Questions & Answers: Basics of Retailing | Retail Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Q1: What is Unorganised Retail?
Ans: Unorganised retailing: It refers to the traditional formats of low-cost retailing, for example, the local kirana shops, owner-manned general stores, paan shops, convenience stores, hand cart and pavement vendors, etc. It is featured by poor and old infrastructure, insufficient funds, lack of technology, insufficient upstream processes and absence of skilled manpower. It is not registered under any legal provision and does not maintain regular accounts. They are small and scattered units which sell products at a fixed or mobile location. Traditional units include Mandis, Haats, Melas, the local Baniya, Kirana shops, Paanwala and others like cobbler, fruit and vegetable vendor, etc.
Q2: What is organised Retail?
Ans: Organised retailing: It refers to trading activities undertaken by licensed retailers, that is, those who are registered for sales tax, income tax, etc. These include the corporate-backed hypermarkets and retail chains, and also the privately-owned large retail businesses. It offers the customers more convenience, choice and control with an experience of comfort and speed. The examples of organised retailing may be supermarkets, departmental stores, hypermarkets, shopping malls, multilevel marketing, teleshopping, etc. Organised retailing is capable of generating employment opportunities. It offers huge potential for growth in the coming years.
Q3: Difference between Organised and Unorganised Retail Business.
Ans: 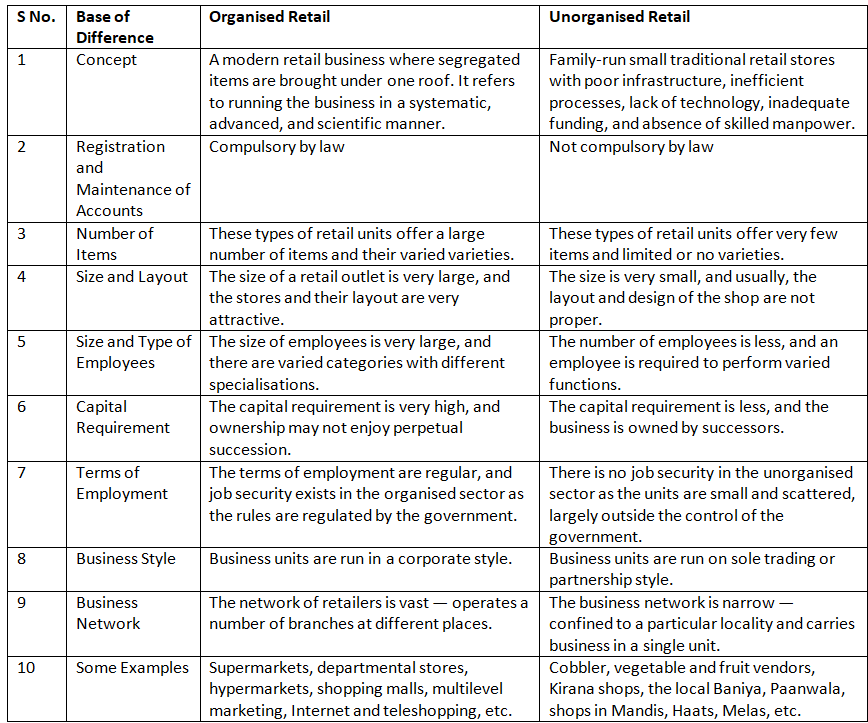
Q4: Explain Different types of retail business establishments.
Ans: Store retailing is classified in two categories.
- Based on merchandise offered
- Based on ownership
Q5: Explain Store retailing on the basis of Merchandise Offered.
Ans:
- Convenience stores: These are small sized stores located in residential areas. They are open for long hours and offer a limited line of convenience products like eggs, bread, milk, vegetables, etc.
- Supermarkets: A supermarket is a self-service shop offering a wide variety of food and household products, organised into aisles.
- Hypermarkets: A hypermarket is a retail store that combines a departmental store and a grocery supermarket. Often a very large establishment, hypermarkets offer a wide variety of products, such as appliances, clothing and groceries. Example: HYPERCITY
- Specialty stores: Consumer outlets, such as furniture, electronics, sports, appliances, jewellery stores, that offer unique, often individualised products or a large amount of products within a particular grouping of consumer goods are considered to be specialty stores.
