DPP for NEET: Daily Practice Problems, Ch: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants | Biology Class 12 PDF Download
Q1: Which one of the following is not related to the other three?
(a) Archegonium
(b) Oogonium
(c) Ovule
(d) Antheridium
Ans: (d)
Antheridium is a male structure and the other three archegonium, oogonium & ovule are female parts. An antheridium is a haploid male reproductive structure producing gametes, occurring in ferns, mosses, fungi and algae. Archegonium is the female, egg-producing reproductive structure on the gametophytes of non-flowering land plants. The archegonium is comprised of an oogonium surrounded by protective layers of thick-walled pigmented cells. In seed plants, ovule is the structure that gives rise to female reproductive cells.
Q2: In a fertilized ovule, n, 2n, and 3n conditions occur respectively in
(a) Antipodal, egg, and endosperm.
(b) Egg, nucellus, and endosperm.
(c) Endosperm, nucellus, and egg.
(d) Antipodals, synergids, and integuments.
Ans: (b)
In a fertilized ovule n, 2n and 3n conditions occur respectively in egg, nucellus and endosperm.
Q3: Statement I: Many citrus and mango varieties show polyembryony.
Statement II: Some of the nucellar cells surrounding the embryo sac are developed into embryos.
(a) Both statements are correct.
(b) Statement I is correct & II is incorrect.
(c) Statement I is incorrect & II is correct.
(d) Both statements are incorrect.
Ans: (a)
Both statements are correct.
Q4: Statement I: Sunbirds, hummingbirds, and bats are pollinating agents.
Statement II: Among the animals, insects, particularly wasps, are the dominant biotic pollinating agents.
(a) Both statements are correct.
(b) Statement I is correct & II is incorrect.
(c) Statement I is incorrect & II is correct.
(d) Both statements are incorrect.
Ans: (b)
(II) Among the animals, insects, particularly bees are the dominant biotic pollinating agents.
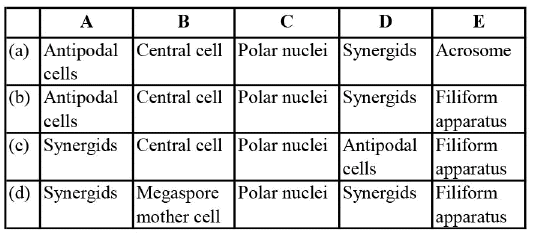
Q5: Match the items given in Column-I with those given in Column-II and choose the correct option. (a) A - II; B - III; C - V; D - I; E - IV
(a) A - II; B - III; C - V; D - I; E - IV
(b) A - I; B - III; C - II; D - IV; E - V
(c) A - II; B - III; C - I; D - IV; E - V
(d) A - II; B - IV; C - V; D - I; E - III
Ans: (a)
Tapetum is a layer of nutritive cells found within the sporangium, particularly within the anther, of flowering plants. Exine is the decay-resistant outer coating of a pollen grain or spore. It is made up of sporopollenin (most resistant organic material known).
The vegetative cells are bigger, has abundant food reserves and a large irregular shaped nucleus.
Sporogenous tissue is a group of compactly arranged homogenous cells. They are involved in the formation of microspores.
Q6: Seed coat is not thin, membranous in
(a) Coconut
(b) Groundnut
(c) Gram
(d) Maize
Ans: (a)
The seed coat develops from integuments originally surrounding the ovule. It is thick and hard in coconut which protects the embryo from mechanical injury and from drying out.
Q7: Which of the following floral parts forms pericarp after fertilization?
(a) Nucellus
(b) Outer integument
(c) Ovary wall
(d) Inner integument
Ans: (c)
Ovary wall forms pericarp after fertilization. Pericarp is the tissue that develops from the ovary wall of the flower and surrounds the seeds. The pericarp is typically made up of three distinct layers: the epicarp (outermost layer); the mesocarp (middle layer); and the endocarp (inner layer surrounding the ovary or the seeds). In a citrus fruit, the epicarp and mesocarp make up the peel.
Q8: Product of sexual reproduction generally generates
(a) Prolonged dormancy.
(b) New genetic combination leading to variation.
(c) Large biomass.
