Halogens | Chemistry A- Level - A Level PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Halogen Properties |

|
| Chemical Properties |

|
| Halogen Compounds |

|
| Uses of Halogens |

|
Halogens are nonmetals. At room temperature, fluorine and chlorine are gases, bromine is a liquid and Iodine and astatine are solids. Halogens are very reactive, the reactivity decreases from fluorine to astatine. Halogens do not exist in elemental form in nature. Astatine isotopes are radioactive with short half-lives.
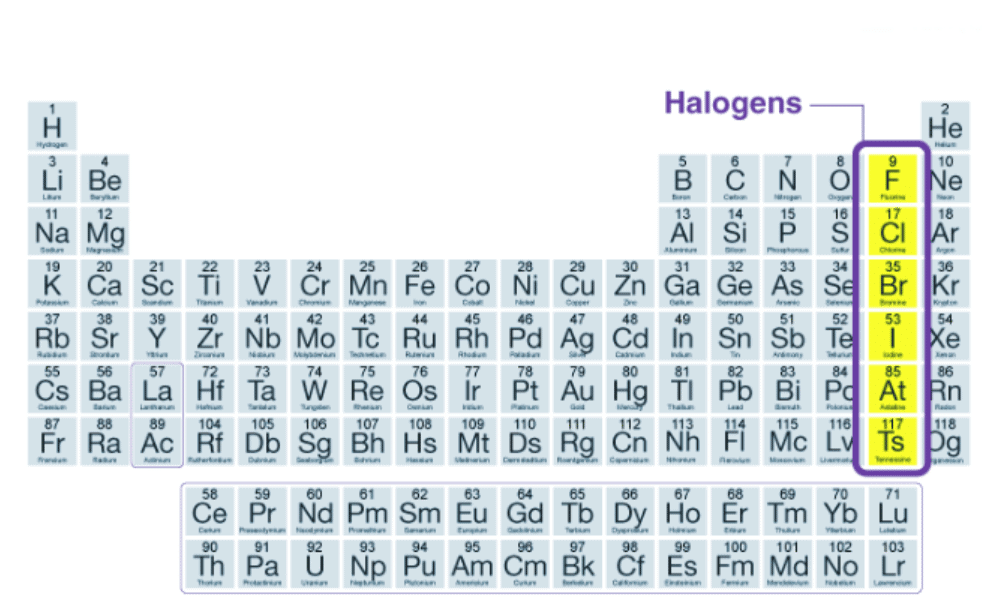
Table salt, bleach, fluoride in toothpaste, and chlorine in swimming pools, what do all of these have in common? Add halogen lamps to the list, and the answer becomes more clear: All involve one or more of the halogens, which form Group 7 of the periodic table, which consists of five chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). The word ‘halogen’ is derived from Greek and originally means “salt-forming“. Halogens are found in the environment only in the form of ions or compounds because of their high reactivity.
Halogen Properties
We will look at some of the physical and chemical properties of Halogens.
Physical Properties
- The group of halogens is the only periodic table group that contains elements in all three familiar states of matter at standard temperature and pressure
- Fluorine (F) is a pale yellow gas
- Chlorine (Cl) is a greenish gas
- Bromine (Br) is a dark red liquid
- Iodine (I) is a black solid, and when heated, it forms a purple vapour
- Astatine (At) is a black solid
- The halogens have a strong and often nasty smell
- The halogen elements are extremely toxic
- They are poor conductors of heat and electricity
- Low melting and boiling points
Chemical Properties
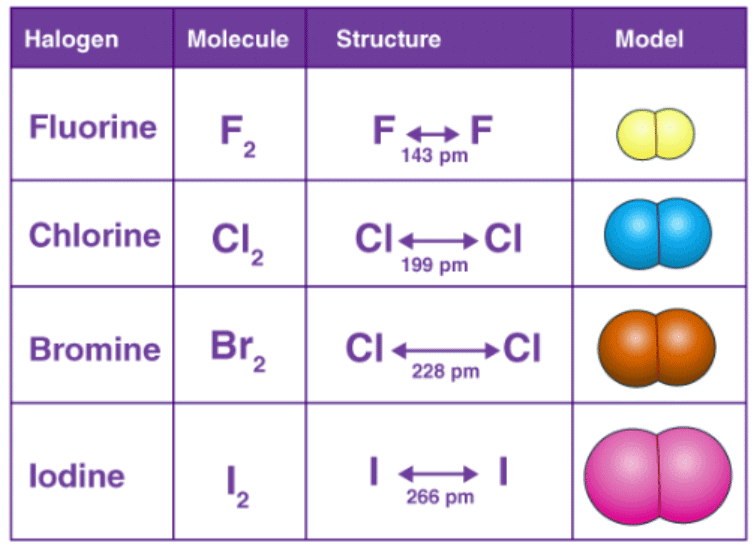
- Molecules of all halogens are homonuclear diatomic. What this means is that their molecules exist with two atoms each.
- Halogens have seven valence electrons; because halogens have one electron missing, they form negative ions and are highly reactive.
- They can gain an electron by reacting with atoms of other elements.
- Fluorine is one of the most reactive elements in existence.
- They have relatively weak intermolecular forces.
Halogen Compounds
One of the definitive properties of halogens is that they are highly reactive. Due to this nature, they can form different compounds such as halides, interhalogens and polyhalogenated compounds. We will look at them in brief below.
Hydrogen Halides
These are binary compounds formed when halogens react with hydrogen. Generally, if we take fluorine, chlorine, and bromine, the reaction appears in the form given below:
H2 + X2 → 2HX
