Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Notes > Theory of Machines (TOM) > Simple Mechanisms
Simple Mechanisms | Theory of Machines (TOM) - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
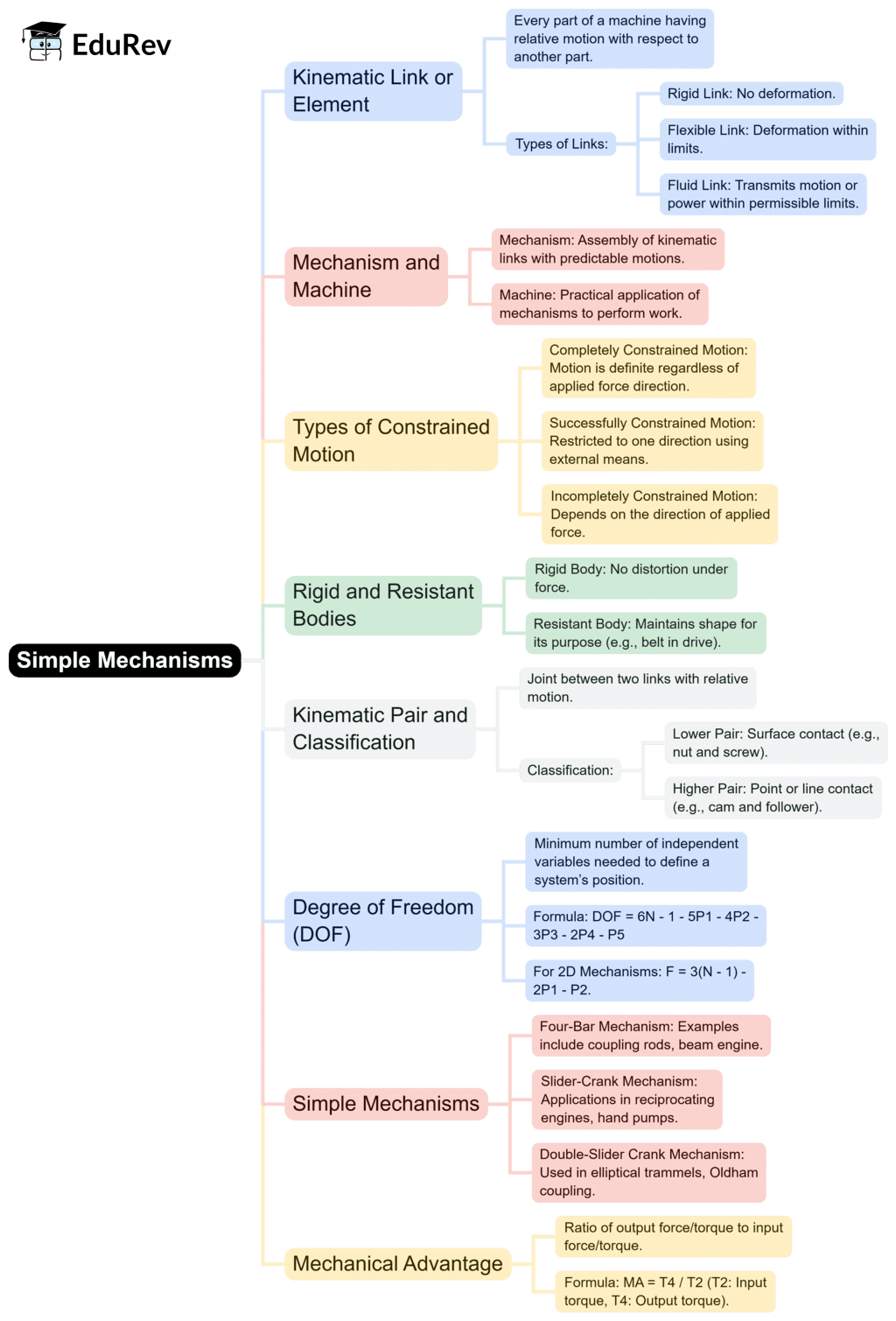
The document Simple Mechanisms | Theory of Machines (TOM) - Mechanical Engineering is a part of the Mechanical Engineering Course Theory of Machines (TOM).
All you need of Mechanical Engineering at this link: Mechanical Engineering
|
87 videos|75 docs|29 tests
|
FAQs on Simple Mechanisms - Theory of Machines (TOM) - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What are the basic types of simple mechanisms in mechanical engineering? |  |
Ans. The basic types of simple mechanisms include levers, pulleys, gears, cams, and linkages. Each of these mechanisms has unique characteristics and applications in various mechanical systems, allowing for the transmission and alteration of motion and force.
| 2. How does a lever work in a simple mechanism? |  |
Ans. A lever operates on the principle of moments, allowing a small input force applied at one end to lift a heavier load at the other end. The lever consists of a rigid beam pivoted at a point called the fulcrum. The distance from the fulcrum to the input force and the distance from the fulcrum to the load determine the mechanical advantage.
| 3. What is the purpose of a pulley in simple mechanisms? |  |
Ans. A pulley is used to change the direction of a force and can provide a mechanical advantage when lifting heavy loads. By using multiple pulleys in a system, the amount of force required to lift an object can be significantly reduced, making it easier to move heavy weights.
| 4. In what applications are gears utilized within simple mechanisms? |  |
Ans. Gears are utilized in various applications, including clocks, bicycles, and vehicles, to transmit motion and torque between rotating shafts. They can change the speed and direction of motion, allowing for efficient power transfer in mechanical systems.
| 5. What role do cams play in mechanical systems? |  |
Ans. Cams are used to convert rotary motion into linear motion. They have specific shapes that dictate the movement of a follower, enabling precise control of timing and movement in applications such as engine valves and automated machinery.
Related Searches
