(d) Longer viability of seeds.
Ans: (b)
Sexual reproduction leads to formation of new combination and appearance of variations. Genetic recombination, interaction etc. during sexual reproduction provides vigour and vitality to the offsprings. They better adapt themselves to changing environmental conditions and also plays an important role in evolution.
Q9: Sequence of development during the formation of embryo sac is
(a) Ovule → Megaspore → Megaspore mother cell → Embryo sac.
(b) Megasporocyte → Ovule → Megaspore → Embryo sac.
(c) Megaspore → Megaspore mother cell → Ovule → Embryo sac.
(d) Ovule → Megaspore mother cell → Megaspore → Embryo sac.
Ans: (d)
Sequence of development during the formation of embryo sac is:
Archesporium → Megaspore mother cell → Megaspore → Embryo sac
Q10: Which of the following processes is necessary for the complete development of male gametophyte?
(a) One meiotic cell division and two mitotic cell divisions.
(b) One meiotic cell division and one mitotic cell division.
(c) Two meiotic cell divisions and one mitotic cell division.
(d) Two mitotic cell divisions.
Ans: (a)
Development of male gametophyte is called micro - gametogenesis. One meiotic division and two mitotic divisions are necessary for the complete development of male gametophyte. Male gametophyte when fully developed is a 3 nucleate structure.
Q11: Which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) Sporogenous tissue is haploid.
(b) Endothecium produces the microspores.
(c) Tapetum nourishes the developing pollen.
(d) Hard outer layer of pollen is called intine.
Ans: (c)
Sporogenous tissue is always diploid, endothecium is second layer of anther wall and perform the function of protection and help in dehiscence of anther to release the pollen. Hard outer layer of pollen is called exine but tapetum always nourishes the developing pollen.
Cells of the tapetum possess dense cytoplasm and generally have more than one nucleus (polypoid).
Q12: Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct about self-incompatibility?
(i) It is a device to prevent inbreeding.
(ii) It provides a biochemical block to self-fertilization.
(iii) It ensures cross-fertilization.
(iv) It is governed by pollen-pistil interaction.
(v) It is governed by a series of multiple alleles.
(vi) It prevents self-pollen (from the same flower or other flowers of the same plant) from fertilizing the ovules by inhibiting pollen germination or pollen tube growth in the pistil.
(a) (i), (ii), and (iii)
(b) (i), (iv), and (v)
(c) All of the above
(d) None of the above
Ans: (c)
All the statements are correct about self - incompatibility. Self-incompatibility is a general name for several genetic mechanisms in angiosperms, which prevent self-fertilization and thus encourage outcrossing and allogamy. In plants with self - incompatibility, when a pollen grain produced in a plant reaches a stigma of the same plant or another plant with a similar genotype, the process of pollen germination, pollen tube growth, ovule fertilization, and embryo development is halted at one of its stages, and consequently no seeds are produced.
Q13: Which of the following statement(s) is/are incorrect?
(i) Endosperm formation starts prior to the first division of the zygote.
(ii) Angiospermic endosperm is mostly 3N while gymnospermic one is N.
(iii) The most common type of endosperm is nuclear.
(iv) Coconut has both liquid nuclear (multinucleate) and cellular endosperm.
(v) Milky water of green tender coconut is liquid female gametophyte.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) Only (iii)
(c) Only (v)
(d) Only (ii)
Ans: (c)
The coconut water from tender coconut is nothing but free nuclear endosperm (made up of thousands of nuclei) and the surrounding white kernel is the cellular endosperm. Female gametophyte is embryo sac.
Q14: Which of the following statements are correct for a typical female gametophyte of a flowering plant?
(i) It is 8-nucleate and 7-celled at maturity.
(ii) It is free-nuclear during the development.
(iii) It is situated inside the integument but outside the nucellus.
(iv) It has an egg apparatus situated at the chalazal end.
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: (c)
Statement (i) and (ii) are correct about typical female gametophyte. Female gametophyte contains the egg cell and central cell that become fertilized and give rise to the embryo and endosperm of the seed, respectively. Female gametophyte development begins early in ovule development with the formation of a diploid megaspore mother cell that undergoes meiosis.
