Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 8 > Mind Map: When People Rebel (1857 and After)
Mind Map: When People Rebel (1857 and After) | Social Studies (SST) Class 8 PDF Download
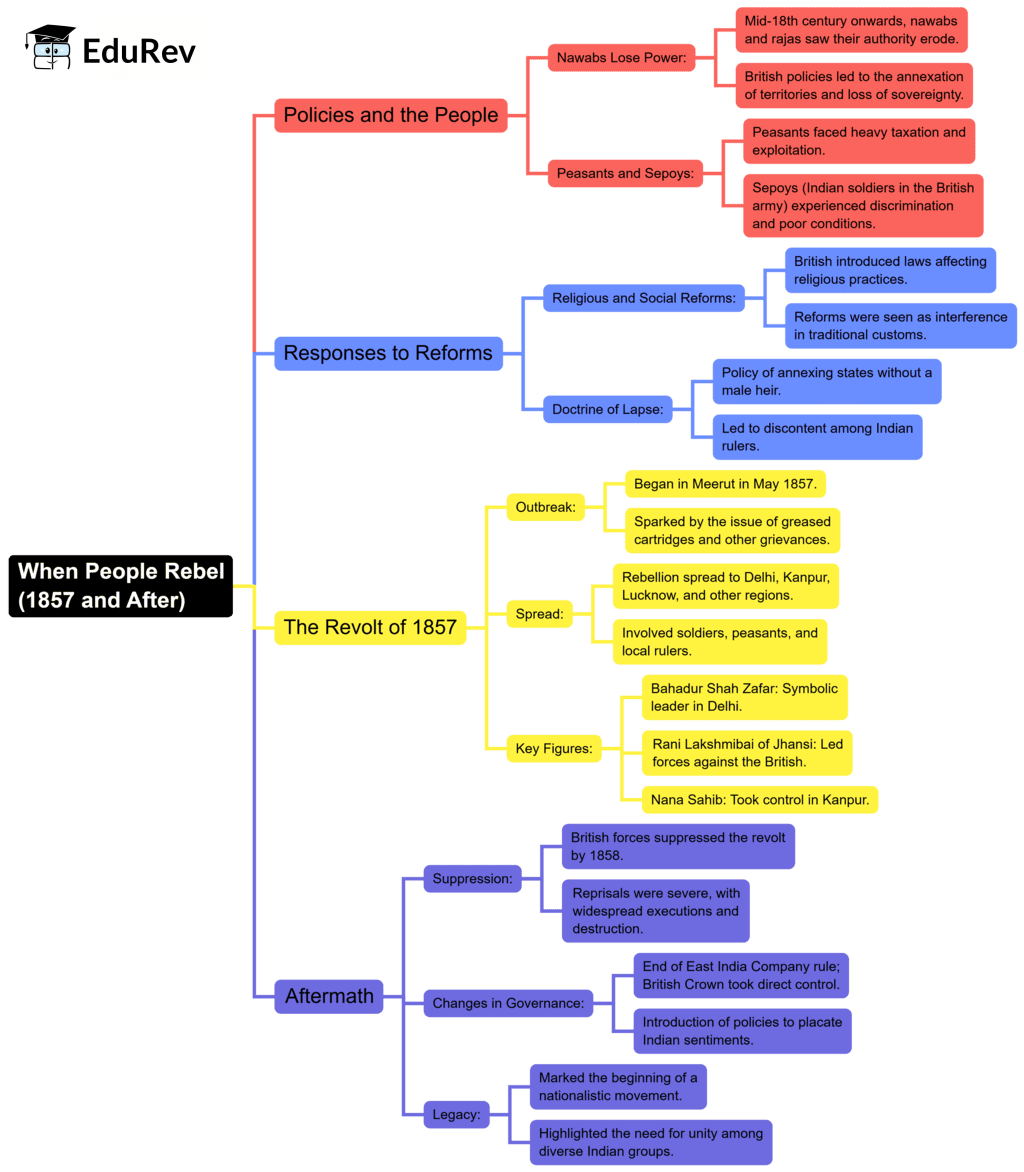
The document Mind Map: When People Rebel (1857 and After) | Social Studies (SST) Class 8 is a part of the Class 8 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
69 videos|431 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: When People Rebel (1857 and After) - Social Studies (SST) Class 8
| 1. What were the main causes of the rebellion in 1857? |  |
Ans. The rebellion in 1857, often referred to as the First War of Indian Independence, was caused by a combination of factors. Key causes included discontent among Indian soldiers (sepoys) due to the introduction of new rifle cartridges rumored to be greased with cow and pig fat, which offended both Hindu and Muslim soldiers. Additionally, widespread resentment against British rule due to economic exploitation, social reforms that disregarded traditional practices, and the annexation of Indian states contributed to the unrest.
| 2. How did the British respond to the 1857 rebellion? |  |
Ans. The British response to the 1857 rebellion was marked by severe military action and reprisals. After suppressing the uprising, the British implemented a policy of brutal repression, executing rebels and destroying villages suspected of supporting the insurgents. The British also reorganized their administrative policies in India, leading to the dissolution of the East India Company and the establishment of direct control by the British Crown over India.
| 3. What role did Indian leaders play in the 1857 rebellion? |  |
Ans. Indian leaders played a crucial role in the 1857 rebellion by organizing and leading various factions against British rule. Key figures included Rani Lakshmibai of Jhansi, who became a symbol of resistance, and Tantia Tope, who led guerrilla warfare. Local rulers, such as Bahadur Shah II, the last Mughal emperor, also rallied support for the rebellion, although they had limited coordination among the various groups involved.
| 4. What were the consequences of the 1857 rebellion for India? |  |
Ans. The consequences of the 1857 rebellion were profound and long-lasting. It marked the beginning of a nationalistic movement against colonial rule, leading to increased awareness and unity among Indians. The rebellion also resulted in significant changes in British policies, including the end of the East India Company's rule and the establishment of direct British governance. Furthermore, it set the stage for future movements for independence, influencing future leaders and uprisings.
| 5. How is the 1857 rebellion viewed in modern India? |  |
Ans. In modern India, the 1857 rebellion is viewed as a significant event in the struggle for independence, often celebrated as the First War of Indian Independence. It holds a symbolic place in Indian history, representing the fight against colonial oppression. Educational curricula emphasize its importance in fostering a sense of national identity and awareness among Indians. Various memorials and events commemorate the bravery of those who fought against British rule.
Related Searches
















