DPP for NEET: Daily Practice Problems: Electrostatics- 1 | Physics Class 12 PDF Download
DIRECTIONS (Q.1-Q.18) : There are 18 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE choice is correct.
Q1: A total charge Q is broken in two parts Q1 and Q2 and they are placed at a distance R from each other. The maximum force of repulsion between them will occur, when
(a)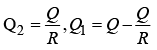 (b)
(b)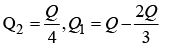 (c)
(c)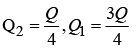 (d)
(d)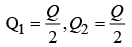
(a)
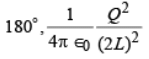 (b)
(b)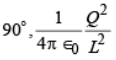 (c)
(c)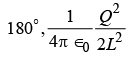 (d)
(d)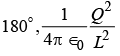
Q3: Electric charges of 1mC , -1mC and 2mC are placed in air at the corners A,B and C respectively of an equilateral triangle ABC having length of each side 10 cm. The resultant force on the charge at C is
(a) 0.9 N
(b) 1.8N
(c) 2.7 N
(d) 3.6 N
Q4: An electron is moving round the nucleus of a hydrogen atom in a circular orbit of radius r. The coulomb force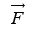 between the two is
between the two is 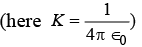 (a)
(a)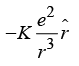 (b)
(b)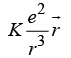
(c)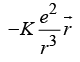 (d)
(d)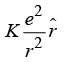
Q5: Equal charges q are placed at the four corners A, B, C,D of a square of length a . The magnitude of the force on the charge at B will be
(a) 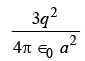 (b)
(b) 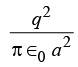 (c)
(c)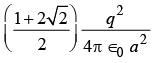 (d)
(d)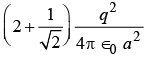
Q6: Electric lines of force about negative point charge are
(a) Circular, anticlockwise
(b) Circular, clockwise
(c) Radial, inward
(d) Radial, outward
Q7: The magnitude of electric field intensity E is such that, an electron placed in it would experience an electrical force equal to its weight is given by
(a) mge
(b) mg/e
(c) e/mg
(d)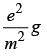
Q8: Two point charges Q and –3Q are placed at some distance apart. If the electric field at the location of Q is E then at the locality of –3Q, it is
(a) –E
(b) E/3
(c) –3E
(d) –E/3
Q9: Charges q, 2q, 3q and 4q are placed at the corners A, B, C and D of a square as shown in the following figure. The direction of electric field at the centre of the square is parallel to side.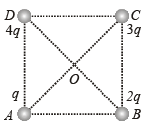 (a) AB
(a) AB
(b) CB
(c) BD
(d) AC
Q10: Three infinitely long non-conducting charge sheets are placed as shown in figure. The electric field at point P is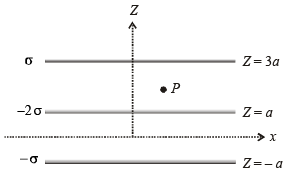 (a)
(a) 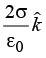 (b)
(b)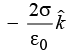 (c)
(c)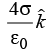 (d)
(d)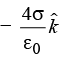
Q11: The electric intensity due to an infinite cylinder of radius R and having charge q per unit length at a distance r(r > R) from its axis is
(a) Directly proprotional to r2
(b) Directly proprotional to r3
(c) Inversely proprotional to r
(d) Inversely proprotional to r2
Q12: A sphere of radius R has a uniform distribution of electric charge in its volume. At a distance x from its centre, for x < R, the eletric field is directly proportional to
(a) 1/x2
(b) 1/x
(c) x
(d) x2
Q13: A charged ball B hangs from a silk thread S, which makes an angle q with a large charged conducting sheet P, as shown in the figure. The surface charge density s of the sheet is proportional to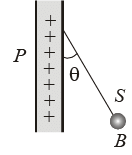 (a) sin q
(a) sin q
(b) tan q
(c) cos q
(d) cot q
Q14: A charge q is placed at the centre of a cube. Then the flux passing through one face of cube will be
(a)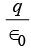 (b)
(b) 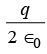 (c)
(c)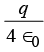 (d)
(d)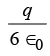
DIRECTIONS (Q.15) : In the following question, more than one of the answers given are correct. Select the correct answers and mark it according to the following codes:
Q15: A solid sphere S1 is connected to a charge reservoir through a heater H as shown in figure.
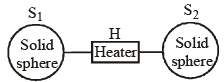
Flux through a closed spherical surface around S1 given by Φ = α t2 where u is a constant and t is time in seconds. If resistance of heater is R then select correct statements
(1) Power consumed by heater will be 4 α2ε02 Rt2.
(2) Electric flux through a closed spherical surface around S2 will be— αt2.
(3) Rate of change of electric flux through a closed spherical surface around S2 will be —2α t
(4) All of the above are correct
Codes :
(a) 1, 2 and 3 are correct
(b) 1 and 2 are correct
(c) 2 and 4 are correct
(d) 1 and 3 are correct
DIRECTIONS (Q.16-Q.18) : Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows :
A sphere of radius R contains charge density r (r ) = A( R-r ), for 0 < r<R. The total electric charge inside the sphere is Q.
Q16: The value of A in terms of Q and R is
(a)
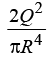 (b)
(b) (c)
(c) 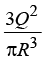 (d)
(d) 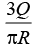
Q17: The electric field inside the sphere is
(a) 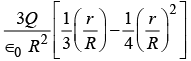
(b)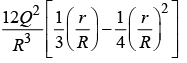
(c) 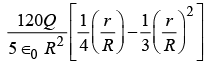
(d) 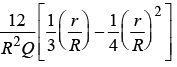
Q18: The electric field outside the sphere is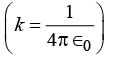 (a) kQ/r
(a) kQ/r
(b) kQ/r2
(c) kQ/r3
(d) kQ2/r2
DIRECTIONS (Q.19 -Q.20 ) : Each of these questi ons contains two statements: Statement-1 (Assertion) and Statement-2 (Reason). Each of these questions has four alternative choices, only one of which is the correct answer.
You have to select the correct choice.
Q19: Statement-1 : Electric lines of force cross each other.
Statement-2 : Electric field at a point superimpose to give one resultant electric field.
(a) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
(b) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
(c) Statement -1 is False, Statement-2 is True.
(d) Statement -1 is True, Statement-2 is False.
Q20: Statement-1 : A point charge is brought in an electric field. The field at a nearby point will increase, whatever be the nature of the charge.
Statement-2 : The electric field is dependent on the nature of charge.
(a) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
(b) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
(c) Statement -1 is False, Statement-2 is True.
(d) Statement -1 is True, Statement-2 is False.
|
88 videos|435 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on DPP for NEET: Daily Practice Problems: Electrostatics- 1 - Physics Class 12
| 1. What is the principle of superposition in electrostatics? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the electric force between two point charges? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between electric field and electric potential? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of equipotential surfaces in electrostatics? |  |
| 5. How does the concept of electric dipole relate to electrostatics? |  |





