Q15: Assertion: If hybrids are made into apomicts, there is no segregation of characters in the hybrid progeny.
Reason: The farmers can keep on using the hybrid seeds to raise new crops year after year and do not have to buy hybrid seeds every year.
(a) Assertion and reason both are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but the reason is wrong.
(d) Assertion and reason both are wrong.
Ans: (b)
Reason : Apomixis is a form of asexual reproduction that mimics sexual reproduction. Advantage of apomictic seeds to farmer: It reduces the cost of hybrid production. There is no segregation of characters in the hybrid progeny. It helps the farmer to keep using the hybrid seeds to raise new crops each year.
Q16: Identify A, B, C, D, and E structures marked in the given figure of a mature embryo sac.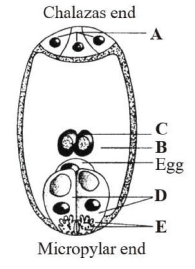
Ans: (b) In the given figure of mature embryo sac, the structure marked as A, B, C, D, and E are respectively antipodal cells, central cells, polar nuclei, svncrgids and filiform apparatus.
Embryo sac is the female gametophyte of a seed plant, containing the egg, synergids, and polar and antipodal nuclei. In this, fusion of the antipodal and a pollen generative nucleus forms the endosperm. The embryo sac develops in the central portion of the ovule (nucellus), where the maternal macrosporocyte, as a result of meiotic division, forms four haploid cells (a tetrad of 25. macrospores), of which one develops (the rest 26. atrophy). During the development of the embryo sac there are three successive synchronous mitotic divisions of its nuclei, so that their number increases in the progression 1: 2: 4: 8 and they are distributed evenly along the ends of the growing embryo sac.
Q17: Study the following statements and select the correct option.
(i) Tapetum nourishes the developing pollen grains.
(ii) Hilum represents the junction between ovule and funicle.
(iii) In aquatic plants, such as water hyacinth and water lily, pollination is by water.
(iv) The primary endosperm nucleus is triploid.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct but (iii) and (iv) are incorrect.
(b) (i), (ii), and (iv) are correct but (iii) is incorrect.
(c) (ii), (iii), and (iv) are correct but (i) is incorrect.
(d) (i) and (iv) are correct but (ii) and (iii) are incorrect.
Ans: (b)
In a majority of water plants like water hyacinth and water lily, flowers emerge above the water level and are pollinated by insects.
Q18: Seeds are adaptively important because
(i) They maintain dormancy.
(ii) They protect young plants during vulnerable stages.
(iii) They store food for young plants and facilitate dispersal.
Identify the correct reasons.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) All of the above
Ans: (d)
Q19: Match the parts of gynoecium given in Column-I with their definitions given in Column-II. Choose the correct combination.
 (a) A - I; B - II; C - III; D - IV; E - V
(a) A - I; B - II; C - III; D - IV; E - V
(b) A - V; B - IV; C - III; D - II; E - I
(c) A - IV; B - II; C - I; D - III; E - V
(d) A - I; B - III; C - V; D - II; E - IV
Ans: (b) Funicle is a filamentous stalk attaching a seed or ovule to the placenta. Hilum is the point at which funiculus touches the ovule. Thus, hilum represents the junction between the ovule and funiculus. Integuments are the protective covering or layers present in the ovule. It encircles the ovule except at the tip where a small opening called micropyle is organised. Chalaza is the basal swollen part of the nucellus (opposite the micropylar end) from where the mteguments originate. Nucellus is the central part of an ovule, containing the embryo sac.
Q20: Assertion: Pollen grains are well preserved as fossils.
Reason: Sporopollenin is present in the exine of seeds.
(a) Assertion and reason both are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but the reason is wrong.
(d) Assertion and reason both are wrong.
Ans: (c)
Reason : Sporopollenin present in exine of pollen grain.
Q21: What type of pollination takes place in Vallisneria?
(a) Pollination occurs in submerged conditions by water.
(b) Flowers emerge above the surface of the water, and pollination occurs by insects.
(c) Flowers emerge above the water surface, and pollen is carried by wind.
(d) Male flowers are carried by water currents to female flowers at the surface of the water.
