simpler tax system for foreign shipping companies operating domestic cruises will promote cruise tourism in India.
- Special safe harbour rates for foreign mining companies selling raw diamonds in India have been introduced.
- The corporate tax rate for foreign companies has been reduced from 40% to 35%.
Deepening the Tax Base
- The Security Transactions Tax on futures and options will be raised to 0.02% and 0.1%, respectively.
- Income from the buyback of shares will be taxable in the hands of the recipient.
Social Security Benefits
- The deduction for employer contributions to the NPS will be increased from 10% to 14% of the employee's salary.
- Non-reporting of small movable foreign assets valued up to ₹ 20 lakh will no longer attract penalties.
Other Major Proposals
- The equalization levy of 2% has been withdrawn.
- Three cancer drugs: Trastuzumab Deruxtecan, Osimertinib, and Durvalumab will be fully exempt from customs duty.
- Customs duties on gold and silver have been reduced to 6%, and on platinum to 6.4%.
- There will be an expansion of tax benefits for specific funds and entities located in IFSCs.
- Individuals who fully disclose their benami transactions will be granted immunity from penalties and prosecution under the Benami Transactions (Prohibition) Act of 1988.
|
106 videos|306 docs|135 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















