Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) > Mind Map: Light
Mind Map: Light | Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
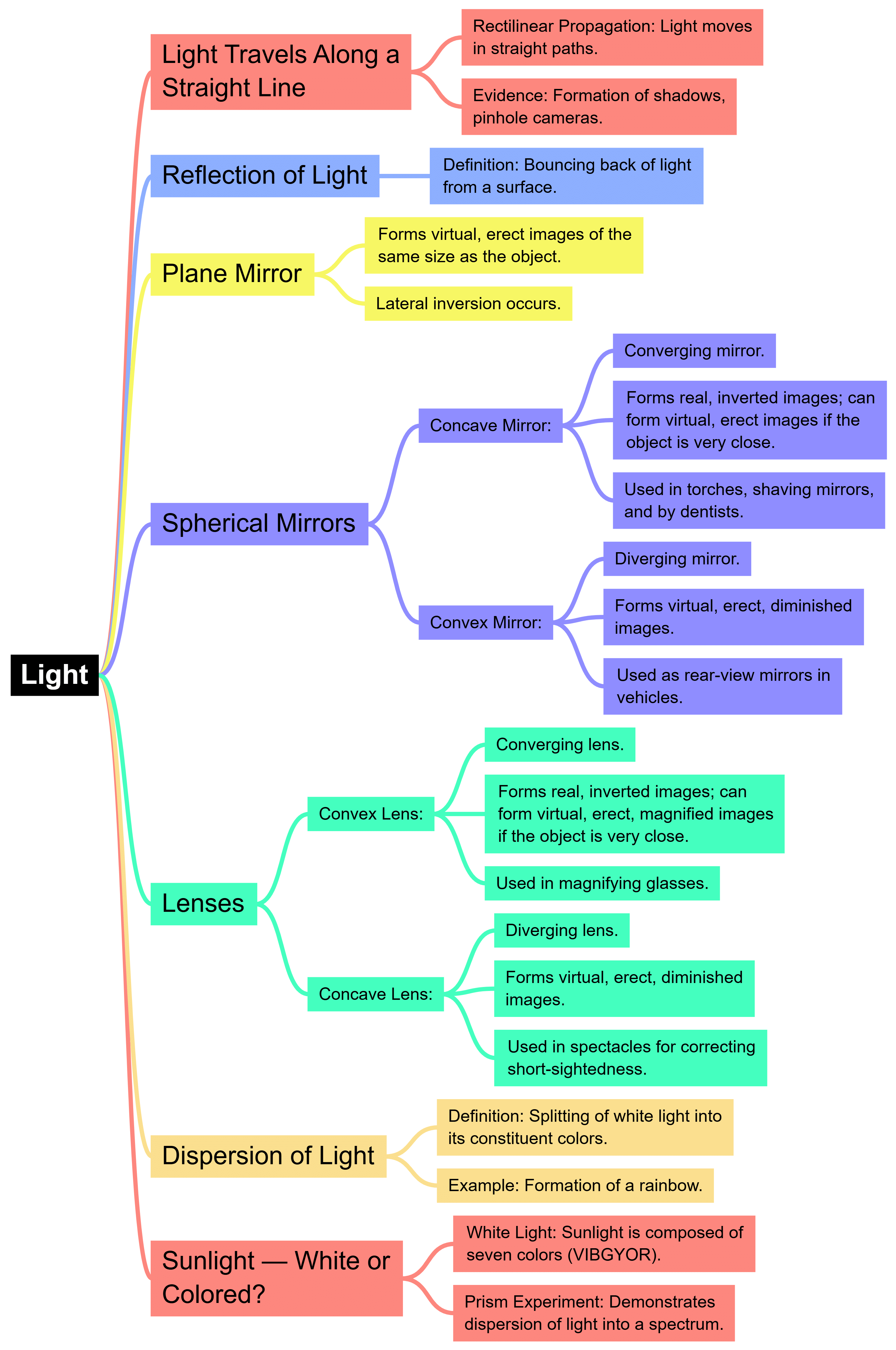
The document Mind Map: Light | Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) is a part of the Class 7 Course Science Class 7 (Old NCERT).
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
111 videos|435 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Light - Science Class 7 (Old NCERT)
| 1. What is light and how does it travel? |  |
Ans. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. It travels in waves and can move through a vacuum at a speed of approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (186,282 miles per second). Light can also travel through different media, like air or glass, but its speed will vary depending on the medium.
| 2. What are the different types of light? |  |
Ans. There are several types of light, including visible light, ultraviolet (UV) light, infrared (IR) light, and others. Visible light is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be seen by the human eye, while UV light has shorter wavelengths and is not visible, and IR light has longer wavelengths and is also not visible.
| 3. How does light interact with matter? |  |
Ans. Light interacts with matter in several ways, including reflection, refraction, absorption, and transmission. Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface, refraction happens when light passes through a medium and bends, absorption is when light is taken in by a material, and transmission is the process of light passing through a substance.
| 4. What is the importance of light in our daily lives? |  |
Ans. Light is crucial in our daily lives as it allows us to see our surroundings, influences our biological processes such as photosynthesis in plants, and plays a key role in various technologies like photography, communication, and medicine. Additionally, natural light affects our mood and well-being.
| 5. How does color relate to light? |  |
Ans. Color is the result of different wavelengths of light that are visible to the human eye. When light hits an object, certain wavelengths are absorbed while others are reflected. The colors we perceive are determined by the wavelengths of light that are reflected back to our eyes. For example, an object that reflects only red wavelengths appears red.
Related Searches

