Ans: (d)
In Vallisneria, the female flower reach the surface of water by the long stalk and the male flowers or pollen grains are released on to the surface of water. They are carried passively by water currents, some of them eventually reach the female flowers and the stigma.
Q22: In which one of the following, both autogamy and geitonogamy are prevented?
(a) Wheat
(b) Papaya
(c) Castor
(d) Maize
Ans: (b)
Q23: Pollen grains can be stored for several years in liquid nitrogen having a temperature of
(a) -120°C
(b) -80°C
(c) -196°C
(d) -160°C
Ans: (c)
Pollen grains can be stored for several years in liquid nitrogen at -196°C. This is also known as cryopreservation.
Q24: Which of the following has proved helpful in preserving pollen as fossils?
(a) Pollenkitt
(b) Cellulosic intine
(c) Oil content
(d) Sporopollenin
Ans: (d)
Exine of pollen grain is made up of highly resistant fatty substance called sporopollenin, which is not degraded by any enzyme. It is not affected by high temperature, strong acid or strong alkali. Because of the sporopollenin, pollen grains are well preserved as microfossils.
Q25: How many microspore mother cells will give rise to 256 microspores after reduction division?
(a) 512
(b) 128
(c) 64
(d) 96
Ans: (c)
Q26: Functional megaspore in an angiosperm develops into a(n)
(a) Endosperm
(b) Embryo sac
(c) Embryo
(d) Ovule
Ans: (b)
In angiosperms, the functional megaspore is the first cell of female gametophyte. It enlarges and undergoes three nuclear mitotic divisions to form embryo sac.
Q27: Attractants and rewards are required for
(a) Entomophily
(b) Hydrophily
(c) Cleistogamy
(d) Anemophily
Ans: (a)
Entomophily is the most common type of zoophily where pollination takes place through the agency of insects. Entomophilous flowers are brightly coloured and secrete nectar to attract visiting insects. Anemophily (wind pollination) and hydrophily (water pollination) do not require attractants or rewards due to the involvement of abiotic pollinating agents. Cleistogamy is self pollination in closed flowers.
Q28: Flowers which have a single ovule in the ovary and are packed into inflorescence are usually pollinated by
(a) Bee
(b) Wind
(c) Bat
(d) Water
Ans: (b)
Single ovule in the ovary and flowers packed into inflorescence are characteristics of wind pollinated flowers.
Q29: A dioecious flowering plant prevents both
(a) Autogamy and geitonogamy
(b) Geitonogamy and xenogamy
(c) Cleistogamy and xenogamy
(d) Autogamy and xenogamy
Ans: (a)
Dioecious plants are those plants in which male flowers and female flowers are borne on different plants. Therefore, they prevent both autogamy and geitonogamy.
Q30: In the majority of angiosperms,
(a) The egg has a filiform apparatus.
(b) There are numerous antipodal cells.
(c) Reduction division occurs in the megaspore mother cells.
(d) A small central cell is present in the embryo sac.
Ans: (c)
Q31: Milky water of green coconut is
(a) Liquid chalaza
(b) Liquid nucellus
(c) Liquid endosperm
(d) Liquid female gametophyte
Ans: (c)
Coconut water is the clear liquid inside young green coconuts. Milky water of green coconut is called liquid endosperm.
Q32: Scutellum is present in the embryo of
(a) Pea
(b) Ranunculus
(c) Grasses
(d) None of these
Ans: (c)
A nature embryo in monocotyledons has a single cotyledon called ‘scutellum’, e.g. Grass family.
Q33: Perisperm is a
(a) Degenerate part of synergids.
(b) Peripheral part of endosperm.
(c) Degenerate part of secondary nucleus.
(d) Remnant of nucellus.
Ans: (d)
In most of the angiosperm, entire part of the nucellus is utilized by developing embryo sac but in some of the angiosperm some part of the nucellus remain inside the ovules. That part of the nucellus present inside the seed in the form of a thin layer is known as perisperm.
Q34: Match the items given in Column-I with their examples in Column-II.
