Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Notes > Soil Mechanics > Mind Map: Origin of Soil & Soil-Water Relationship
Mind Map: Origin of Soil & Soil-Water Relationship | Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
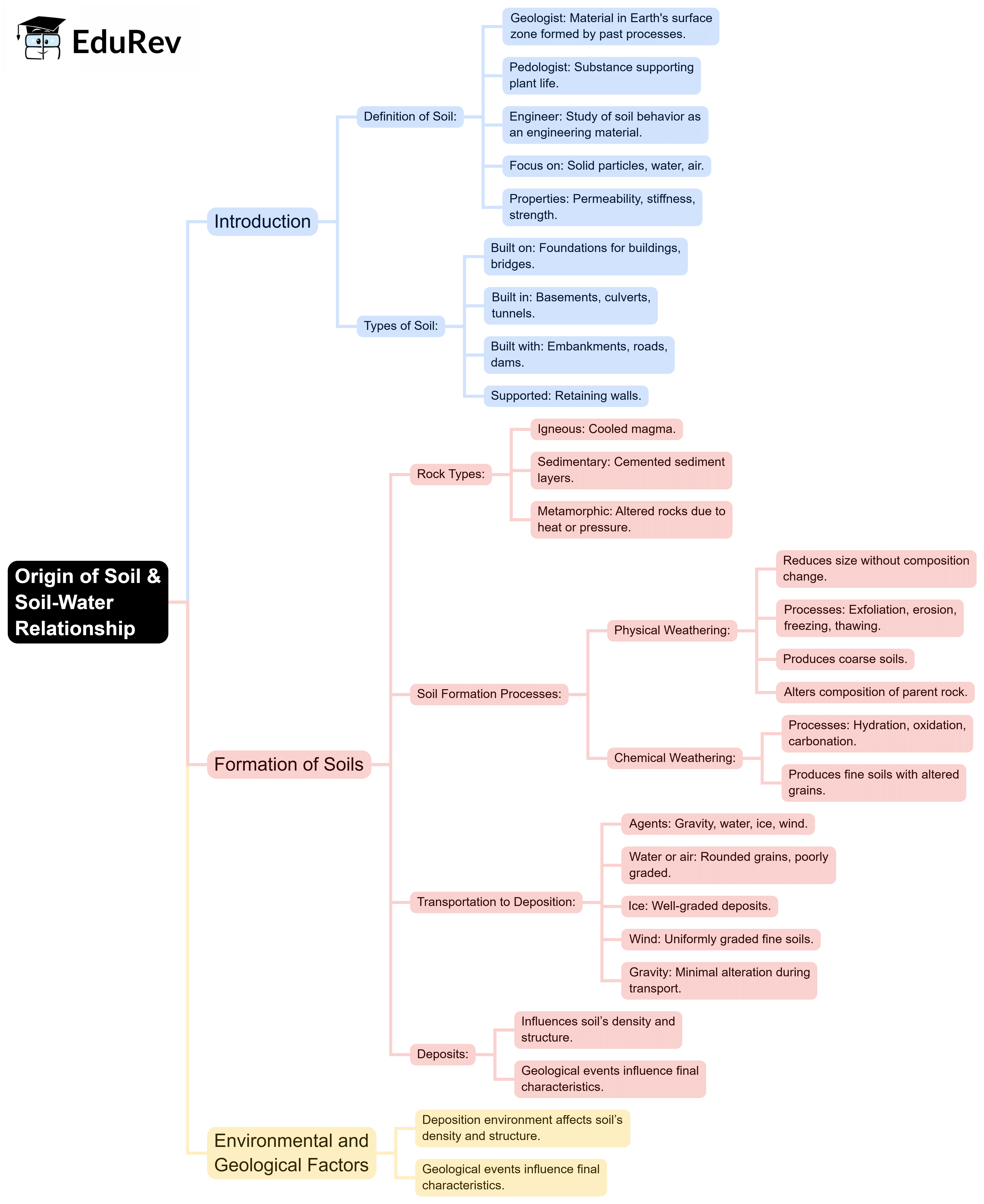
The document Mind Map: Origin of Soil & Soil-Water Relationship | Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE) is a part of the Civil Engineering (CE) Course Soil Mechanics.
All you need of Civil Engineering (CE) at this link: Civil Engineering (CE)
|
30 videos|108 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Origin of Soil & Soil-Water Relationship - Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What are the main processes involved in the formation of soil? |  |
Ans.The main processes involved in the formation of soil include weathering of rocks, organic matter decomposition, accumulation of minerals, and the influence of climate and topography. Weathering breaks down rocks into smaller particles, while organic matter from decaying plants and animals enriches the soil with nutrients. Additionally, minerals from parent material contribute to soil texture, and climate affects moisture and temperature, which are critical for soil development.
| 2. How does soil texture affect water retention? |  |
Ans.Soil texture refers to the size of soil particles, which can be classified into sand, silt, and clay. Sandy soils have larger particles and larger pore spaces, leading to quick drainage and low water retention. In contrast, clay soils have smaller particles and smaller pore spaces, allowing them to hold more water, but they drain more slowly. Loamy soils, which are a mix of sand, silt, and clay, provide an ideal balance for retaining moisture while allowing for adequate drainage.
| 3. What is the role of organic matter in the soil-water relationship? |  |
Ans.Organic matter plays a crucial role in the soil-water relationship by improving soil structure, enhancing nutrient retention, and increasing water-holding capacity. It helps to bind soil particles together, creating aggregates that improve porosity and aeration. Additionally, organic matter can hold significant amounts of water, making it available for plant use, and also aids in the infiltration of water into the soil.
| 4. How does soil permeability affect drainage and water supply? |  |
Ans.Soil permeability is the ability of soil to transmit water through its pore spaces. High permeability means water can flow through the soil easily, which can lead to good drainage but may also result in lower water retention during dry periods. Conversely, low permeability can cause water to accumulate and lead to poor drainage, which can adversely affect plant roots and soil health. Understanding permeability helps in managing irrigation and preventing waterlogging.
| 5. What is the significance of soil moisture in civil engineering projects? |  |
Ans.Soil moisture is significant in civil engineering projects as it affects the strength, stability, and behavior of soil under load. Adequate moisture levels are essential for maintaining soil cohesion and preventing erosion, while excessive moisture can lead to soil instability, landslides, or foundation issues. Engineers must assess soil moisture conditions when designing foundations, roadways, and other infrastructure to ensure safety and durability.
Related Searches
