Hydrogen halides are strong hydrohalic acids when dissolved in water. These acids are dangerous.
Metal Halides
- These are compounds formed by the reaction of halogens with metals. Metal halides can be highly ionic compounds, monomeric covalent compounds or polymeric covalent compounds.
- They are usually obtained through direct combination or through the neutralisation of a basic metal salt with hydrohalic acid.
Interhalogen Compounds
- When halogens react with each other, they form interhalogen compounds. Their properties and behaviours are intermediates of those of the two-parent halogens. Some properties may differ, though.
- All interhalogens, apart from IF7, can be formed by directly combining pure halogens in set conditions.
Halogenated/Organohalogen Compounds
- These compounds are also known as organic halides.
- They can be categorised as organic compounds containing halogen atoms. Organohalogens are usually manufactured through nucleophilic abstraction reactions.
Polyhalogenated Compounds
- Compounds that are substituted with multiple halogens are categorised as polyhalogenated compounds.
- They are industrially created compounds, and most of these are toxic and bioaccumulated in humans. Some of the polyhalogenated compound examples include PCBs, PBDEs, and PFCs.
Uses of Halogens
- Bromine and chlorine are often used as disinfectants for purifying water in swimming pools, fresh wounds, dishes and sterilising surfaces.
- Small amounts of a halogen, such as iodine or bromine, are found in halogen lamps.
- Fluoride is found in products such as toothpaste, baby formulas and vitamin supplements.
- Chlorine accounts for about 0.15 per cent of human body weight and plays several important roles in the body’s functioning. Compounds of both chlorine and bromine are used as disinfectants for sterilisation.
- Fluoride anions are found in some quantity in different organisms. It is essential for humans as well. Iodine is also another compound.
- Halogen atoms are mostly lipophilic and less water-soluble. Thus, it has been used in drug components to provide improved penetration through lipid membranes and tissues. However, halogenated drugs can pile up in adipose tissue.
- Polyhalogenated compounds (PHCs) are used in a wide array of manufactured products and in pest control.
|
143 videos|201 docs|185 tests
|
FAQs on Halogens - Chemistry A- Level - A Level
| 1. What are the physical and chemical properties of halogens? |  |
| 2. What types of compounds do halogens form? |  |
| 3. What are some common uses of halogens in everyday life? |  |
| 4. How do halogens react with other elements? |  |
| 5. Are halogens harmful to humans and the environment? |  |