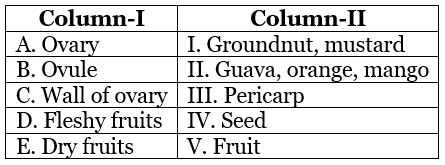 (a) A - V; B - IV; C - III; D - II; E - I
(a) A - V; B - IV; C - III; D - II; E - I
(b) A - I; B - II; C - III; D - IV; E - V
(c) A - I; B - III; C - II; D - IV; E - V
(d) A - V; B - IV; C - I; D - II; E - III
Ans: (a)
Fruit is mature or ripened ovary, developed after fertilization. The ovules after fertilization, develop into seeds. The wall of the ovary develops into the wall of fruit called pericarp. In fleshy fruits pericarp is generally distinguished into three layers epicarp, mesocarp and endocarp. Mesocarp is fleshy or fibrous. These fruits are indehiscent. e.g., guava, orange, mango etc. In dry fruits pericarp is not distinguished into three layers. They may be dehiscent, indehiscent and splitting e.g., groundnut, mustard, etc.
Q35: The seed in which the endosperm is used by the embryo is called __________ seed.
(a) Single
(b) Albuminous
(c) Endospermic
(d) Non-endospermic
Ans: (d)
Seeds which do not have an endosperm at maturity, are called non-endospermic or Ex- albuminous seeds. The endospermic tissues are absorbed during the development of embryo. The absorbed food materials from the endosperm is stored in cotyledons that is why they become so large and fleshy. But Castor seed is endospermic.
Q36: Apomixis is the
(a) Development of plants in darkness.
(b) Development of plants without fusion of gametes.
(c) Inability to perceive stimulus for flowering.
(d) Effect of low temperature on plant growth.
Ans: (b)
Apomixis is the production of seeds without fertilization. The term apomixis was given by winker (1908). There are several ways of development of apomictic seeds. In some species the diploid egg cell is formed without reduction division & develops into the embryo without fertilization. In some species the nucellar cells surrounding the embryo sac start dividing, protrude into the embryo sac & develop into embryos. Some apomictic plants are citrus.
Q37: Which of the following statements is incorrect about emasculation?
(a) During the emasculation process, stigma is removed.
(b) Emasculated flowers are bagged in order to prevent self-pollination.
(c) Emasculation is the removal of stamens before the maturation of selected bisexual flowers.
(d) It is one of the steps for artificial hybridization.
Ans: (a)
Emasculation is removal of anthers from the flower bud before the anther dehisces in bisexual flowers.
Q38: Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) When pollen is shed at the two-celled stage, double fertilization does not take place.
(b) Vegetative cell is larger than the generative cell.
(c) Pollen grains in some plants remain viable for months.
(d) Intine is made up of cellulose and pectin.
Ans: (a)
In over 60 per cent of angiosperms, pollen grains are shed at cell 2-celled stage. In the remaining species the generative cell divides mitotically to give rise to the two male gametes before pollen grains are shed (3-celled stage.)
Q39: Which of the following statements about sporopollenin is incorrect?
(a) Exine is made up of sporopollenin.
(b) Sporopollenin is one of the most resistant organic materials.
(c) Exine has apertures called germ pores where sporopollenin is present.
(d) Sporopollenin can withstand high temperatures and strong acids.
Ans: (c)
Exine has apertures which are called germ pores (if rounded) or germinal furrows (if elongated). These are the areas where sporopollenin is absent.
Q40: Which one of the following events takes place after double fertilization?
(a) The pollen grain germinates on the stigma.
(b) The pollen tubes enter the embryo sac.
(c) Two male gametes are discharged into the embryo sac.
(d) The PEN (Primary Endosperm Nucleus) develops into endosperm.
Ans: (d)
Double fertilization forms a diploid zygote nucleus and a triploid primary endosperm nucleus (PEN). After that, the two products of double fertilization i.e., zygote and PEN, develop into embryo and endosperm respectively.
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on DPP for NEET: Daily Practice Problems, Ch: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Biology Class 12
| 1. What are the main stages of sexual reproduction in flowering plants? |  |
| 2. How does pollination occur in flowering plants? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the ovule in sexual reproduction? |  |
| 4. What are the differences between self-pollination and cross-pollination? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of double fertilization in flowering plants? |  |





