- Departmental stores: A departmental store is a retail establishment offering a wide range of consumer goods in different product categories known as ‘departments’. Departments are made as per different types of goods to be sold. It requires a lot of capital to maintain different departments and a huge stock of goods.
- Catalogue showrooms: Catalogue retailers usually specialize in hard goods (houseware, jewellery, consumer electronics, etc). In a catalogue showroom (store), the customers view products from printed or online catalogues in the store and fill out an order form. This order is then brought to the sales counter, where an associate arranges to retrieve the items from the warehouse.
- Discount store: In this store products sell at a discounted price, which is less than the actual price of the products.
- Shopping mall: A shopping mall is a modern term for a form of shopping center, in which one or more buildings form a complex of shops representing merchandisers with interconnecting walkways that enable customers to walk from unit to unit.
- General store: General store is a retail store in a small town or rural community that carries a wide variety of goods, including groceries. These stores often sell staple food items, such as milk and bread, and various household goods, such as hardware and electrical supplies.
- Warehouse store: A warehouse store is a food and grocery retailer that operates stores geared towards offering deeper discounted prices than a traditional supermarket. Warehouse clubs sometimes charge a membership fee also.
- Variety store: A variety store is a retail store that sells a wide range of inexpensive household goods.
Q6: Explain Store retailing on Based on Ownership.
Ans:
- Independent retailer: An independent retailer is a small business, owned and operated by an individual versus a corporation. An independent retailer has direct contact with customers. For example, local Baniya or Kirana store, and Paanwala. He or she decides the retail strategy based on store location and product mix.
- Corporate retail chain: A retail chain is one of a group of stores engaged in the same kind of business in different locations and under the same ownership and management. Chain stores in malls or shopping centers are always looking to improve their position and strengthen their brand identity in the marketplace For example, Reliance, Bata, Arrow, Louis Philippe, Food World, etc.
- Franchising: Franchising is an arrangement where one party (the franchiser) grants another party (the franchisee) the right to use its trademark or tradename as well as certain business systems and processes, to produce and market a good or service according to certain specifications. For example, Mc Donald’s, Pizza Hut, Van Heusen, etc.
- Consumer cooperatives: Consumers’ cooperatives are enterprises owned and managed by consumers which aim at fulfilling the needs and aspirations of their members. Consumers’ cooperatives often take the form of retail outlets owned and operated by their consumers. The customers or consumers of the goods and/or services the cooperative provides are often also the individuals who have provided the capital required to launch or purchase that enterprise. For example, Apna Bazaars in Mumbai, etc.
Q7: Write short note on the following:
(i) E-retailers:
Ans: E-retailing is a form of electronic commerce which allows consumers to directly buy goods or services from a seller over the Internet using a web browser. Consumers find a product of interest by visiting the website of the e-retailer directly or by searching among alternative vendors using a shopping search engine, which displays the same product’s availability and pricing at different e-retailers. E-retailers, for example, Amazon, Flipkart, etc., accept the payment through online or at the time of delivery but the customer receives product directly from manufacturer or wholesaler. It is ideal for the customers who do not want to visit the retail stores. However, the customers should be careful of defective products and non-secure credit card transactions.
(ii) Vending machines:
Ans: A vending machine is a machine from which products are sold. The customer inserts money in a slot, selects a product from the menu and the product is dispensed from the machine.
(iii) Automated retail stores:
Ans: Automated retail is the category of self-service, standalone kiosks in heavily trafficked locations, such as airports, malls and convenience stores. They accept credit cards and are usually open 24 hours throughout the week. For example, Zoom shops, Red-box.
Q8: Explain the Functions of retailer
Ans: The Functions of retailer are:
- Breaking bulk into small quantities.
- Providing products information to customers
- Providing customer services
- Creating a convenient, comfortable and pleasant shopping experience for consumers
- Providing feedback to producers about customer needs
Q9: Explain the Essential Requirements of Retailers
Ans: The retailer should:
- Establish the shop where customers are attracted.
- Stock the goods which are needed by the customers.
- Sell quality goods at a competitive price.
- Be up-to-date about the latest trends in the market.
- Ensure window and counter display to promote sales.
- Always be accessible to customers.
|
23 videos|12 docs
|
















